Preview Sample 2
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
The Law of Conservation of Momentum
... An 8 000 kg elephant running at 7 m/s has more momentum than a 50 kg cheetah running at 30 m/s. As noted above, momentum is one of the physical properties that are conserved. If the elephant and cheetah were traveling in opposite directions and collided, the momentum of the combined cheetahphant wou ...
... An 8 000 kg elephant running at 7 m/s has more momentum than a 50 kg cheetah running at 30 m/s. As noted above, momentum is one of the physical properties that are conserved. If the elephant and cheetah were traveling in opposite directions and collided, the momentum of the combined cheetahphant wou ...
Lectures in physics Part 1: Mechanics Przemysław Borys 7.11.2013
... To understand the second way of denoting vectors, we shall first learn the rules for vector addition and subtraction. Before we do this, I emphasise a general remmark, which should be apparent at this point. Vectors and scalars are different mathematical objects! It is impossible to put an equality ...
... To understand the second way of denoting vectors, we shall first learn the rules for vector addition and subtraction. Before we do this, I emphasise a general remmark, which should be apparent at this point. Vectors and scalars are different mathematical objects! It is impossible to put an equality ...
general relativity and gravitational waves
... When we draw spherical coordinates on a sphere, and follow two lines, that are perpendicular to the equation, in the direction of the North pole, we observe that two initial parallel lines meet at a point on the curved surface. The fifth postulate of Euclid does not hold for a curved space: parallel ...
... When we draw spherical coordinates on a sphere, and follow two lines, that are perpendicular to the equation, in the direction of the North pole, we observe that two initial parallel lines meet at a point on the curved surface. The fifth postulate of Euclid does not hold for a curved space: parallel ...
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 14 14A. Force and
... the constant force exerted by the sandpile. By facts from Section 14.1B, ...
... the constant force exerted by the sandpile. By facts from Section 14.1B, ...
Sample
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
Test Review Problems
... If you try to touch your toes while standing flat against a wall, you probably will fall over. The reason this happens is that a. your center of gravity is not located directly above your support area. b. your center of gravity is outside your support area. c. both A and B When an ice skater pulls i ...
... If you try to touch your toes while standing flat against a wall, you probably will fall over. The reason this happens is that a. your center of gravity is not located directly above your support area. b. your center of gravity is outside your support area. c. both A and B When an ice skater pulls i ...
narayana - Docslide.net
... Every body continues to remain in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless an external force is applied on it i.e. If a particle is at rest, it will remain at rest and if it is moving with constant speed, it will continue to move in the same direction with same constant speed unless an external ...
... Every body continues to remain in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless an external force is applied on it i.e. If a particle is at rest, it will remain at rest and if it is moving with constant speed, it will continue to move in the same direction with same constant speed unless an external ...
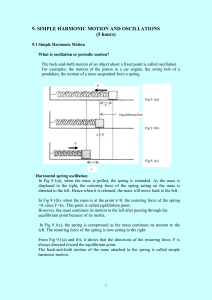
simple harmonic motion and oscilation
... displaced to the right, the restoring force of the spring acting on the mass is directed to the left. Hence when it is released, the mass will move back to the left. In Fig 9.1(b), when the mass is at the point x=0, the restoring force of the spring =0, since F=kx. This point is called equilibrium p ...
... displaced to the right, the restoring force of the spring acting on the mass is directed to the left. Hence when it is released, the mass will move back to the left. In Fig 9.1(b), when the mass is at the point x=0, the restoring force of the spring =0, since F=kx. This point is called equilibrium p ...
Chapter 15—Oscillatory Motion MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A body of
... 29. Ellen says that whenever the acceleration is directly proportional to the displacement of an object from its equilibrium position, the motion of the object is simple harmonic motion. Mary says this is true only if the acceleration is opposite in direction to the displacement. Which one, if eithe ...
... 29. Ellen says that whenever the acceleration is directly proportional to the displacement of an object from its equilibrium position, the motion of the object is simple harmonic motion. Mary says this is true only if the acceleration is opposite in direction to the displacement. Which one, if eithe ...
Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam
... 3.A.1: An observer in a particular reference frame can describe the motion of an object using such quantities as position, displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. 4.A.2: The acceleration is equal to the rate of change of velocity with time, and velocity is equal to the rate of cha ...
... 3.A.1: An observer in a particular reference frame can describe the motion of an object using such quantities as position, displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. 4.A.2: The acceleration is equal to the rate of change of velocity with time, and velocity is equal to the rate of cha ...
Chapter 15 Problems
... released from rest to oscillate without friction. What is its position x at a time 84.4 s later? (b) What If? A hanging spring stretches by 35.5 cm when an object of mass 440 g is hung on it at rest. We define this new position as x = 0. This object is also pulled down an additional 18.0 cm and rele ...
