Production of materials
... In the twentieth century materials based upon non-metals such as carbon and semi-metals such as silicon have revolutionised transportation and communication. Increasing affluence and the importance placed upon material possessions and mobility have increased incentives to develop alternative materia ...
... In the twentieth century materials based upon non-metals such as carbon and semi-metals such as silicon have revolutionised transportation and communication. Increasing affluence and the importance placed upon material possessions and mobility have increased incentives to develop alternative materia ...
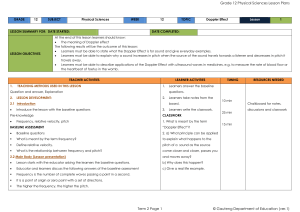
Physical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2
... 1.3 The police car moves away from the man at constant velocity, then slows down and finally comes to rest. ...
... 1.3 The police car moves away from the man at constant velocity, then slows down and finally comes to rest. ...
The Mole Concept
... 6. The molar mass SO2 = 64 grams SO2 Example 2: The formula for methane the major component in natural gas is CH4. The formula weight for methane = weight from hydrogen + weight from carbon The formula weight for methane = 4 H atoms x 1. + 1 C atom x 12. = 16. The molar mass for methane = 16.0 grams ...
... 6. The molar mass SO2 = 64 grams SO2 Example 2: The formula for methane the major component in natural gas is CH4. The formula weight for methane = weight from hydrogen + weight from carbon The formula weight for methane = 4 H atoms x 1. + 1 C atom x 12. = 16. The molar mass for methane = 16.0 grams ...
Solvent Denaturation and Stabilization of Globular Proteins?
... theory for the folded and unfolded states of the protein. Thermodynamic treatments of this problem have been given by Schellman (1975, 1978, 1987) and Tanford (1970). They are premised on the idea that protein denaturation is a twostate process and that the relevant difference between the two states ...
... theory for the folded and unfolded states of the protein. Thermodynamic treatments of this problem have been given by Schellman (1975, 1978, 1987) and Tanford (1970). They are premised on the idea that protein denaturation is a twostate process and that the relevant difference between the two states ...
ksp - lozon.ca
... induced to come to equilibrium by the addition of a "seed" which may be a tiny crystal of the solute, or a tiny solid particle, which initiates precipitation. This equilibrium constant is dimensionless as activity is a dimensionless quantity. However, use of activities is very inconvenient, so the e ...
... induced to come to equilibrium by the addition of a "seed" which may be a tiny crystal of the solute, or a tiny solid particle, which initiates precipitation. This equilibrium constant is dimensionless as activity is a dimensionless quantity. However, use of activities is very inconvenient, so the e ...
Mechanochemistry: the varied applications of mechanical bond
... Gerd Kaupp received his Diploma and Doctor’s degrees from the University of Würzburg in 1962 and 1964, ...
... Gerd Kaupp received his Diploma and Doctor’s degrees from the University of Würzburg in 1962 and 1964, ...
Exemplar Paper
... 2. When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of sodium thiosulfate in a beaker, solid sulfur forms in the solution. Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + SO2(aq) + S(s) + H2O(ℓ) The effect of concentration on the rate of reaction can be studied by varying the sodium thiosulfate concentra ...
... 2. When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of sodium thiosulfate in a beaker, solid sulfur forms in the solution. Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + SO2(aq) + S(s) + H2O(ℓ) The effect of concentration on the rate of reaction can be studied by varying the sodium thiosulfate concentra ...
Chap 3 - HCC Learning Web
... Since C4H10 contains 4 carbon atoms, so we need four carbon atoms at the right side, which leads us to put 4 (called coefficient) in front of the CO2. Now the equation is updated to be 1 C4H10 + O2 4 CO2 + H2O As there are 10 hydrogen atoms in C4H10, thus we need to balance the hydrogen atoms, wh ...
