Physics
... When a tetherball is whirling around the pole, the net force is directed (A) toward the top of the pole (B) toward the ground (C) horizontally away from the pole (D) horizontally toward the pole You are standing in a bus that makes a sharp left turn. Which of the following is true? (A) you lean to t ...
... When a tetherball is whirling around the pole, the net force is directed (A) toward the top of the pole (B) toward the ground (C) horizontally away from the pole (D) horizontally toward the pole You are standing in a bus that makes a sharp left turn. Which of the following is true? (A) you lean to t ...
PHY131 E1
... 12 kg. Everything is now transported to the Moon where free-fall acceleration is 1/6 that on Earth. The new readings of the balance and spring scale (respectively) are: -kx = mg (gmoon = 1.66 m/s2) Ans: 12 kg, 2 kg ...
... 12 kg. Everything is now transported to the Moon where free-fall acceleration is 1/6 that on Earth. The new readings of the balance and spring scale (respectively) are: -kx = mg (gmoon = 1.66 m/s2) Ans: 12 kg, 2 kg ...
Presentation
... marked x in the figure below. The two adults push with forces F1 and F2 as shown in the figure. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the smallest force that the child should exert to move the cart in the x direction only. (b) If the child exerts the minimum force found in part (a), the cart accel ...
... marked x in the figure below. The two adults push with forces F1 and F2 as shown in the figure. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the smallest force that the child should exert to move the cart in the x direction only. (b) If the child exerts the minimum force found in part (a), the cart accel ...
Newtonian Mechanics
... Vectors. For two- or three-dimensional motion, the position, velocity, and accleration are all vectors—mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written equations, vecto ...
... Vectors. For two- or three-dimensional motion, the position, velocity, and accleration are all vectors—mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written equations, vecto ...
force
... Zero. Think about if friction could be eliminated~once an object is in motion, it will continue in motion at a constant velocity (same speed and straight line). Newton’s 1st Law INERTIA Remember Galileo postulated that if friction could be entirely eliminated an object in motion would continue to ...
... Zero. Think about if friction could be eliminated~once an object is in motion, it will continue in motion at a constant velocity (same speed and straight line). Newton’s 1st Law INERTIA Remember Galileo postulated that if friction could be entirely eliminated an object in motion would continue to ...
Moment of Inertia
... In applying Newton’s Second Law of Motion to rotational motion, it is known that the relation between torque and angular acceleration depends on both the mass and the distribution of that mass; this relationship is known as the moment of inertia. The moment of inertia for discrete distributions of m ...
... In applying Newton’s Second Law of Motion to rotational motion, it is known that the relation between torque and angular acceleration depends on both the mass and the distribution of that mass; this relationship is known as the moment of inertia. The moment of inertia for discrete distributions of m ...
The astronauts in the upper left of this photo are working on the
... © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
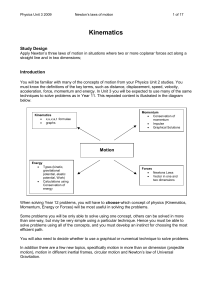
Kinematics - Vicphysics
... instantaneous quantities i.e. the value of a quantity at a specific time. For example, a velocity time graph (v-t) can be used to determine how fast an object was moving at a specific time. It could also be used to determine how far the object has moved up to that time (by finding the area under the ...
... instantaneous quantities i.e. the value of a quantity at a specific time. For example, a velocity time graph (v-t) can be used to determine how fast an object was moving at a specific time. It could also be used to determine how far the object has moved up to that time (by finding the area under the ...
Physics Beyond 2000
... • What are the forces acting on the man? Normal contact force N. This is the reading on the balance. ...
... • What are the forces acting on the man? Normal contact force N. This is the reading on the balance. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.