compound
... Matter is made up of building blocks: atom – smallest unit of an element. element – a pure substance made of only one kind of atom. compound – made of two or more atoms ...
... Matter is made up of building blocks: atom – smallest unit of an element. element – a pure substance made of only one kind of atom. compound – made of two or more atoms ...
Course Description Word File
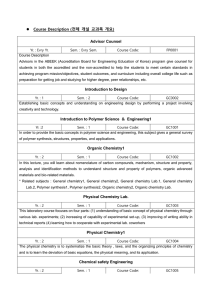
... Design for Polymer Analysis Yr. : 3 Sem. : 2 Course Code: GC1022 To increase the design ability of polymer materials by studying the fundamentals of polymer materials and characterization, by selecting polymer materials, which can be found in our living environment and industries, and performing tea ...
... Design for Polymer Analysis Yr. : 3 Sem. : 2 Course Code: GC1022 To increase the design ability of polymer materials by studying the fundamentals of polymer materials and characterization, by selecting polymer materials, which can be found in our living environment and industries, and performing tea ...
of light - Nutley Public Schools
... h. Shadow : A shaded region that results when light falls on an object and thus cannot reach into a region on the far side of the object. i. Transparent : The term applied to materials that allow light to pass through them in straight lines. j. Ultraviolet: Electromagnetic waves of frequencies highe ...
... h. Shadow : A shaded region that results when light falls on an object and thus cannot reach into a region on the far side of the object. i. Transparent : The term applied to materials that allow light to pass through them in straight lines. j. Ultraviolet: Electromagnetic waves of frequencies highe ...
reflection, refraction, and dispersion
... When a light ray traveling in one medium encounters a boundary with another medium, part of the incident light is reflected The reflected rays are parallel to each other, as indicated in the figure. The direction of a reflected ray is in the plane perpendicular to the reflecting surface that contai ...
... When a light ray traveling in one medium encounters a boundary with another medium, part of the incident light is reflected The reflected rays are parallel to each other, as indicated in the figure. The direction of a reflected ray is in the plane perpendicular to the reflecting surface that contai ...
FACTORS AFFECTING PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... Part I. Plants need CO2 INTRODUCTION In order for a plant to produce its own food, it needs raw materials. Plants use energy from the sun to synthesis water and carbon dioxide into a simple sugar. In Part I of this experiment, you will prove that carbon dioxide must be present before photosynthesis ...
... Part I. Plants need CO2 INTRODUCTION In order for a plant to produce its own food, it needs raw materials. Plants use energy from the sun to synthesis water and carbon dioxide into a simple sugar. In Part I of this experiment, you will prove that carbon dioxide must be present before photosynthesis ...
butterfly - Tufts University
... •scales are generally about 100m long •lower lamina is generally smooth •upper lamina has prominent features: –ridges extend up in lines along the length of scale –cross-ribs connect ridges transversely ...
... •scales are generally about 100m long •lower lamina is generally smooth •upper lamina has prominent features: –ridges extend up in lines along the length of scale –cross-ribs connect ridges transversely ...
Examine each example and determine which color the paper
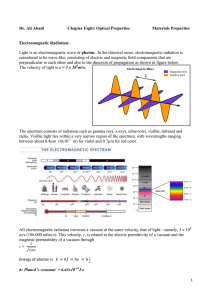
... 42. Know the electromagnetic spectrum in order, relative energy and some uses. ...
... 42. Know the electromagnetic spectrum in order, relative energy and some uses. ...
Ch. 18 Powerpoint
... Explain the differences among opaque, transparent, and translucent materials. List and explain three things that can happen to a light wave when it enters a new medium. What is the difference between diffuse reflection and regular reflection? ...
... Explain the differences among opaque, transparent, and translucent materials. List and explain three things that can happen to a light wave when it enters a new medium. What is the difference between diffuse reflection and regular reflection? ...
Dr. Ali Abadi Chapter Eight: Optical Properties Materials Properties
... If absorption is uniform for all visible wavelengths, the material appears colorless; examples include high-purity inorganic glasses and high-purity and single-crystal diamonds and sapphire. Usually, any selective absorption is by electron excitation the fraction of the visible light having energie ...
