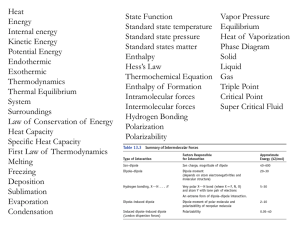
Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H SO ? A)
... In any oxidation-reduction reaction, the total number of electrons gained is A) greater than the total number of electrons lost B) equal to the total number of electrons lost ...
... In any oxidation-reduction reaction, the total number of electrons gained is A) greater than the total number of electrons lost B) equal to the total number of electrons lost ...
REACTION DYNAMICS
... Vibrational excitation to v=1 in HCl increases σr much more than the equivalent amount of energy in translational excitation. What qualitative conclusion can you draw about the shape of the potential energy surface? ...
... Vibrational excitation to v=1 in HCl increases σr much more than the equivalent amount of energy in translational excitation. What qualitative conclusion can you draw about the shape of the potential energy surface? ...
IntroRedoxDCIAns
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
Honors Chemistry
... 10. Give the different waves of the magnetic spectrum. 11. Which wave has more energy: red or blue? Short or long? Microwave or x-ray? 12. What does Bohr’s Model say about the hydrogen atom? 13. What does it mean when an electron is excited? What happens when the excited electron returns to the grou ...
... 10. Give the different waves of the magnetic spectrum. 11. Which wave has more energy: red or blue? Short or long? Microwave or x-ray? 12. What does Bohr’s Model say about the hydrogen atom? 13. What does it mean when an electron is excited? What happens when the excited electron returns to the grou ...
Introduction to Oxidation Reduction
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
unit 4 review sheet
... the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? i. When “e” is correctly balanced usi ...
... the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? i. When “e” is correctly balanced usi ...
PowerPoint
... methane, with water as a byproduct. The water that is produced can then react with CO in the water-gas shift reaction, equation (2). In addition, both CO and methane can decompose to form carbon as in equations (3) and (4). ...
... methane, with water as a byproduct. The water that is produced can then react with CO in the water-gas shift reaction, equation (2). In addition, both CO and methane can decompose to form carbon as in equations (3) and (4). ...
Redox in Electrochemistry
... measure of the amount of current that can be generated from a voltaic cell to do work. Electric charge can flow between two points only when a difference in electrical potential energy exists between the two points. In an electrochemical cell, these two points are the two ___________________. The po ...
... measure of the amount of current that can be generated from a voltaic cell to do work. Electric charge can flow between two points only when a difference in electrical potential energy exists between the two points. In an electrochemical cell, these two points are the two ___________________. The po ...
Chem 101 notes review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
Production of Materials by Jimmy Huang
... The alkene further splits into smaller alkenes until either ethylene or propene (or both) is formed e.g. C5H10 C2H4 + C3H6. Therefore, the overall products of catalytic cracking are alkanes of shorter chain lengths and small alkenes. The catalysts used are inorganic compounds known as zeolites, wh ...
... The alkene further splits into smaller alkenes until either ethylene or propene (or both) is formed e.g. C5H10 C2H4 + C3H6. Therefore, the overall products of catalytic cracking are alkanes of shorter chain lengths and small alkenes. The catalysts used are inorganic compounds known as zeolites, wh ...
CH 115 Exam 2 - UAB General Chemistry Supplemental Instruction
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... processes always occur together. In other words, you can’t just let electrons loose into space—they must be grabbed by some other atom. Likewise, you can’t just grab electrons from space—they must be taken from some other atom. An easy way to remember these processes is to remember the phrase “LEO t ...
... processes always occur together. In other words, you can’t just let electrons loose into space—they must be grabbed by some other atom. Likewise, you can’t just grab electrons from space—they must be taken from some other atom. An easy way to remember these processes is to remember the phrase “LEO t ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... electromagnetic spectrum (91) is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The “electromagnetic spectrum” of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object. wavelen ...
... electromagnetic spectrum (91) is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The “electromagnetic spectrum” of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object. wavelen ...
document
... ___T______20. The number of atoms on both sides of an equation must be equal for each element. Part C: For each of the following compounds, identify the number of atoms of each element. ...
... ___T______20. The number of atoms on both sides of an equation must be equal for each element. Part C: For each of the following compounds, identify the number of atoms of each element. ...
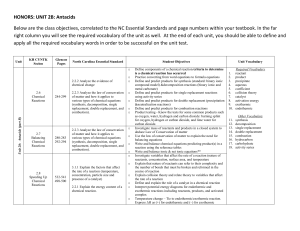
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Investigate mass of reactants and products in a closed system to deduce Law of Conservation of matter Use the law of conservation of matter to explain the need for balancing equations Write and balance chemical equations predicting product(s) in a reaction using the reference tables Write and balanc ...
... Investigate mass of reactants and products in a closed system to deduce Law of Conservation of matter Use the law of conservation of matter to explain the need for balancing equations Write and balance chemical equations predicting product(s) in a reaction using the reference tables Write and balanc ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... How will we figure it out for other molecules? There are rules. ...
... How will we figure it out for other molecules? There are rules. ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... for molecules oxidation numbers are a convention ! in which we imagine what the ! charge would be if it broke up into ionic pieces! (we can't really assign electrons to different elements)! ...
... for molecules oxidation numbers are a convention ! in which we imagine what the ! charge would be if it broke up into ionic pieces! (we can't really assign electrons to different elements)! ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... reduced? How many electrons? 2. C atom goes from -2 to -4. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 3. An atom goes from +5 to +3. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 4. An atom goes from -6 to -1. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? ...
... reduced? How many electrons? 2. C atom goes from -2 to -4. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 3. An atom goes from +5 to +3. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 4. An atom goes from -6 to -1. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? ...
Redox Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Mg loses 2 electrons to become Mg+2 O gains 2 electrons to become O-2 ( we have O2 molecule that contains 2 oxygen atom, both atoms are gaining electrons : O2 gains 4 electrons to become 2O-2) ...
... Mg loses 2 electrons to become Mg+2 O gains 2 electrons to become O-2 ( we have O2 molecule that contains 2 oxygen atom, both atoms are gaining electrons : O2 gains 4 electrons to become 2O-2) ...
Document
... it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. ...
... it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. ...
Balancing Redox Equations
... e.g. Na, Mg, Al, Zn Metal hydrides e.g. NaH, CaH2 H2 can act as either: Oxidizing agent when it combines with metals. Reducing agent when it combines with nonmetals. ...
... e.g. Na, Mg, Al, Zn Metal hydrides e.g. NaH, CaH2 H2 can act as either: Oxidizing agent when it combines with metals. Reducing agent when it combines with nonmetals. ...
Chapter 7 Homework questions
... Compare the energy of photons of violet light with those of red light. Which is more energetic and by what factor? 29. Place the following types of radiation in order of increasing energy per photon: (a) Radar signals (b) Radiation within a microwave oven (c) Gamma rays from a nuclear reaction (d) R ...
... Compare the energy of photons of violet light with those of red light. Which is more energetic and by what factor? 29. Place the following types of radiation in order of increasing energy per photon: (a) Radar signals (b) Radiation within a microwave oven (c) Gamma rays from a nuclear reaction (d) R ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.