Kinematics - Vicphysics
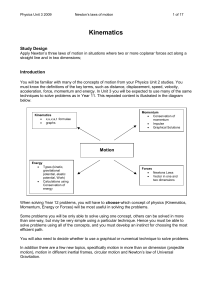
... instantaneous quantities i.e. the value of a quantity at a specific time. For example, a velocity time graph (v-t) can be used to determine how fast an object was moving at a specific time. It could also be used to determine how far the object has moved up to that time (by finding the area under the ...
... instantaneous quantities i.e. the value of a quantity at a specific time. For example, a velocity time graph (v-t) can be used to determine how fast an object was moving at a specific time. It could also be used to determine how far the object has moved up to that time (by finding the area under the ...
008 Newton`s Second Law Explored
... • For most practical situations in biomechanics, velocity has more meaning than acceleration. • Further, practitioners such as coaches are usually interested in the velocity after a net force has acted. ...
... • For most practical situations in biomechanics, velocity has more meaning than acceleration. • Further, practitioners such as coaches are usually interested in the velocity after a net force has acted. ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... the average the angular speed (or angular velocity) of the system. Record any other information you will need to analyze the force on the spring, such as the radius and the total force (determined while the system was stationary). Make sure you have a column for the speed of the rotating object, whi ...
... the average the angular speed (or angular velocity) of the system. Record any other information you will need to analyze the force on the spring, such as the radius and the total force (determined while the system was stationary). Make sure you have a column for the speed of the rotating object, whi ...
Physics Beyond 2000
... • What are the forces acting on the man? Normal contact force N. This is the reading on the balance. ...
... • What are the forces acting on the man? Normal contact force N. This is the reading on the balance. ...
Chapter 4 forces - student practice notes
... Galileo vs. Newton report – 1 to 1.5 pg, dbl spaced, 12pt font, MLA format, at least 2 citations, in text citing, summative grade. Summarize the contributions of both Galileo and Newton to the understanding of moving bodies and gravity. Were their findings independent or did one build on the other? ...
... Galileo vs. Newton report – 1 to 1.5 pg, dbl spaced, 12pt font, MLA format, at least 2 citations, in text citing, summative grade. Summarize the contributions of both Galileo and Newton to the understanding of moving bodies and gravity. Were their findings independent or did one build on the other? ...
Lecture 5 - HKU Physics
... Explain the following description. A bucket of water can be swung round in a vertical circle without falling spilling. If the weight mg of the water is less than mv2/r, the normal force N of the bottom of the bucket on the water provides the rest of the force required to maintain the water in its ci ...
... Explain the following description. A bucket of water can be swung round in a vertical circle without falling spilling. If the weight mg of the water is less than mv2/r, the normal force N of the bottom of the bucket on the water provides the rest of the force required to maintain the water in its ci ...
Planetary Orbit Simulator – Student Guide
... o Change the semimajor axis to something about Mars or Jupiter o Change the eccentricity to a non-zero – somewhere around 0.5 Question 11: Where (or when) is the sweep segment the “skinniest”? ...
... o Change the semimajor axis to something about Mars or Jupiter o Change the eccentricity to a non-zero – somewhere around 0.5 Question 11: Where (or when) is the sweep segment the “skinniest”? ...
Ch. 12 Notes - leavellphysicalscience
... after it is given an initial forward velocity Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. Key Concept: The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward vertical force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved ...
... after it is given an initial forward velocity Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. Key Concept: The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward vertical force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved ...
CTCirca
... Answer: The only correct statement here is : After Bowman releases the pen, the net force on the pen is zero. There is no gravity here and since nothing is touching the pen, there is no force on it (I am ignoring the small drag force due to the air in the centrifuge.). Before the pen is released, it ...
... Answer: The only correct statement here is : After Bowman releases the pen, the net force on the pen is zero. There is no gravity here and since nothing is touching the pen, there is no force on it (I am ignoring the small drag force due to the air in the centrifuge.). Before the pen is released, it ...
Circular Motion
... • Linear speed - is distance/time • Since the outer edge of on object moving in a circle moves further it has greater linear speed. ...
... • Linear speed - is distance/time • Since the outer edge of on object moving in a circle moves further it has greater linear speed. ...
Document
... Look at your diagram and determine if the torque would cause a + or a – rotation (according to your choice of +). In this case, the rotation would be -, so z=-RF sinθ. ...
... Look at your diagram and determine if the torque would cause a + or a – rotation (according to your choice of +). In this case, the rotation would be -, so z=-RF sinθ. ...
File - wentworth science
... • The same force exerted on a small mass produces a large acceleration. • The same force exerted on a large mass produces a small acceleration. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • The same force exerted on a small mass produces a large acceleration. • The same force exerted on a large mass produces a small acceleration. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Space astrometry 2: Scientific results from Hipparcos
... • Oort limit (Holmberg & Flynn 2004): ρ0 = 0.102 M⊙ pc-3 • vertical oscillation period: P⊥ = (π/Gρ0)0.5 = 82 Myr ...
... • Oort limit (Holmberg & Flynn 2004): ρ0 = 0.102 M⊙ pc-3 • vertical oscillation period: P⊥ = (π/Gρ0)0.5 = 82 Myr ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.