
8-23-10 Newtons laws template
... • Friction on a sloping surface is less than friction on a flat surface (since the normal force is less on a slope). • Increasing weight of an object increases the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on. • Weighting down a car over the drive wheels increases the friction betwee ...
... • Friction on a sloping surface is less than friction on a flat surface (since the normal force is less on a slope). • Increasing weight of an object increases the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on. • Weighting down a car over the drive wheels increases the friction betwee ...
Astronomy 140 Lecture Notes, Spring 2008 c
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
Local Group Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org Mario L Mateo
... Group members is due to the availability of the many largescale photographic surveys of the sky carried out since the seminal Palomar Sky Survey of the 1950s. Soon after these surveys were begun, visual searches of the photographic plates identified new nearby galaxies. Starting in the 1970s, automa ...
... Group members is due to the availability of the many largescale photographic surveys of the sky carried out since the seminal Palomar Sky Survey of the 1950s. Soon after these surveys were begun, visual searches of the photographic plates identified new nearby galaxies. Starting in the 1970s, automa ...
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical
... also be opposite of the displacement. 2. The object is accelerating, and the acceleration is not uniform. This results in a curved velocity-time graph. From chapter 1, we know that the slope of the velocity-time graph represents acceleration. The acceleration of the object is greatest at the object’ ...
... also be opposite of the displacement. 2. The object is accelerating, and the acceleration is not uniform. This results in a curved velocity-time graph. From chapter 1, we know that the slope of the velocity-time graph represents acceleration. The acceleration of the object is greatest at the object’ ...
Summary of Talks at Growing Black Holes 2004 in Garching
... -> High resolution CO observations of the object resolve it spatially into two peaks. It also resolved in velocity space, with a CO line width of 280 km/s and a bulge mass estimate of 1e10 solar masses within 2kpc, which is lower than expected from M sigma relation. Is this object not fully assemble ...
... -> High resolution CO observations of the object resolve it spatially into two peaks. It also resolved in velocity space, with a CO line width of 280 km/s and a bulge mass estimate of 1e10 solar masses within 2kpc, which is lower than expected from M sigma relation. Is this object not fully assemble ...
4.1 Speed
... To determine the slope of a line in a graph, first choose two points on the line. Then count how many steps up or down you must move to be on the same horizontal line as your second point. Multiply this number by the scale of your horizontal axis. For example, if your x-axis has a scale of 1 box = 2 ...
... To determine the slope of a line in a graph, first choose two points on the line. Then count how many steps up or down you must move to be on the same horizontal line as your second point. Multiply this number by the scale of your horizontal axis. For example, if your x-axis has a scale of 1 box = 2 ...
Motion in a Circle
... horizontal plane. Notice that the horizontal component of the tension will now provide the centripetal force while the vertical component balances the weight of the pendulum. Their vector sum is not zero since there must be a resultant force as the centripetal force. ...
... horizontal plane. Notice that the horizontal component of the tension will now provide the centripetal force while the vertical component balances the weight of the pendulum. Their vector sum is not zero since there must be a resultant force as the centripetal force. ...
Forces - Lemon Bay High School
... • Equilibrium is the state in which the net force on an object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If ...
... • Equilibrium is the state in which the net force on an object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If ...
Folie 1
... How to answer some of these? Monitor the brightness of many YSOs over a long period of time. ...
... How to answer some of these? Monitor the brightness of many YSOs over a long period of time. ...
408 4 Biomechanics for the Speed and Power Events
... technique, we try to maximize the benefit derived with respect to one particular biomechanical parameter without examining the cost in other areas. Often a tradeoff exists in the benefits derived from application of differing biomechanical principles. This text will not attempt to indicate optimal d ...
... technique, we try to maximize the benefit derived with respect to one particular biomechanical parameter without examining the cost in other areas. Often a tradeoff exists in the benefits derived from application of differing biomechanical principles. This text will not attempt to indicate optimal d ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, the answer to all the question ...
... Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, the answer to all the question ...
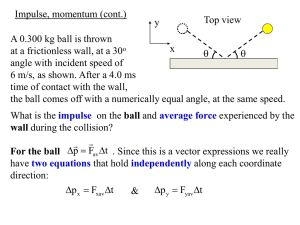
A 0.300 kg ball is thrown at a frictionless wall, at a 30o angle with
... Maria wins, even if she merely holds on with one hand and Arnold does all the pulling. No matter how hard one or the other (or both) pull, they will meet at their center of mass. We’ll soon see why this happens. For now we just want to define the center of mass and learn how to calculated it in var ...
... Maria wins, even if she merely holds on with one hand and Arnold does all the pulling. No matter how hard one or the other (or both) pull, they will meet at their center of mass. We’ll soon see why this happens. For now we just want to define the center of mass and learn how to calculated it in var ...
FREE Sample Here
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Second ...
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Second ...
Friction, Circular Motion
... acceleration of gravity on the Moon is about g / 6) but all else stayed the same? 13. (II) A 1280-kg car pulls a 350-kg trailer. The car exerts a horizontal force of 3.6 3 103 N against the ground in order to accelerate. What force does the car exert on the trailer? Assume an effective friction coef ...
... acceleration of gravity on the Moon is about g / 6) but all else stayed the same? 13. (II) A 1280-kg car pulls a 350-kg trailer. The car exerts a horizontal force of 3.6 3 103 N against the ground in order to accelerate. What force does the car exert on the trailer? Assume an effective friction coef ...
Chapter 5 Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes
... Friction: Harmful and Helpful • Without friction, a car’s tires could not push against the ground to move the car forward, and the brakes could not stop the car. Without friction, a car is useless. • However, friction can also cause problems in a car. Friction between moving engine parts increases t ...
... Friction: Harmful and Helpful • Without friction, a car’s tires could not push against the ground to move the car forward, and the brakes could not stop the car. Without friction, a car is useless. • However, friction can also cause problems in a car. Friction between moving engine parts increases t ...
A Force That Opposes Motio
... Friction: Harmful and Helpful • Without friction, a car’s tires could not push against the ground to move the car forward, and the brakes could not stop the car. Without friction, a car is useless. • However, friction can also cause problems in a car. Friction between moving engine parts increases t ...
... Friction: Harmful and Helpful • Without friction, a car’s tires could not push against the ground to move the car forward, and the brakes could not stop the car. Without friction, a car is useless. • However, friction can also cause problems in a car. Friction between moving engine parts increases t ...
Preview Sample 2
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
... 31) How many forces act on an upwardly tossed coin when it gets to the top of its path? A) one; the force due to gravity B) two; gravity and the force in the coin itself C) three; gravity, the coin's internal force, and a turnaround force D) none of the above Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Secon ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.

















![Module 4.1 - The Scale of the Universe [slide 1] We now turn to](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002846843_1-9e0ec9d1a2abbbab3c0d406694bfc4e2-300x300.png)




