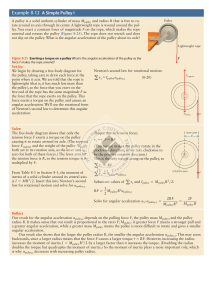
Chris Khan 2007 Physics Chapter 6 FF represents the force of
... of the circle. This means that the ball accelerates towards the center of the circle even though speed is constant because acceleration is produced whenever the speed or direction of velocity changes. Here, direction changes constantly. The center-seeking acceleration is known as centripetal acceler ...
... of the circle. This means that the ball accelerates towards the center of the circle even though speed is constant because acceleration is produced whenever the speed or direction of velocity changes. Here, direction changes constantly. The center-seeking acceleration is known as centripetal acceler ...
Notes
... Questions and Problems: 1. Where is the CG of the earth’s atmosphere? 2. Why is it dangerous to slide open the top drawers of a fully loaded file cabinet or dresser that is not secured to the floor or wall? 3. When a car drives off a cliff, why does it rotate forward as it falls? 4. Why doesn’t the ...
... Questions and Problems: 1. Where is the CG of the earth’s atmosphere? 2. Why is it dangerous to slide open the top drawers of a fully loaded file cabinet or dresser that is not secured to the floor or wall? 3. When a car drives off a cliff, why does it rotate forward as it falls? 4. Why doesn’t the ...
Circular Motion - juan
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Section 6.2 Circular Motion Acceleration
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
(T) involved in our formula? 12-3 Kepler`s Laws of
... due to gravity. There are no exceptions – if you have mass, every other mass is attracted to you, and you are attracted to every other mass. Look around the room – everybody here is attracted to you! Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation gives us a formula to calculate the attractive force between 2 ...
... due to gravity. There are no exceptions – if you have mass, every other mass is attracted to you, and you are attracted to every other mass. Look around the room – everybody here is attracted to you! Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation gives us a formula to calculate the attractive force between 2 ...
Test 2 Review
... to forces by looking at the behavior of the center of mass. This makes it a very significant point to engineers. Engineers try to design a sports car so its center of gravity is as low as possible to make the car handle better. For a plane to be safe to fly, the center of gravity should be about one ...
... to forces by looking at the behavior of the center of mass. This makes it a very significant point to engineers. Engineers try to design a sports car so its center of gravity is as low as possible to make the car handle better. For a plane to be safe to fly, the center of gravity should be about one ...
Related topics Velocity, acceleration, force, gravitational
... The evaluation process is explained based on the following model experiment. The accelerating distance is 0.76 m, the accelerating mass m1 is 10 g, the total mass m2 of the cart is 395 g (including the needle with plug, holding magnet with plug, needle, and tab). Transfer the video that has been rec ...
... The evaluation process is explained based on the following model experiment. The accelerating distance is 0.76 m, the accelerating mass m1 is 10 g, the total mass m2 of the cart is 395 g (including the needle with plug, holding magnet with plug, needle, and tab). Transfer the video that has been rec ...
Chapter 6 Notes Circular Motion and Gravity
... For object’s experiencing circular motion, the acceleration that is the result of an the object's change in velocity is called centripetal acceleration and it points toward the center of the object's circular path. ac = v2/r I am not going to derive this equation!! ...
... For object’s experiencing circular motion, the acceleration that is the result of an the object's change in velocity is called centripetal acceleration and it points toward the center of the object's circular path. ac = v2/r I am not going to derive this equation!! ...
FACULTY OF SCIENCE SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION PHYSICS 198-101A (2000) MECHANICS AND WAVES
... You are sitting on a bathroom scale in an airplane. (Don't ask why you might be doing this, perhaps you are a bathroom-scale fetiscist.) As the plane enters an "airpocket" you notice that the scale reads 45 kg. If you know that you weigh 80 kg, what is the vertical acceleration of the plane ? (3 mar ...
... You are sitting on a bathroom scale in an airplane. (Don't ask why you might be doing this, perhaps you are a bathroom-scale fetiscist.) As the plane enters an "airpocket" you notice that the scale reads 45 kg. If you know that you weigh 80 kg, what is the vertical acceleration of the plane ? (3 mar ...
Ch7 notes
... speed will increase with time If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in opposite directions, the angular speed will decrease with time ...
... speed will increase with time If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in opposite directions, the angular speed will decrease with time ...
gravitation - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... M located at the same place as the center of the sphere. That is, the gravitational field due to 3(a) is exactly the same as the field due to 3(b) for every point r > R. (For r < R, the fields are very different for these two situations.) Therefore, whenever you encounter a spherically symmetric obj ...
... M located at the same place as the center of the sphere. That is, the gravitational field due to 3(a) is exactly the same as the field due to 3(b) for every point r > R. (For r < R, the fields are very different for these two situations.) Therefore, whenever you encounter a spherically symmetric obj ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR When a cannon is fired, the accelerations of the cannon and cannonball are different because the forces don’t occur at the same time. forces, although theoretically the same, in practice are not. C. masses are different. D. ratios of force to mass are the same. A. B. ...
... CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR When a cannon is fired, the accelerations of the cannon and cannonball are different because the forces don’t occur at the same time. forces, although theoretically the same, in practice are not. C. masses are different. D. ratios of force to mass are the same. A. B. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.