The fate of black hole singularities and the parameters of the
... beginning with an initial value p∗ and letting the system evolve through N generations. Let us define a function B(p) on P that is the expected number of future singularities generated during a lifetime of a universe with parameters5 p. We may observe that, for most p, B(p) is one, but there are sma ...
... beginning with an initial value p∗ and letting the system evolve through N generations. Let us define a function B(p) on P that is the expected number of future singularities generated during a lifetime of a universe with parameters5 p. We may observe that, for most p, B(p) is one, but there are sma ...
Ch 08 B1 QFD.cwk (WP)
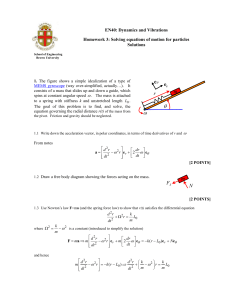
... A lawn roller in the form of a hollow cylinder of mass M is pulled horizontally with constant force F applied by a handle attached to the axle. If it rolls without slipping then find the acceleration of the roller and the friction force that act on it. Answer in terms of F and M. The rotational iner ...
... A lawn roller in the form of a hollow cylinder of mass M is pulled horizontally with constant force F applied by a handle attached to the axle. If it rolls without slipping then find the acceleration of the roller and the friction force that act on it. Answer in terms of F and M. The rotational iner ...
Kick velocity
... But they suffered one SN explosion and there was no Roche-lobe overflow. This means that kicks in these systems were low. The same is true for some of NS+NS binaries. The proposed mechanism is related to e- -capture SN. Such explosions can appear not only in binary systems, but in binaries they can ...
... But they suffered one SN explosion and there was no Roche-lobe overflow. This means that kicks in these systems were low. The same is true for some of NS+NS binaries. The proposed mechanism is related to e- -capture SN. Such explosions can appear not only in binary systems, but in binaries they can ...
Black Hole Simulations for Gravitational Waves Modeling
... • Sajid Ali: A study of positive energy condition in Bianchi universes via Noether symmetries • Muhammad Zaeem Ul Haq Bhatti: Energy Density Irregularities in Self-gravitating systems • Ugur Camci: On first integrals of the geodesic equations for spacetimes via Noether symmetry • Alejandro Cárdenas ...
... • Sajid Ali: A study of positive energy condition in Bianchi universes via Noether symmetries • Muhammad Zaeem Ul Haq Bhatti: Energy Density Irregularities in Self-gravitating systems • Ugur Camci: On first integrals of the geodesic equations for spacetimes via Noether symmetry • Alejandro Cárdenas ...
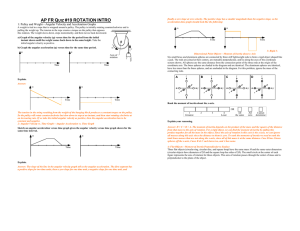
AP Quiz #z19 Rotation Intro AP FR Quiz #19 Rotation Introduction
... from that mass to the axis of rotation. For a rigid object, we can find the moment of inertia by adding this product together for all the mass in the object. Since the axis of rotation in this case is the x-axis, we can ignore all masses along this axis since the distance to them is zero. To rank th ...
... from that mass to the axis of rotation. For a rigid object, we can find the moment of inertia by adding this product together for all the mass in the object. Since the axis of rotation in this case is the x-axis, we can ignore all masses along this axis since the distance to them is zero. To rank th ...
Newton`s Third Law - Jan Roscoe Publications
... NEWTON’s FIRST LAW OF MOTION NEWTON’S FIRST LAW THE EFFECT OF FORCES • this law does not mean that there are no forces • very large forces can act • but if the object is going at constant speed • these forces MUST cancel out ...
... NEWTON’s FIRST LAW OF MOTION NEWTON’S FIRST LAW THE EFFECT OF FORCES • this law does not mean that there are no forces • very large forces can act • but if the object is going at constant speed • these forces MUST cancel out ...
AS90183_NBC_1a
... into open space. Trigger the plunger and observe what happens. 2. Now place the trolley so that the plunger will strike a solid object, such as a wall. Trigger the plunger and observe what happens this time 3. Now place two trolleys so that the plunger will strike one of the trolleys while both trol ...
... into open space. Trigger the plunger and observe what happens. 2. Now place the trolley so that the plunger will strike a solid object, such as a wall. Trigger the plunger and observe what happens this time 3. Now place two trolleys so that the plunger will strike one of the trolleys while both trol ...
Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR MIDTERM 2
... As the worker has been lowering the engine, as described in (a), it has been gaining speed. To slow the engine down, he adjusts the force he applies such that the engine has an acceleration with a magnitude of 0.5 m/s2. Find the new tension in the supporting cable (T1) and the tension in the positio ...
... As the worker has been lowering the engine, as described in (a), it has been gaining speed. To slow the engine down, he adjusts the force he applies such that the engine has an acceleration with a magnitude of 0.5 m/s2. Find the new tension in the supporting cable (T1) and the tension in the positio ...
Honors Physics Unit 4 Notes
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...
December - Rose City Astronomers
... and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embedded in a background haze of a half dozen more fainter suns. The Triangulum o ...
... and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embedded in a background haze of a half dozen more fainter suns. The Triangulum o ...
Downloaded from: www.jsuniltutorial.weebly.com
... There are four fundamental forces in nature that govern the diverse phenomena of the macroscopic and the microscopic world. These are the „gravitational force „, the electromagnetic force‟, „the strong nuclear force‟, and the weak nuclear force‟ The physical quantities that remain unchanged in a ...
... There are four fundamental forces in nature that govern the diverse phenomena of the macroscopic and the microscopic world. These are the „gravitational force „, the electromagnetic force‟, „the strong nuclear force‟, and the weak nuclear force‟ The physical quantities that remain unchanged in a ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The Planetary Nebula Luminosity Function continues to be a useful tool for extragalactic astronomy and cosmology. • The PNLF is the only standard candle capable of measuring distances to all the large galaxies of the local supercluster. • The PNLF cutoff, M*, is the same for old and young ...
... The Planetary Nebula Luminosity Function continues to be a useful tool for extragalactic astronomy and cosmology. • The PNLF is the only standard candle capable of measuring distances to all the large galaxies of the local supercluster. • The PNLF cutoff, M*, is the same for old and young ...
Newton`s Third Law 1.0
... force Fmax and the interaction time t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, t is the time interval during which one cart feels the force due to the other cart. The average value of the time-dependent force (over the t ...
... force Fmax and the interaction time t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, t is the time interval during which one cart feels the force due to the other cart. The average value of the time-dependent force (over the t ...
answers - Stevenson High School
... A 40kg boy is playing with his 20 kg sister who is sitting in a box on the floor. Starting from rest, he pushes the box with a constant horizontal force of 150 N for 2m and then jumps into the box, which moves at a constant speed for a given time period. What is the net force during that given time ...
... A 40kg boy is playing with his 20 kg sister who is sitting in a box on the floor. Starting from rest, he pushes the box with a constant horizontal force of 150 N for 2m and then jumps into the box, which moves at a constant speed for a given time period. What is the net force during that given time ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.