Chapter Objectives
... 4. Differentiate between a hypothesis, theory, and law 5. Use falsifiability to differentiate between a scientific and non-scientific hypothesis Ch. 2 1. Identify the conditions for equilibrium 2. Distinguish between mass and inertia 3. Apply Newton’s First Law to find the net force on an object in ...
... 4. Differentiate between a hypothesis, theory, and law 5. Use falsifiability to differentiate between a scientific and non-scientific hypothesis Ch. 2 1. Identify the conditions for equilibrium 2. Distinguish between mass and inertia 3. Apply Newton’s First Law to find the net force on an object in ...
Electrostatics - Coulomb`s Law
... As gravity is a force that resulting from the interaction of objects with mass, the electromagnetic force results from the interaction of particles that have a property called electric charge. Electric charge is a property that is as fundamental as mass. The atom is made up of protons, neutrons and ...
... As gravity is a force that resulting from the interaction of objects with mass, the electromagnetic force results from the interaction of particles that have a property called electric charge. Electric charge is a property that is as fundamental as mass. The atom is made up of protons, neutrons and ...
posted
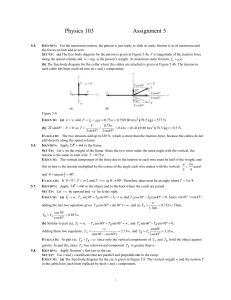
... F T k mB g Use the first equation to replace T in the second: F k mA g k mB g. (a) F k (mA mB ) g (b) T k mA g EVALUATE: We can also consider both crates together as a single object of mass (mA mB ). Fx max for this combined object gives F f k k (mA mB ) g , in agreeme ...
... F T k mB g Use the first equation to replace T in the second: F k mA g k mB g. (a) F k (mA mB ) g (b) T k mA g EVALUATE: We can also consider both crates together as a single object of mass (mA mB ). Fx max for this combined object gives F f k k (mA mB ) g , in agreeme ...
Forces (PPT) - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Now we can see that the gravitational acceleration g is a consequence of the gravitational force. Its magnitude depends on how far is the object from the center of the earth. Double the distance from the centre, r = 2 rE , g is 4 times less, g = 2.45 m/s2 , and so is weight ...
... Now we can see that the gravitational acceleration g is a consequence of the gravitational force. Its magnitude depends on how far is the object from the center of the earth. Double the distance from the centre, r = 2 rE , g is 4 times less, g = 2.45 m/s2 , and so is weight ...
Ch_07
... Conservation of energy and momentum can also be used to analyze collisions in two or three dimensions, but unless the situation is very simple, the math quickly becomes unwieldy. Here, a moving object collides with an object initially at rest. Knowing the masses and initial velocities is not enough; ...
... Conservation of energy and momentum can also be used to analyze collisions in two or three dimensions, but unless the situation is very simple, the math quickly becomes unwieldy. Here, a moving object collides with an object initially at rest. Knowing the masses and initial velocities is not enough; ...
Energy Review
... between an object's mass (m), its acceleration (a), and the applied force (F) is F=ma. ...
... between an object's mass (m), its acceleration (a), and the applied force (F) is F=ma. ...
quantities and units for centrifugation in the
... example, in labaratoriesperforming biochemical analysts on body fluids it is routinely used to separate blood cells firm plasma, to separate sediment from urine, to measure the volume fraction of erythrocytesin blood (thehemabait), and to separate bound from free components in protein binding and im ...
... example, in labaratoriesperforming biochemical analysts on body fluids it is routinely used to separate blood cells firm plasma, to separate sediment from urine, to measure the volume fraction of erythrocytesin blood (thehemabait), and to separate bound from free components in protein binding and im ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... The distances that appeared on the right are the distances to 10 randomly chosen stars from this map. They illustrate the point that even though we believe these stars to be most common, they are not good indicators of galactic structure because they cannot be seen at sufficient distances to resolve ...
... The distances that appeared on the right are the distances to 10 randomly chosen stars from this map. They illustrate the point that even though we believe these stars to be most common, they are not good indicators of galactic structure because they cannot be seen at sufficient distances to resolve ...
7-2 Conservation of Momentum - wths
... The ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a projectile, such as a bullet. The projectile (mass m) is fired into a large block of mass M, which is suspended like a pendulum. (Usually M is >> m) As a result of the collision, the pendulum & projectile together swing up to a ...
... The ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a projectile, such as a bullet. The projectile (mass m) is fired into a large block of mass M, which is suspended like a pendulum. (Usually M is >> m) As a result of the collision, the pendulum & projectile together swing up to a ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
Ch. 6 Newton`s Second law of Motion Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... the Earth” experiment? Cavendish’s experiment often is called “weighing Earth,” because his experiment helped determine Earth’s mass. Once the value of G is known, not only the mass of Earth, but also the mass of the Sun can be determined. In addition, the gravitational force between any two objects ...
... the Earth” experiment? Cavendish’s experiment often is called “weighing Earth,” because his experiment helped determine Earth’s mass. Once the value of G is known, not only the mass of Earth, but also the mass of the Sun can be determined. In addition, the gravitational force between any two objects ...
Neistein_dekel60
... • How each process affects the galaxy mass? (feedback, SF, Cooling) • Why changing the parameters of a given process (e.g. SF) do not affect the galaxies? What is `self-regulation’? • What is the physics missing in order to reproduce the observational results (e.g. the LF)? • Can we extrapolate the ...
... • How each process affects the galaxy mass? (feedback, SF, Cooling) • Why changing the parameters of a given process (e.g. SF) do not affect the galaxies? What is `self-regulation’? • What is the physics missing in order to reproduce the observational results (e.g. the LF)? • Can we extrapolate the ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.