... Since C4H10 contains 4 carbon atoms, so we need four carbon atoms at the right side, which leads us to put 4 (called coefficient) in front of the CO2. Now the equation is updated to be 1 C4H10 + O2 4 CO2 + H2O As there are 10 hydrogen atoms in C4H10, thus we need to balance the hydrogen atoms, wh ...
Quarter 1
... 1. The average atomic mass of Chlorine is 35.453 amu. The isotopes of Chlorine are Chlorine35 and Chlorine-37. Determine which isotope will be found in greatest abundance given the atomic mass. Answer: Chlorine exists as two common isotopes. Chlorine-35 has an atomic mass of about 35 amu, Chlorine-3 ...
... 1. The average atomic mass of Chlorine is 35.453 amu. The isotopes of Chlorine are Chlorine35 and Chlorine-37. Determine which isotope will be found in greatest abundance given the atomic mass. Answer: Chlorine exists as two common isotopes. Chlorine-35 has an atomic mass of about 35 amu, Chlorine-3 ...
+ 2 H2O(l Ca(OH)2 aq)
... c) Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is a nonmetal oxide that reacts with oxygen, O2, to form the higher oxide, SO3. Δ 2 SO (g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ── ...
... c) Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is a nonmetal oxide that reacts with oxygen, O2, to form the higher oxide, SO3. Δ 2 SO (g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ── ...
Kinetic modelling of the Maillard reaction between proteins and sugars
... Trying to describe the changes of acompound (either areactant or areaction product) in time with zero-, first- or second-order reactions is too simplistic. The observed reaction rate ...
... Trying to describe the changes of acompound (either areactant or areaction product) in time with zero-, first- or second-order reactions is too simplistic. The observed reaction rate ...
Igneous Petrology 2001
... conflict with genuine equilibration which is not obtained as is indicated by presence of remnant minerals from the previous assemblage. The mitigating factor is the reaction rate. Reaction kinetics influenced by factors such as temperature, grain-to-grain contact, deformation rate, presence of fluid ...
... conflict with genuine equilibration which is not obtained as is indicated by presence of remnant minerals from the previous assemblage. The mitigating factor is the reaction rate. Reaction kinetics influenced by factors such as temperature, grain-to-grain contact, deformation rate, presence of fluid ...
Support Material
... semiconductors by adding an appropriate amount of suitable impurity in Si or Ge. * n-type semiconductors : Silicon or Germinium (group-14) doped with electron rich impurity (group-15 element like P or As), Here conductivity is due to the extra electrons or delocalized electrons. * p-type semiconduct ...
... semiconductors by adding an appropriate amount of suitable impurity in Si or Ge. * n-type semiconductors : Silicon or Germinium (group-14) doped with electron rich impurity (group-15 element like P or As), Here conductivity is due to the extra electrons or delocalized electrons. * p-type semiconduct ...
Optical pumping studies of vibrational energy transfer
... functions of diatomic species in N2 /CO and N2 /CO/O2 gas mixtures optically pumped by a CO laser in the pressure range 410–760 torr. In N2 /CO mixtures, as many as 38 vibrational levels of CO are observed, in addition to six levels of N2. The CO vibrational distribution function is highly non-Boltz ...
... functions of diatomic species in N2 /CO and N2 /CO/O2 gas mixtures optically pumped by a CO laser in the pressure range 410–760 torr. In N2 /CO mixtures, as many as 38 vibrational levels of CO are observed, in addition to six levels of N2. The CO vibrational distribution function is highly non-Boltz ...
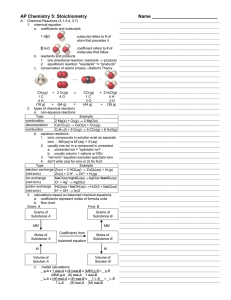
AP Chemistry
... conservation of mass, which states that the total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants. Likewise, the same numbers of atoms of each type are present before and after a chemical reaction. A balanced chemical equation shows equal numbers of atoms o ...
... conservation of mass, which states that the total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants. Likewise, the same numbers of atoms of each type are present before and after a chemical reaction. A balanced chemical equation shows equal numbers of atoms o ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.