Chapter 24
... A hang glider is flying at an altitude of H=120m. Green light (555nm)enters the pilot’s eye through a pupil that has a diameter D=2.5 mm. The average index of refraction of the eye is 1.33. Determine how far apart two point objects must be on the ground if the pilot is to have any hope of distinguis ...
... A hang glider is flying at an altitude of H=120m. Green light (555nm)enters the pilot’s eye through a pupil that has a diameter D=2.5 mm. The average index of refraction of the eye is 1.33. Determine how far apart two point objects must be on the ground if the pilot is to have any hope of distinguis ...
Review: 22.4: Dispersion Refraction in a Prism
... called the angle of deviation, δ Since all the colors have different angles of deviation, they will spread out into a spectrum ...
... called the angle of deviation, δ Since all the colors have different angles of deviation, they will spread out into a spectrum ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... Chemical properties of matter describe its "potential" to undergo some chemical change or reaction by virtue of its composition. What elements, electrons, and bonding are present to give the potential for chemical change? ...
... Chemical properties of matter describe its "potential" to undergo some chemical change or reaction by virtue of its composition. What elements, electrons, and bonding are present to give the potential for chemical change? ...
Yoko MIYAMOTO Laboratory(PDF:1009 KB)
... This beam has the ability to transfer its rotation to an object through which it passes. Absorption is one mechanism for transferring rotation; another occurs when the magnitude of the rotation of the beam (integer m discussed above) is changed by the shape of the object. In both cases, the differen ...
... This beam has the ability to transfer its rotation to an object through which it passes. Absorption is one mechanism for transferring rotation; another occurs when the magnitude of the rotation of the beam (integer m discussed above) is changed by the shape of the object. In both cases, the differen ...
recent advances - University of St Andrews
... were an important proof of principle. A solid-state polymer laser, though, would be attractive because it could be more compact and robust, and would be better suited for electrical pumping in the future. However, this proved to be a more challenging problem. In the same year as Moses reported a sol ...
... were an important proof of principle. A solid-state polymer laser, though, would be attractive because it could be more compact and robust, and would be better suited for electrical pumping in the future. However, this proved to be a more challenging problem. In the same year as Moses reported a sol ...
1 teachers` guidelines thin film waveguides and
... (xerogels, ambigels, cryogels, aerogels). Common features of these products include the preservation of the nanosizes of the structural elements and sufficiently high values of specific surface area (hundreds of m2/g), although the bulk density can vary by hundreds of ...
... (xerogels, ambigels, cryogels, aerogels). Common features of these products include the preservation of the nanosizes of the structural elements and sufficiently high values of specific surface area (hundreds of m2/g), although the bulk density can vary by hundreds of ...
File
... Periscope is an instrument for observation from a concealed position. In its simplest form it is a tube in each end of which are mirrors set parallel to each other and at an angle of 45° with a line between them. A periscope may be used as a toy or for seeing over people's heads in a crowd. This for ...
... Periscope is an instrument for observation from a concealed position. In its simplest form it is a tube in each end of which are mirrors set parallel to each other and at an angle of 45° with a line between them. A periscope may be used as a toy or for seeing over people's heads in a crowd. This for ...
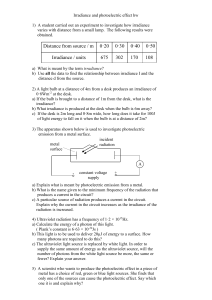
Irradiance and photoelectric effect hw
... b) This light is to be used to deliver 20µJ of energy to a surface. How many photons are required to do this? c) The ultraviolet light source is replaced by white light. In order to supply the same amount of energy as the ultraviolet source, will the number of photons from the white light source be ...
... b) This light is to be used to deliver 20µJ of energy to a surface. How many photons are required to do this? c) The ultraviolet light source is replaced by white light. In order to supply the same amount of energy as the ultraviolet source, will the number of photons from the white light source be ...
Resumen Science I Trimestre II Parcial Definitions: Element: pure
... Molecule: particle of a compound; formed when atoms of 2 or more elements join together. Compound: pure substances composed of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined; elements combine reaction with one another. Chemical Formula: is the fundamental unit of an element. The symbols for the ele ...
... Molecule: particle of a compound; formed when atoms of 2 or more elements join together. Compound: pure substances composed of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined; elements combine reaction with one another. Chemical Formula: is the fundamental unit of an element. The symbols for the ele ...