... released from rest to oscillate without friction. What is its position x at a time 84.4 s later? (b) What If? A hanging spring stretches by 35.5 cm when an object of mass 440 g is hung on it at rest. We define this new position as x = 0. This object is also pulled down an additional 18.0 cm and rele ...
universe
... Dark matter is not confined to spiral galaxies . Clouds of hot gas are found to surround elliptically shaped galaxies and the gravitational force produced by the visible matter in the galaxies is not sufficient to keep the gas from evaporating . Compare this to the Earth and moon . The gravitationa ...
... Dark matter is not confined to spiral galaxies . Clouds of hot gas are found to surround elliptically shaped galaxies and the gravitational force produced by the visible matter in the galaxies is not sufficient to keep the gas from evaporating . Compare this to the Earth and moon . The gravitationa ...
Chapter 02 Motion
... 19. Suppose that a rock tied to a string is swinging in a circle. If the string length is increased so that the length doubled but the same speed is maintained, then the force now exerted on the string is A. the same as before. B. doubled. C. half as great. D. four times as great. Accessibility: Key ...
... 19. Suppose that a rock tied to a string is swinging in a circle. If the string length is increased so that the length doubled but the same speed is maintained, then the force now exerted on the string is A. the same as before. B. doubled. C. half as great. D. four times as great. Accessibility: Key ...
the science and detection of gravitational waves - LIGO
... achievement, we can fully expect that we will open up a new way to study the basic structure of gravitation on one hand, and on the other hand we will be able to use gravitational waves themselves as a new probe of astrophysics and the Universe. For fundamental physics, the direct observation of gra ...
... achievement, we can fully expect that we will open up a new way to study the basic structure of gravitation on one hand, and on the other hand we will be able to use gravitational waves themselves as a new probe of astrophysics and the Universe. For fundamental physics, the direct observation of gra ...
1201 lab 6 - U of M Physics
... Find the best place for the adjustable end stop on the track. Do not stretch the springs past 60 cm, but stretch them enough so they oscillate the cart smoothly. Practice releasing the cart smoothly. Use a stopwatch to roughly determine the period of oscillation. Use this to set up the time axis in ...
... Find the best place for the adjustable end stop on the track. Do not stretch the springs past 60 cm, but stretch them enough so they oscillate the cart smoothly. Practice releasing the cart smoothly. Use a stopwatch to roughly determine the period of oscillation. Use this to set up the time axis in ...
Chapter 2 - OnCourse
... a. How long before Fido lands? b. How far did Fido go? c. If he is trying to land on a doggy bone at 125 meters, how close will he be? d. What is his velocity in the y direction just before he lands? _______ sec ______ m ______ m/sec 25. If you were one of Napoleon’s artillery men and you found that ...
... a. How long before Fido lands? b. How far did Fido go? c. If he is trying to land on a doggy bone at 125 meters, how close will he be? d. What is his velocity in the y direction just before he lands? _______ sec ______ m ______ m/sec 25. If you were one of Napoleon’s artillery men and you found that ...
from z=0 to z=1
... luminosity, galaxies at z=0.6 have stellar mass ~2 times less than their z=0 counterparts. No evidence for any evolution in the IR/UV ratio (attenuation) for UV galaxies. For IR (24m) selected galaxies at z~0.6, no evidence is found for evolution of either the stellar mass or the IR/UV ratio for gi ...
... luminosity, galaxies at z=0.6 have stellar mass ~2 times less than their z=0 counterparts. No evidence for any evolution in the IR/UV ratio (attenuation) for UV galaxies. For IR (24m) selected galaxies at z~0.6, no evidence is found for evolution of either the stellar mass or the IR/UV ratio for gi ...
Electrogravitics Systems - Reports On a New Propulsion Methodology
... barium titanium oxide (a baked ceramic) can offer 6,000 and there is promise of 30,000, which would be sufficient for supersonic speed. The original Brown rig produced 30 fps on a voltage of around 50,000 and a small amount of current in the milliamp range. There was no detailed explanation of grav ...
... barium titanium oxide (a baked ceramic) can offer 6,000 and there is promise of 30,000, which would be sufficient for supersonic speed. The original Brown rig produced 30 fps on a voltage of around 50,000 and a small amount of current in the milliamp range. There was no detailed explanation of grav ...
Paper 25 - Free-Energy Devices
... barium titanium oxide (a baked ceramic) can offer 6,000 and there is promise of 30,000, which would be sufficient for supersonic speed. The original Brown rig produced 30 fps on a voltage of around 50,000 and a small amount of current in the milliamp range. There was no detailed explanation of grav ...
... barium titanium oxide (a baked ceramic) can offer 6,000 and there is promise of 30,000, which would be sufficient for supersonic speed. The original Brown rig produced 30 fps on a voltage of around 50,000 and a small amount of current in the milliamp range. There was no detailed explanation of grav ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.