Chapter 9. Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
... • If the kinetic energy of the system is conserved, such a collision is called an elastic collision. • If the kinetic energy of the system is not conserved, such a collision is called an inelastic collision. • The inelastic collision of two bodies always involves a loss in the kinetic energy of the ...
... • If the kinetic energy of the system is conserved, such a collision is called an elastic collision. • If the kinetic energy of the system is not conserved, such a collision is called an inelastic collision. • The inelastic collision of two bodies always involves a loss in the kinetic energy of the ...
cos1+2+3
... – sits near the outer edge of a supercluster, the Virgo cluster. – the Milky Way and Andromeda are moving toward each other, – the Local Group is falling into the middle of the Virgo cluster, and ...
... – sits near the outer edge of a supercluster, the Virgo cluster. – the Milky Way and Andromeda are moving toward each other, – the Local Group is falling into the middle of the Virgo cluster, and ...
Life cycle of low mass stars
... Life cycle of a very small star: Red Dwarf Red Dwarf = a very small star. 1/10 to 1/2 the size of our sun. Very slow to non-existent rate of nuclear fusion Dies as an inert ball of helium, cooling an shrinking. Have the longest lifespan of any star (up to 100 billion yr.) may die as a hel ...
... Life cycle of a very small star: Red Dwarf Red Dwarf = a very small star. 1/10 to 1/2 the size of our sun. Very slow to non-existent rate of nuclear fusion Dies as an inert ball of helium, cooling an shrinking. Have the longest lifespan of any star (up to 100 billion yr.) may die as a hel ...
solution
... direction 662 N 2T = 45g 882 N T = |F| = 22.5g = 220.5 N. 1100 N If you wish, you may assume the mass of the box2 to be m: then the downward acceleration a satisfies Newton's second law: ma = mg. 2. Two boxes are initially stationary and connected by a string over a frictionless pulley, as shown in ...
... direction 662 N 2T = 45g 882 N T = |F| = 22.5g = 220.5 N. 1100 N If you wish, you may assume the mass of the box2 to be m: then the downward acceleration a satisfies Newton's second law: ma = mg. 2. Two boxes are initially stationary and connected by a string over a frictionless pulley, as shown in ...
UCM HONORS PHYSICS 2016 2017
... unless a force acts on it to change that. In other words, in the absence of a modifying force, it is not natural for an object to travel in a circular path. So for a ball swung in vertical circles on a string, the modifying force is the tension in the string that forces it to move in a circle. It pu ...
... unless a force acts on it to change that. In other words, in the absence of a modifying force, it is not natural for an object to travel in a circular path. So for a ball swung in vertical circles on a string, the modifying force is the tension in the string that forces it to move in a circle. It pu ...
Static, Infinite, Etern and Auto sustentable Universe
... consider that by the distance that separates the galaxies, and still greater distance between clusters of galaxies, its gravity force between them is very small, and therefore a semi classical approach is well. In addition, the complexity of the General Relativity equations doesn‟t allow a calculati ...
... consider that by the distance that separates the galaxies, and still greater distance between clusters of galaxies, its gravity force between them is very small, and therefore a semi classical approach is well. In addition, the complexity of the General Relativity equations doesn‟t allow a calculati ...
L9 - University of Iowa Physics
... between it and the dash, otherwise it moves in a straight line • The car actually slides out from under the object • the apparent outward force (as seen by someone in the car) is called the centrifugal force • it is NOT A REAL force! It is a fictitious force • an object will not move in a circle ...
... between it and the dash, otherwise it moves in a straight line • The car actually slides out from under the object • the apparent outward force (as seen by someone in the car) is called the centrifugal force • it is NOT A REAL force! It is a fictitious force • an object will not move in a circle ...
AP physics final AP test review Mechanics
... Called centripetal acceleration. Centripetal Acceleration ac = v2/r Force in Uniform Circular Motion Any force responsible for uniform circular motion is called a centripetal force. Centripetal force can arise from one force, or a combination of sources. F = mac = m v2 / r Since speed of object rem ...
... Called centripetal acceleration. Centripetal Acceleration ac = v2/r Force in Uniform Circular Motion Any force responsible for uniform circular motion is called a centripetal force. Centripetal force can arise from one force, or a combination of sources. F = mac = m v2 / r Since speed of object rem ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... A thin-walled hollow cylinder (mass = mh, radius = rh) and a solid cylinder (mass = ms, radius = rs) start from rest at the top of an incline. ...
... A thin-walled hollow cylinder (mass = mh, radius = rh) and a solid cylinder (mass = ms, radius = rs) start from rest at the top of an incline. ...
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
... During the early part of the twentieth century, an astronomer by the name of Vesto Slipher discovered that the spectra of galaxies indicated that most of them were moving away from our Galaxy. By noting the shift of characteristic lines towards the red end of the spectrum, he surmised that most gala ...
... During the early part of the twentieth century, an astronomer by the name of Vesto Slipher discovered that the spectra of galaxies indicated that most of them were moving away from our Galaxy. By noting the shift of characteristic lines towards the red end of the spectrum, he surmised that most gala ...
A Aberration The apparent change in position of a light
... that the act of murder cannot have an influence on the murderer's decision to commit it. If the murderer were to somehow see himself committing the act and change his mind, then a murder would have been committed in the future without a prior cause (he changed his mind). This represents a causality ...
... that the act of murder cannot have an influence on the murderer's decision to commit it. If the murderer were to somehow see himself committing the act and change his mind, then a murder would have been committed in the future without a prior cause (he changed his mind). This represents a causality ...
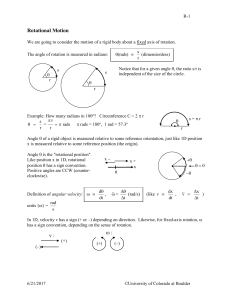
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
REVIEW: Rotational Equilibrium (Chapter 11)
... Gravity acceleration as a function of altitude The g constant of gravitational acceleration has a value of 9.8 m/s2 on the Earth’s surface. However, g will get smaller with altitude. Suppose we are at a distance h above the Earth’s surface. What will the value of g be then? We first solve for g at t ...
... Gravity acceleration as a function of altitude The g constant of gravitational acceleration has a value of 9.8 m/s2 on the Earth’s surface. However, g will get smaller with altitude. Suppose we are at a distance h above the Earth’s surface. What will the value of g be then? We first solve for g at t ...
Acceleration,
... • How does your acceleration compare to your classmate’s acceleration? • In 1 second, you increase your velocity by 6 m/s. Your friend increases her velocity by 3 m/s. • Because your velocity changes more, you have a greater acceleration than your friend does. • It is important to remember that acce ...
... • How does your acceleration compare to your classmate’s acceleration? • In 1 second, you increase your velocity by 6 m/s. Your friend increases her velocity by 3 m/s. • Because your velocity changes more, you have a greater acceleration than your friend does. • It is important to remember that acce ...
Introductory module: a video introduction to Modellus
... method. This means that, for example, in the case constant acceleration, it doesn’t know that the solution for the function x is ½ axt2. But the method used by Modellus is powerful enough to give a numerical solution that is equal or almost equal to the analytical solution in this case and in many m ...
... method. This means that, for example, in the case constant acceleration, it doesn’t know that the solution for the function x is ½ axt2. But the method used by Modellus is powerful enough to give a numerical solution that is equal or almost equal to the analytical solution in this case and in many m ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.