The five main types of redox reactions are combination
... are those in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. This occurs because in such reactions, electrons are always transferred between species. Redox reactions take place through either a simple process, such as the burning of carbon in oxygen to yield carbon dioxide (CO2), or a more compl ...
... are those in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. This occurs because in such reactions, electrons are always transferred between species. Redox reactions take place through either a simple process, such as the burning of carbon in oxygen to yield carbon dioxide (CO2), or a more compl ...
Modelling Mass Transfer in Nitrification Processes Using
... current research activities in the field - Imagine - Test - Fit - Try again…. The combination of spectroscopic techniques and kinetic data offered a real opportunity to unravel the secrets of selective catalysis. This began with a thorough investigation of oxide lattice structure. Initially catalyst ...
... current research activities in the field - Imagine - Test - Fit - Try again…. The combination of spectroscopic techniques and kinetic data offered a real opportunity to unravel the secrets of selective catalysis. This began with a thorough investigation of oxide lattice structure. Initially catalyst ...
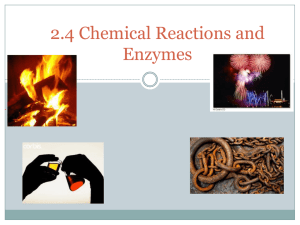
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
... Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. • Enzymes are catalysts in living things. ...
... Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. • Enzymes are catalysts in living things. ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... 26) How does the following orbital box diagram for Nitrogen violate Hund’s rule? The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have s ...
... 26) How does the following orbital box diagram for Nitrogen violate Hund’s rule? The electrons are not “singly before pairing.” Electrons repel each other, so they do want not pair until there is no more “space” left in the sublevel. Periodic Table and Periodic Trends 27) Which elements would have s ...
lect 7
... cycles, and then dump the electron to an electron acceptor. When oxygen is not present, microorganisms must seek alternate electron acceptors. The energy gain for the organisms is the energy difference between reduced carbon and the electron acceptor. In order of favorability, electron acceptors are ...
... cycles, and then dump the electron to an electron acceptor. When oxygen is not present, microorganisms must seek alternate electron acceptors. The energy gain for the organisms is the energy difference between reduced carbon and the electron acceptor. In order of favorability, electron acceptors are ...
Electrons
... 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. 7. Oxidation numbers do not have to be integers. Oxidation number of oxygen in the superoxide ion, O2-, is ____. ...
... 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. 7. Oxidation numbers do not have to be integers. Oxidation number of oxygen in the superoxide ion, O2-, is ____. ...
CHM 101
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
AP Chemistry
... 1. Concept of dynamic equilibrium, physical and chemical; Le Chatelier’s principle; equilibrium constants 2. Quantitative treatment a. Equilibrium constants for gaseous reactions: Kp, Kc b. Equilibrium constants for reactions in solution (1) Constants for acids and bases, (2) Solubility product cons ...
... 1. Concept of dynamic equilibrium, physical and chemical; Le Chatelier’s principle; equilibrium constants 2. Quantitative treatment a. Equilibrium constants for gaseous reactions: Kp, Kc b. Equilibrium constants for reactions in solution (1) Constants for acids and bases, (2) Solubility product cons ...
Exam #2
... mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. The electron diffraction experiment demonstrated Heisenberg’s hypothesis that matter and energy are interconvertable. The solution to the Schrodinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom does not provide a detailed description of the electro ...
... mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. The electron diffraction experiment demonstrated Heisenberg’s hypothesis that matter and energy are interconvertable. The solution to the Schrodinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom does not provide a detailed description of the electro ...
Topic 10: Making Electricity
... Topic 10: Making Electricity Introduction This topic deals with batteries as storage devices for chemical energy and as changers of chemical to electrical energy. The word battery has been used deliberately to help pupils link the work done to everyday experiences. Pupils to use the word cell, in ad ...
... Topic 10: Making Electricity Introduction This topic deals with batteries as storage devices for chemical energy and as changers of chemical to electrical energy. The word battery has been used deliberately to help pupils link the work done to everyday experiences. Pupils to use the word cell, in ad ...
Viju B - IS MU
... Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5/A8, 625 00, Brno, Czech Republic ...
... Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5/A8, 625 00, Brno, Czech Republic ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... <8 valence electrons exceptions: Be=4, B=6 (formal charge) >8 valence electrons: 3rd row elements and below Consider formal charges in evaluating structures When to draw resonance structures, and how many (resonance = average) VSEPR structures predict 3‐dimensional arrangement of elect ...
... <8 valence electrons exceptions: Be=4, B=6 (formal charge) >8 valence electrons: 3rd row elements and below Consider formal charges in evaluating structures When to draw resonance structures, and how many (resonance = average) VSEPR structures predict 3‐dimensional arrangement of elect ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
Honors Midterm Review – 2015-16
... _________ responsible for the uncertainty principle which states that it is impossible to know (with any great degree of certainty) both the location and velocity of an electron) _________ responsible for the planetary model of the atom, where electrons traveled in distinct paths around the nucleus ...
... _________ responsible for the uncertainty principle which states that it is impossible to know (with any great degree of certainty) both the location and velocity of an electron) _________ responsible for the planetary model of the atom, where electrons traveled in distinct paths around the nucleus ...
Chemical Reactions
... the elements in the molecule recombines with the original element. • The reactants and products are both one element and one molecule. A + BC AC + B “unhappy breakup” ...
... the elements in the molecule recombines with the original element. • The reactants and products are both one element and one molecule. A + BC AC + B “unhappy breakup” ...
A simple calorimeter was used as a vessel to measure the heat
... g) A student combines Ammonium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate to perform a reaction. The solution vessel felt cold to the touch. This reaction produces +126kJ of energy. i. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction (double replacement with energy ...
... g) A student combines Ammonium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate to perform a reaction. The solution vessel felt cold to the touch. This reaction produces +126kJ of energy. i. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction (double replacement with energy ...
Basic Background Review: Acid-Base , Redox, and Stable Isotopes
... Why do useful differences occur in Nature? Reactions with kinetic component, always end up enriching in LIGHT isotope. • Note: Natural processes: often may have both a passive (diffusion) and active (biochemical reaction) component. BOTH parts will fractionate for light isotope. ...
... Why do useful differences occur in Nature? Reactions with kinetic component, always end up enriching in LIGHT isotope. • Note: Natural processes: often may have both a passive (diffusion) and active (biochemical reaction) component. BOTH parts will fractionate for light isotope. ...
Fall Exam 3
... Superimposing the electron density in a filled set of s, p and d orbitals results in a cubic distribution of electron density. ...
... Superimposing the electron density in a filled set of s, p and d orbitals results in a cubic distribution of electron density. ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.