Can Chemical Effects Rival the First Indirect Effect?
... The ”Twomey effect” is assessed by calculating the change in droplet number for a doubling of the baseline aerosol concentration. We then compare the ”Twomey effect” to the change in droplet number seen, if some chemical effect would be present in the baseline aerosol (i.e. no changes in size distri ...
... The ”Twomey effect” is assessed by calculating the change in droplet number for a doubling of the baseline aerosol concentration. We then compare the ”Twomey effect” to the change in droplet number seen, if some chemical effect would be present in the baseline aerosol (i.e. no changes in size distri ...
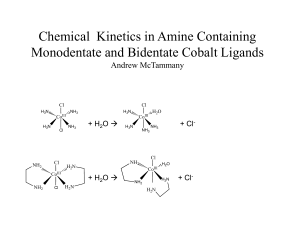
Chemical Kinetics in Monodentate and Bidentate Cobalt Compounds
... repeated. The trans-Co(NH3)4Cl2 should be synthesized using a lower temperature and lower concentration of acid. A mixture of HCl and H2SO4 could be used instead. From there the effect of different ligands can be ...
... repeated. The trans-Co(NH3)4Cl2 should be synthesized using a lower temperature and lower concentration of acid. A mixture of HCl and H2SO4 could be used instead. From there the effect of different ligands can be ...
2 - Scheikundeolympiade
... If yes, calculate the concentration. Yes (1 pt) We can suppose that this solution would be quite acidic, so the 3rd and 4th dissociation steps can be disregarded. (1 pt) The following equations are thus ...
... If yes, calculate the concentration. Yes (1 pt) We can suppose that this solution would be quite acidic, so the 3rd and 4th dissociation steps can be disregarded. (1 pt) The following equations are thus ...
Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, term061
... SeO2 ; SeCl6 ; SeF2 A) SeCl6 < SeF2 < SeO2 B) SeO2 < SeF2 < SeCl6 C) SeO2 < SeCl6 < SeF2 D) SeCl6 < SeO2 < SeF2 E) SeF2 < SeO2 < SeCl6 ...
... SeO2 ; SeCl6 ; SeF2 A) SeCl6 < SeF2 < SeO2 B) SeO2 < SeF2 < SeCl6 C) SeO2 < SeCl6 < SeF2 D) SeCl6 < SeO2 < SeF2 E) SeF2 < SeO2 < SeCl6 ...
Organic Chemistry II
... along with 2.0 mL of 85% phosphoric acid and a few black boil easers. Use care in handling the phosphoric acid. Carefully swirl the flask to ensure the liquids mix. Place the flask in a 50 mL heating mantle and arrange a fractional distillation apparatus on the flask. Be sure the receiving vessel is ...
... along with 2.0 mL of 85% phosphoric acid and a few black boil easers. Use care in handling the phosphoric acid. Carefully swirl the flask to ensure the liquids mix. Place the flask in a 50 mL heating mantle and arrange a fractional distillation apparatus on the flask. Be sure the receiving vessel is ...
NO - Blue Devil Chem
... 1. 3Co2+ + 2Al → 3Co + 2Al3+ 2. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 3. 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 4. 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → 2H2O + Mg(NO3)2 5. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O • Double replacement reactions are never oxidation reduction reactions since none of the atoms change oxidation numbers. ...
... 1. 3Co2+ + 2Al → 3Co + 2Al3+ 2. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 3. 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 4. 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → 2H2O + Mg(NO3)2 5. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O • Double replacement reactions are never oxidation reduction reactions since none of the atoms change oxidation numbers. ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... 3 NO2 + H2O NO + 2 HNO3 How many moles of water are needed to react with 8.4 mol NO2? a. 2.8 mol b. 3.0 mol c. 8.4 mol d. 25 mol ...
... 3 NO2 + H2O NO + 2 HNO3 How many moles of water are needed to react with 8.4 mol NO2? a. 2.8 mol b. 3.0 mol c. 8.4 mol d. 25 mol ...
5.111 Principles of Chemical Science
... (b) Is this drug likely to be a useful pharmaceutical agent? Since the vast majority of the compound is in the inactive form at physiological pH, it is unlikely to be a useful pharmaceutical agent.* Ideally, most of the compound would be active in the body. *However, if the active compound is highly ...
... (b) Is this drug likely to be a useful pharmaceutical agent? Since the vast majority of the compound is in the inactive form at physiological pH, it is unlikely to be a useful pharmaceutical agent.* Ideally, most of the compound would be active in the body. *However, if the active compound is highly ...
Chemistry - A Quantitative Science
... done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to discuss the number of atoms in moles than it is as individual items - 0.10 mol H2O is a mu ...
... done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to discuss the number of atoms in moles than it is as individual items - 0.10 mol H2O is a mu ...
OC 583- ISOTOPE BIGEOCHEMISTRY
... one empirically determines the magnitude of α for this reaction -The measured value of α for this equilibrium reaction is 0.45, which means that the D/H for water is more than twice the D/H for hydrogen sulfide. -what determines the equilibrium distribution of isotopes between species? b. Zero Point ...
... one empirically determines the magnitude of α for this reaction -The measured value of α for this equilibrium reaction is 0.45, which means that the D/H for water is more than twice the D/H for hydrogen sulfide. -what determines the equilibrium distribution of isotopes between species? b. Zero Point ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.