... If absorption is uniform for all visible wavelengths, the material appears colorless; examples include high-purity inorganic glasses and high-purity and single-crystal diamonds and sapphire. Usually, any selective absorption is by electron excitation the fraction of the visible light having energie ...
Light guide technology enables uniform and bi
... displays utilizing a single light guide. These light guides, however, typically produced light in a fairly indirect and relatively uncontrolled distribution. The more common request has been for a semi-Lambertian distribution in the ...
... displays utilizing a single light guide. These light guides, however, typically produced light in a fairly indirect and relatively uncontrolled distribution. The more common request has been for a semi-Lambertian distribution in the ...
lesson-3-explore-page-141-mirrors-lenses-and
... Just like a concave mirror, a concave lens has a focal point and a focal length. The more curved the lens is, the shorter the focal length. Concave Lenses A concave lens is curved inward on at least one side and thicker at its edges. The image formed by a concave lens is upright and smaller th ...
... Just like a concave mirror, a concave lens has a focal point and a focal length. The more curved the lens is, the shorter the focal length. Concave Lenses A concave lens is curved inward on at least one side and thicker at its edges. The image formed by a concave lens is upright and smaller th ...
Physical and Chemical Changes
... b. some mass is converted to energy c. some form of light is given off d. a new material is formed ...
... b. some mass is converted to energy c. some form of light is given off d. a new material is formed ...
Doppler Effect Real Life Example of Doppler Effect
... • Redshift (to longer wavelengths): The source is moving away from the observer • Blueshift (to shorter wavelengths): The source is moving towards the observer ...
... • Redshift (to longer wavelengths): The source is moving away from the observer • Blueshift (to shorter wavelengths): The source is moving towards the observer ...
Laboratory: Geometrical Optics
... 40. Under Interactive Java Tutorial, select Image Formation with Converging Lenses. 41. Use the tutorial to observe the relationship between object position and image position for a bi-convex lens. 42. Is it possible to create a virtual image using only a bi-convex lens? YES / NO 43. If yes, in what ...
... 40. Under Interactive Java Tutorial, select Image Formation with Converging Lenses. 41. Use the tutorial to observe the relationship between object position and image position for a bi-convex lens. 42. Is it possible to create a virtual image using only a bi-convex lens? YES / NO 43. If yes, in what ...
Photophobia - North American Neuro
... botulinum toxin. Traumatic brain injuries require supportive care from a team of professionals who are specifically trained to manage these injuries. Optical Treatments: Never wear sunglasses indoors! By wearing dark glasses indoors, you can make your eyes MORE sensitive to light so that when you ta ...
... botulinum toxin. Traumatic brain injuries require supportive care from a team of professionals who are specifically trained to manage these injuries. Optical Treatments: Never wear sunglasses indoors! By wearing dark glasses indoors, you can make your eyes MORE sensitive to light so that when you ta ...
Conformational Evolution of Elongated Polymer Solutions Tailors
... molecular alignment, we use a model of the polymer network and perform simulations of its dynamics, as previously developed for fully flexible and semiflexible polymer chains.24−26 Simulations are here aimed at better rationalizing the observed chain orientation in the core, and at assessing the relev ...
... molecular alignment, we use a model of the polymer network and perform simulations of its dynamics, as previously developed for fully flexible and semiflexible polymer chains.24−26 Simulations are here aimed at better rationalizing the observed chain orientation in the core, and at assessing the relev ...
The Colors of Light
... Closure: What will the teacher do to bring the lesson to a close? How will the students make sense of the investigation? Direct Instruction: The electromagnetic spectrum is the entire range of electromagnetic waves arranged according to their wavelengths. The visible light section is the only part w ...
... Closure: What will the teacher do to bring the lesson to a close? How will the students make sense of the investigation? Direct Instruction: The electromagnetic spectrum is the entire range of electromagnetic waves arranged according to their wavelengths. The visible light section is the only part w ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.