
Our Changing Earth
... Sand dunes are large hills of sand often found in the desert. These huge features are made by wind erosion. The size and shape of dunes depend on the amount of sand, the number of plants in the area, and the strength of the winds. Winds can also blow sand dunes across the desert. The wind picks up s ...
... Sand dunes are large hills of sand often found in the desert. These huge features are made by wind erosion. The size and shape of dunes depend on the amount of sand, the number of plants in the area, and the strength of the winds. Winds can also blow sand dunes across the desert. The wind picks up s ...
Physics 105 TEST II part II questions
... compresses its interior to a greater extent than that of Saturn. E) It is not denser than Saturn. 4) Why does Jupiter have several distinct cloud layers? 4) _______ A) Clouds form randomly, so on average there are always several layers. B) Different layers represent the various regions where the tem ...
... compresses its interior to a greater extent than that of Saturn. E) It is not denser than Saturn. 4) Why does Jupiter have several distinct cloud layers? 4) _______ A) Clouds form randomly, so on average there are always several layers. B) Different layers represent the various regions where the tem ...
File
... melts surrounding rock and intrudes into other rocks, causing them to fall into the magma “body.” Magma that gets to the surface is called lava. When this magma/lava cools, it is called igneous rock, if it cools INSIDE the crust, it is called intrusive igneous rock or a pluton. ...
... melts surrounding rock and intrudes into other rocks, causing them to fall into the magma “body.” Magma that gets to the surface is called lava. When this magma/lava cools, it is called igneous rock, if it cools INSIDE the crust, it is called intrusive igneous rock or a pluton. ...
1 Earth`s Shape
... 2. Convection: If a material is able to move, even if it moves very slowly, convection currents can form. Convection in the mantle is the same as convection in a pot of water on a stove. Convection currents within Earth’s mantle form as material near the core heats up. As the core heats the bottom l ...
... 2. Convection: If a material is able to move, even if it moves very slowly, convection currents can form. Convection in the mantle is the same as convection in a pot of water on a stove. Convection currents within Earth’s mantle form as material near the core heats up. As the core heats the bottom l ...
plate - TeacherWeb
... • The exception to this arrangement are "Hot Spots" which are plumes of hot material (rather than belts) in the middle of plates. These spots stay stationary while the plate moves above it. The spot melts through the plate like a blow torch and produces a volcano above it. As the plate moves, the sp ...
... • The exception to this arrangement are "Hot Spots" which are plumes of hot material (rather than belts) in the middle of plates. These spots stay stationary while the plate moves above it. The spot melts through the plate like a blow torch and produces a volcano above it. As the plate moves, the sp ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... A geologically active area where tectonic shifts make volcanoes and earthquakes common. Tsunamis may also be caused by underwater landslides or volcanic eruptions. Or by the impact of a large meteorite plunging into an ocean. ...
... A geologically active area where tectonic shifts make volcanoes and earthquakes common. Tsunamis may also be caused by underwater landslides or volcanic eruptions. Or by the impact of a large meteorite plunging into an ocean. ...
Earthquakes - Siemens Science Day
... An earthquake is the shaking of the ground caused by the rapid movement of underground rock. Earthquakes occur when rocks in the crust break or move suddenly along faults. Earthquakes change Earth’s surface rapidl ...
... An earthquake is the shaking of the ground caused by the rapid movement of underground rock. Earthquakes occur when rocks in the crust break or move suddenly along faults. Earthquakes change Earth’s surface rapidl ...
Slide 1
... rocks in that they: 1. Are formed from layers of sediment built up over many years. 2. Are grains of sediment cemented together by various minerals. 3. May contain fossils - remains of plants and animals that were caught up in the sediment. ...
... rocks in that they: 1. Are formed from layers of sediment built up over many years. 2. Are grains of sediment cemented together by various minerals. 3. May contain fossils - remains of plants and animals that were caught up in the sediment. ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... cool, strong and rigid layer. Its uppermost part is called the crust and is divided into oceanic and continental-type crusts discussed in the next section. Asthenosphere. The upper reaches of the mantle are not solid; they are considered plastic and flow very slowly. This is due to the reduction in ...
... cool, strong and rigid layer. Its uppermost part is called the crust and is divided into oceanic and continental-type crusts discussed in the next section. Asthenosphere. The upper reaches of the mantle are not solid; they are considered plastic and flow very slowly. This is due to the reduction in ...
SIXTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES
... As they go through different substances, seismic waves will change speed and sometimes change direction. In lab, students will look at some of these changes. During an earthquake wave motion can cause serious damage. For example, an earthquake may cause little damage at its epicenter if that area is ...
... As they go through different substances, seismic waves will change speed and sometimes change direction. In lab, students will look at some of these changes. During an earthquake wave motion can cause serious damage. For example, an earthquake may cause little damage at its epicenter if that area is ...
Module 3, Investigation 3: Plate Tectonics Introduction Welcome
... In Investigation 2, Folder 3: "The Hypothesis", you also learned that liquid iron in the outer core moves in large convection currents. The heat carried by these currents is generated from radioactive decay of several chemical elements in the Earth's core, including potassium, uranium, and thorium. ...
... In Investigation 2, Folder 3: "The Hypothesis", you also learned that liquid iron in the outer core moves in large convection currents. The heat carried by these currents is generated from radioactive decay of several chemical elements in the Earth's core, including potassium, uranium, and thorium. ...
