syllabus chemical science - SLET-NE
... due to ambiguity and vagueness in language. The candidates are also supposed to have a general acquaintance with the nature of a concept, meaning and criteria of truth, and the source of knowledge. There will be 60 questions, out of which the candidates can attempt any 50. In the event of the candid ...
... due to ambiguity and vagueness in language. The candidates are also supposed to have a general acquaintance with the nature of a concept, meaning and criteria of truth, and the source of knowledge. There will be 60 questions, out of which the candidates can attempt any 50. In the event of the candid ...
Chemical equilibrium, redox and pE
... • Thermodynamics applied to redox speciation • Redox speciation has profound effects on chemical and biological processes • Photosynthetic organisms, altered Earth’s redox conditions from reducing to oxidising • Profound consequences for life • Anoxic conditions exist today ...
... • Thermodynamics applied to redox speciation • Redox speciation has profound effects on chemical and biological processes • Photosynthetic organisms, altered Earth’s redox conditions from reducing to oxidising • Profound consequences for life • Anoxic conditions exist today ...
Chemical Reactions
... • The principle that during chemical reactions, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants, is known as the law of conservation of mass ...
... • The principle that during chemical reactions, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants, is known as the law of conservation of mass ...
CHEMISTRY
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
Chemical Reactions
... Chemical reactions involve changes in the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds. ...
... Chemical reactions involve changes in the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds. ...
Ch. 20- Electrochemistry
... the -2 oxidation state. However, this is not an ionic equation, so there is not a complete transfer of electros from hydrogen to oxygen. 2. Keeping track of oxidation states is a convenient form of “bookkeeping”, but you ...
... the -2 oxidation state. However, this is not an ionic equation, so there is not a complete transfer of electros from hydrogen to oxygen. 2. Keeping track of oxidation states is a convenient form of “bookkeeping”, but you ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
Electrochemistry
... A. Any chemical process in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is an _________-__________ reaction. 1. The name for this type of reaction is often shortened to what is called a ________ reaction. 2. A species _____ _________ when _______ (LEO). A species _____ ________ when ____ ...
... A. Any chemical process in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is an _________-__________ reaction. 1. The name for this type of reaction is often shortened to what is called a ________ reaction. 2. A species _____ _________ when _______ (LEO). A species _____ ________ when ____ ...
18 - cloudfront.net
... but with a trace of finely divided platinum (Pt) as a catalyst, the reaction is rapid. 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) Because a catalyst is not consumed during a reaction, it does not appear as a reactant or product in the chemical equation. Instead, the catalyst is often written above the yield arrow, as ...
... but with a trace of finely divided platinum (Pt) as a catalyst, the reaction is rapid. 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) Because a catalyst is not consumed during a reaction, it does not appear as a reactant or product in the chemical equation. Instead, the catalyst is often written above the yield arrow, as ...
PowerPoint for Cornell Notes
... to another. For oxidation to occur, one substance must lose electrons and a second substance must gain the lost electrons. The substance gaining electrons is said to be reduced and the substance losing the electrons is said to be oxidized. Thus an oxidation reaction is called a Redox reaction. In th ...
... to another. For oxidation to occur, one substance must lose electrons and a second substance must gain the lost electrons. The substance gaining electrons is said to be reduced and the substance losing the electrons is said to be oxidized. Thus an oxidation reaction is called a Redox reaction. In th ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 3. _____ (T/F) The number of valence electrons is very important in determining the chemical properties of an element. 4. _____ (T/F) The elements of a group have different numbers of valence electrons. 5. _____ (T/F) The representative groups 1A-7A have the same number of valence electrons as their ...
... 3. _____ (T/F) The number of valence electrons is very important in determining the chemical properties of an element. 4. _____ (T/F) The elements of a group have different numbers of valence electrons. 5. _____ (T/F) The representative groups 1A-7A have the same number of valence electrons as their ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... • the more an element reacts with other substances, the greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a ...
... • the more an element reacts with other substances, the greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a ...
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 16 Homework Packet Reaction Energy
... 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g) 2 KClO3 (s) given the following data: K (s) + ½ Cl2 (g) KCl (s) ...
... 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g) 2 KClO3 (s) given the following data: K (s) + ½ Cl2 (g) KCl (s) ...
Chapter 5
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
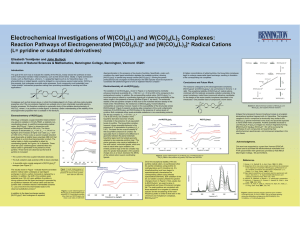
Electrochemical Investigations of W(CO) (L) and W(CO) (L) Complexes:
... tetracarbonyl pyridine fragment with 4,4'-bipyridine. The tungsten complex in such a compound is structurally very similar to the W(CO)4(L)2 species examined in this study and would be expected to have similar redox properties. Another possibility would be to use W(CO)4(4,4'-bpy)2 to bridges two rhe ...
... tetracarbonyl pyridine fragment with 4,4'-bipyridine. The tungsten complex in such a compound is structurally very similar to the W(CO)4(L)2 species examined in this study and would be expected to have similar redox properties. Another possibility would be to use W(CO)4(4,4'-bpy)2 to bridges two rhe ...
half-reactions - Clayton State University
... - Involve transfer of electrons from one species to another Oxidation - loss of electrons Reduction - gain of electrons - Ionic solid sodium chloride (Na+ and Cl- ions) formed from solid sodium and chlorine gas 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) - The oxidation (rusting) of iron by reaction with moist air 4 ...
... - Involve transfer of electrons from one species to another Oxidation - loss of electrons Reduction - gain of electrons - Ionic solid sodium chloride (Na+ and Cl- ions) formed from solid sodium and chlorine gas 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) - The oxidation (rusting) of iron by reaction with moist air 4 ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... Essential Content and Skills: How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
... Essential Content and Skills: How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
Activity Series Unit
... as it exists in solution) This is called the total ionic equation. Ca(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2(g) Ca(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + H2(g) No reaction for Copper and HCl Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + H2(g) Fe(s) + 2HCl(a ...
... as it exists in solution) This is called the total ionic equation. Ca(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2(g) Ca(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + H2(g) No reaction for Copper and HCl Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + H2(g) Fe(s) + 2HCl(a ...
Mechanisms 3
... Free radical substitution reactions are quite random, generally any of the C-H bonds can become a C-Cl bond. Products containing more than one halogen atom can be formed by further substitution on molecules that already contain a halogen atom. ...
... Free radical substitution reactions are quite random, generally any of the C-H bonds can become a C-Cl bond. Products containing more than one halogen atom can be formed by further substitution on molecules that already contain a halogen atom. ...
Review AGº = -RTlnKº Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc at 25 ºC
... energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the overall process. (also works for ΔG and ΔS because ...
... energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the overall process. (also works for ΔG and ΔS because ...
SCH3U Course Review
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.