Orbits - Macmillan Academy
... (a) When light travels from air into glass it _________ towards the normal. This process is called __________ and is due to a change in __________ of the light. (b) White light is made up of __________ than one colour and when these colours travel through glass they are ____________, with __________ ...
... (a) When light travels from air into glass it _________ towards the normal. This process is called __________ and is due to a change in __________ of the light. (b) White light is made up of __________ than one colour and when these colours travel through glass they are ____________, with __________ ...
Light
... * A light-year is not a measure of time. It measures the distance that light travels through space in one year. ...
... * A light-year is not a measure of time. It measures the distance that light travels through space in one year. ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... 0040-6031/© 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
... 0040-6031/© 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
LIGHT: What is it?
... Waves carry energy from one place to another Identify transverse and longitudinal waves in mechanical media such as spring, ropes, and the earth (seismic waves) Solve problems involving wavelength, frequency, & speed. ...
... Waves carry energy from one place to another Identify transverse and longitudinal waves in mechanical media such as spring, ropes, and the earth (seismic waves) Solve problems involving wavelength, frequency, & speed. ...
4.1 Refraction Index
... • Fiber optic systems can carry signals faster than electricity and do not lose energy like electrical system do. (Electrical systems have internal resistance in wires which generates energy loss as heat) • Fiber optic cables can carry many more messages at a much faster rate than conventional elect ...
... • Fiber optic systems can carry signals faster than electricity and do not lose energy like electrical system do. (Electrical systems have internal resistance in wires which generates energy loss as heat) • Fiber optic cables can carry many more messages at a much faster rate than conventional elect ...
Measuring the speed of light
... These two sockets can be used to evaluate the signal emitted and the signal received by means of a 2-channel oscilloscope. The phases of the two signals relative to each other are of particular importance here. In order not to have to use the fastest oscilloscope for this task, each of the signals a ...
... These two sockets can be used to evaluate the signal emitted and the signal received by means of a 2-channel oscilloscope. The phases of the two signals relative to each other are of particular importance here. In order not to have to use the fastest oscilloscope for this task, each of the signals a ...
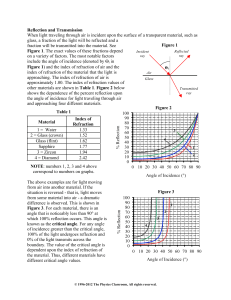
Reflection and Transmission When light traveling through air is
... shows the dependence of the percent reflection upon the angle of incidence for light traveling through air and approaching four different materials. Figure 2 Table 1 Material 1 = Water 2 = Glass (crown) Glass (flint) Sapphire 3 = Zircon 4 = Diamond ...
... shows the dependence of the percent reflection upon the angle of incidence for light traveling through air and approaching four different materials. Figure 2 Table 1 Material 1 = Water 2 = Glass (crown) Glass (flint) Sapphire 3 = Zircon 4 = Diamond ...
Long Term Forecast SCIENCE Key Stage 1 2014-15
... materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials Describe magnets as having two poles Predict whether magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing ...
... materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials Describe magnets as having two poles Predict whether magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing ...
1. Which band of the electromagnetic spectrum has: a. the lowest
... ../ The total internal reflection is the complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is greater than the critical angle ../ The critical angle is the angle of incidence at which the refracted light makes an angle of 90° w ...
... ../ The total internal reflection is the complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is greater than the critical angle ../ The critical angle is the angle of incidence at which the refracted light makes an angle of 90° w ...
Ch 27 Light Notes (WP)
... IR waves absorbed by obj. causing particles in obj to vibrate faster, therefore, increasing temp of obj sun not only source of IR waves: stars, planets, buildings, organisms Visible Light: very narrow range in EM spectrum that humans can see visible spectrum- range of colors of light ROYGBIV Ultravi ...
... IR waves absorbed by obj. causing particles in obj to vibrate faster, therefore, increasing temp of obj sun not only source of IR waves: stars, planets, buildings, organisms Visible Light: very narrow range in EM spectrum that humans can see visible spectrum- range of colors of light ROYGBIV Ultravi ...
Diffuse Greenhouse Covering Materials – Material Technology
... view, we do not yet know the ideal haze characteristic of a covering. This is presently under investigation and we hope to present the results in the near future. In general, the potential for diffuse covering materials is much higher for semi-arid climates than for marine winter climates; the direc ...
... view, we do not yet know the ideal haze characteristic of a covering. This is presently under investigation and we hope to present the results in the near future. In general, the potential for diffuse covering materials is much higher for semi-arid climates than for marine winter climates; the direc ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.