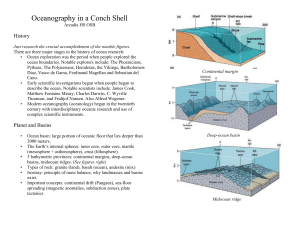
InAConchShell - some tryout study material
... electrodialysis, salt absorption Hydrologic cycle (evaporation, condensation, etc.) ...
... electrodialysis, salt absorption Hydrologic cycle (evaporation, condensation, etc.) ...
Living in an Active Zone
... travelling through the earth crust • The source of the earthquake is called the focus, the epicentre is the point immediately above it on the surface • Size of an earthquake can be measured by a seismometer along the Richter scale • Tsunamis are a secondary hazard of an earthquake ...
... travelling through the earth crust • The source of the earthquake is called the focus, the epicentre is the point immediately above it on the surface • Size of an earthquake can be measured by a seismometer along the Richter scale • Tsunamis are a secondary hazard of an earthquake ...
Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]
... • Subduction. The old, cold, thick oceanic plate dives down into the mantle beneath either a continental or another oceanic plate. Bending of the plate results in a deep trench. • Water. Sea water subducted down into the mantle along with the oceanic plate decreases the melting temperature of the ma ...
... • Subduction. The old, cold, thick oceanic plate dives down into the mantle beneath either a continental or another oceanic plate. Bending of the plate results in a deep trench. • Water. Sea water subducted down into the mantle along with the oceanic plate decreases the melting temperature of the ma ...
earth dynamics - Index of /~pgres
... Programmes in Earth Science. Earth Dynamics is not only the ‘starter’ course for most of our degrees, but also a course designed to be of interest to students who just want to find a few things out about the Earth and its many processes. This booklet provides you with information about the course an ...
... Programmes in Earth Science. Earth Dynamics is not only the ‘starter’ course for most of our degrees, but also a course designed to be of interest to students who just want to find a few things out about the Earth and its many processes. This booklet provides you with information about the course an ...
Explain the different soil types (bedrock/compact soil/loose sand
... • How do scientists know what layers are under the earth’s crust? • Earthquake waves travel through the earth and the speeds and locations help us determine what materials they are traveling through. ...
... • How do scientists know what layers are under the earth’s crust? • Earthquake waves travel through the earth and the speeds and locations help us determine what materials they are traveling through. ...
Section 1 Inside the Earth Chapter 15 Tectonic Plates, continued A
... tectonic plates and how they fit together. • The presentation also illustrates what a tectonic plate might look like if you could lift it out of its place. ...
... tectonic plates and how they fit together. • The presentation also illustrates what a tectonic plate might look like if you could lift it out of its place. ...
Chapter 2 Earthquakes
... occurring. The __________ a building is from a fault the __________ strong the shaking will be. 2. Construction methods-A building that rests on shock absorbing pads or springs will have less energy from an earthquake reach them. This type of building is called a _____-__________ building. 3. Protec ...
... occurring. The __________ a building is from a fault the __________ strong the shaking will be. 2. Construction methods-A building that rests on shock absorbing pads or springs will have less energy from an earthquake reach them. This type of building is called a _____-__________ building. 3. Protec ...
Local copy - John C Lahr
... Because of the overwhelming amount of data collected, the possible complications imposed by the propagation of ground motion through a complex earth, and the complications imposed by some of the necessary simplifications required by the ...
... Because of the overwhelming amount of data collected, the possible complications imposed by the propagation of ground motion through a complex earth, and the complications imposed by some of the necessary simplifications required by the ...
available
... well-constrained by the seafloor magnetic anomaly data oldest anomalies in NW Pacific ~160 Ma actually positions between continents always being ‘tweaked’ ‘rigid’ vs. ‘non-rigid’ plates ...
... well-constrained by the seafloor magnetic anomaly data oldest anomalies in NW Pacific ~160 Ma actually positions between continents always being ‘tweaked’ ‘rigid’ vs. ‘non-rigid’ plates ...
Chapter 8 Science Test Notes
... • Fossils cannot provide evidence about how Earth looked 4.5 billion years ago. • The idea that geological change happens suddenly is called catastrophism. ...
... • Fossils cannot provide evidence about how Earth looked 4.5 billion years ago. • The idea that geological change happens suddenly is called catastrophism. ...
WELIM Solar Energy
... carry contain minerals that have low melting points, having been formed at the Earth’s surface at cool temperatures. Subducting slabs are also accompanied by water, which further depresses melting points for the minerals. Consequently, as the slabs are carried into the deeper, hotter mantle, they he ...
... carry contain minerals that have low melting points, having been formed at the Earth’s surface at cool temperatures. Subducting slabs are also accompanied by water, which further depresses melting points for the minerals. Consequently, as the slabs are carried into the deeper, hotter mantle, they he ...
1. What is rock? 2. The layer of solid rock that surrounds Earth`s
... On the T/F questions, 6. What is the theory of plate tectonics? correct the underlined 7. What does the theory of plate tectonics explain? word(s) if it’s false!! 8. The plates of the lithosphere float on material in the …? ...
... On the T/F questions, 6. What is the theory of plate tectonics? correct the underlined 7. What does the theory of plate tectonics explain? word(s) if it’s false!! 8. The plates of the lithosphere float on material in the …? ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.













![Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000728998_1-eea64118f8dd5f3d44e4d2914cefeaa2-300x300.png)








