Name
... Sediments precipitated by processes such as temperature change, evaporation, and chemical activity are called biochemical sediments. Which one of the following is NOT a variety of limestone? Which common mineral found in igneous rocks is most abundant in detrital ...
... Sediments precipitated by processes such as temperature change, evaporation, and chemical activity are called biochemical sediments. Which one of the following is NOT a variety of limestone? Which common mineral found in igneous rocks is most abundant in detrital ...
Unit 3 Geochemical Cycles in the Earth`s System
... • __________ – compacted fragments • Ex: __________ (smooth) and ________(sharp fragments) • __________ – minerals dissolved in water • Ex: Evaporites • __________– remains of organisms • Ex: Coal ...
... • __________ – compacted fragments • Ex: __________ (smooth) and ________(sharp fragments) • __________ – minerals dissolved in water • Ex: Evaporites • __________– remains of organisms • Ex: Coal ...
Rocks and Fossil Fuels
... Sediment is tiny bits of weathered and eroded rock. Sediment can even be once living plants or animals! ...
... Sediment is tiny bits of weathered and eroded rock. Sediment can even be once living plants or animals! ...
Rocks Minerals Pictures
... What do we call a rock that forms from material that has settled into layers that are squeezed together over time? ...
... What do we call a rock that forms from material that has settled into layers that are squeezed together over time? ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... 1. ________________ – clastic sedimentary rocks are formed when already existing rocks _________ into smaller ________________ 2. ___________ – weathered rock _________ are _____________ by rivers, winds, waves, and glaciers 3. _____________ – sediments are ____________ when the transport system (ie ...
... 1. ________________ – clastic sedimentary rocks are formed when already existing rocks _________ into smaller ________________ 2. ___________ – weathered rock _________ are _____________ by rivers, winds, waves, and glaciers 3. _____________ – sediments are ____________ when the transport system (ie ...
Features of Sedimentary Rocks
... FOSSILS Sedimentary rock often contains fossils. A fossil is the remains, impression, or any other evidence of a plant or animal preserved in rock. Fossilization occurs when a dead plant or animal is buried by sediments that gradually turn to rock. The soft parts of the animals and plants usually de ...
... FOSSILS Sedimentary rock often contains fossils. A fossil is the remains, impression, or any other evidence of a plant or animal preserved in rock. Fossilization occurs when a dead plant or animal is buried by sediments that gradually turn to rock. The soft parts of the animals and plants usually de ...
sedimentary rocks (clastic)
... eggs. On a cut or broken surface they look circular, and internal concentric laminations may be seen with a hand lens or microscope. ...
... eggs. On a cut or broken surface they look circular, and internal concentric laminations may be seen with a hand lens or microscope. ...
Sedimentary Rocks ID Lab
... Other sedimentary rocks are made when they are left behind when seawater evaporates. Others are made when biologic remains (yes, things that were alive and now are pretty dead) are compacted together and/or cemented together by mineral material. Remember, fossils (evidence of past life) are almost e ...
... Other sedimentary rocks are made when they are left behind when seawater evaporates. Others are made when biologic remains (yes, things that were alive and now are pretty dead) are compacted together and/or cemented together by mineral material. Remember, fossils (evidence of past life) are almost e ...
Types of Rock - Teacher Bulletin
... – Formed as magma cools – Intrusive rocks cool slowly below ground and have a coarse texture. – Example: granite ...
... – Formed as magma cools – Intrusive rocks cool slowly below ground and have a coarse texture. – Example: granite ...
Instructor Copy
... How can rocks be identified? Rocks may show ripple marks, mudcracks, raindrops and fossils. Can often see sand, pebbles, or stones in the rock. ...
... How can rocks be identified? Rocks may show ripple marks, mudcracks, raindrops and fossils. Can often see sand, pebbles, or stones in the rock. ...
Discuss on Chemical Sedimentary Rocks Submitted by WWW
... also known as geodes, are commonly found in limestones and less so in clastic sedimentary rocks. They form in pockets or voids that might have once been occupied by gas or organic material that has since been removed or decomposed. Cherts can also occur as continuous layers in sedimentary rocks. Che ...
... also known as geodes, are commonly found in limestones and less so in clastic sedimentary rocks. They form in pockets or voids that might have once been occupied by gas or organic material that has since been removed or decomposed. Cherts can also occur as continuous layers in sedimentary rocks. Che ...
More Principles of Relative Dating Note 2 Inclusions:
... - pieces of one rock are contained (included ) in another - Included rock is the remains of the older rock (usually sedimentary) - rock that has included pieces is younger (usually igneous) ...
... - pieces of one rock are contained (included ) in another - Included rock is the remains of the older rock (usually sedimentary) - rock that has included pieces is younger (usually igneous) ...
Chapter 6, Sedimentary Rock
... Dolomite (or Dolostone) - CaCO3 with some Mg Chalk - CaCO3 o Siliceous - hard, compact, fine-grained, formed almost entirely of silica. Examples: A ‘limestone’ made up of shell Diatomite - silica, SiO2; from microscopic skeletons fragments, also called Coquina Chert - silica, SiO2; mainly fr ...
... Dolomite (or Dolostone) - CaCO3 with some Mg Chalk - CaCO3 o Siliceous - hard, compact, fine-grained, formed almost entirely of silica. Examples: A ‘limestone’ made up of shell Diatomite - silica, SiO2; from microscopic skeletons fragments, also called Coquina Chert - silica, SiO2; mainly fr ...
Chapter Outlines
... Dolomite (or Dolostone) - CaCO3with some Mg Chalk - CaCO3 o Siliceous - hard, compact, fine-grained, formed almost entirely of silica. Examples: A ‘limestone’ made up of shell Diatomite - silica, SiO2; from microscopic skeletons fragments, also called Coquina Chert - silica, SiO2; mainly fro ...
... Dolomite (or Dolostone) - CaCO3with some Mg Chalk - CaCO3 o Siliceous - hard, compact, fine-grained, formed almost entirely of silica. Examples: A ‘limestone’ made up of shell Diatomite - silica, SiO2; from microscopic skeletons fragments, also called Coquina Chert - silica, SiO2; mainly fro ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Flowing water or air can transport sand grains. These will form ripples (small scale) or dunes (large scale). The position of the front of the ripple or dune can be preserved in the sediment as the ripple moves forward. This is called crossbedding. (l) Sketch a ripple and show how the symmetry of th ...
... Flowing water or air can transport sand grains. These will form ripples (small scale) or dunes (large scale). The position of the front of the ripple or dune can be preserved in the sediment as the ripple moves forward. This is called crossbedding. (l) Sketch a ripple and show how the symmetry of th ...
Sedimentary rock
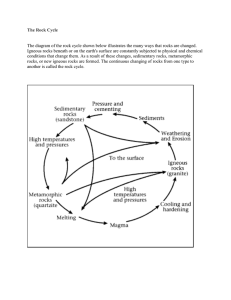
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.