Children with congenital unilateral sensorineural hearing loss: The
... Marlin Johansson, Division of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases marlin.johansson@ki.se ...
... Marlin Johansson, Division of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases marlin.johansson@ki.se ...
Special senses
... --collect sound waves and pass them inwards. --It consists of pinna, external auditory meatus & tympanic membrane. The middle ear (Tympanic cavity) is a small airfilled cavity in the temporal bone. --it is lined by epithelium & contain auditory ossicles(malleus, incus & stapes) and auditory tube(Eus ...
... --collect sound waves and pass them inwards. --It consists of pinna, external auditory meatus & tympanic membrane. The middle ear (Tympanic cavity) is a small airfilled cavity in the temporal bone. --it is lined by epithelium & contain auditory ossicles(malleus, incus & stapes) and auditory tube(Eus ...
669791508362MyersMod_LG_13
... 1. Explain the auditory process, including the stimulus input and the structure and function of the ear. Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. The pressure waves we experience as sound vary in amplitude and frequency and correspondingly in perceived loudness and pitch. Decibels are the measuring ...
... 1. Explain the auditory process, including the stimulus input and the structure and function of the ear. Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. The pressure waves we experience as sound vary in amplitude and frequency and correspondingly in perceived loudness and pitch. Decibels are the measuring ...
Reviewing the Purpose of Story Boxes
... The outer hair cells of the cochlea serve as an amplifier while the inner hair cells turn the sounds waves into electrical impulses. The impulses are transmitted to the auditory nerve, which carries the sound to the brain, where it is interpreted. Something can go wrong anywhere in the process. What ...
... The outer hair cells of the cochlea serve as an amplifier while the inner hair cells turn the sounds waves into electrical impulses. The impulses are transmitted to the auditory nerve, which carries the sound to the brain, where it is interpreted. Something can go wrong anywhere in the process. What ...
Special Senses - El Camino College
... ________ (hammer) - articulates with tympanic membrane _______ (anvil) - articulates with malleus & stapes ...
... ________ (hammer) - articulates with tympanic membrane _______ (anvil) - articulates with malleus & stapes ...
Midterm 1
... back and forth to test the hypothesis that hearing depends on the motion of your inner ear. You do not hear anything even though they are trying really hard to shake you up. Explain why your experiment has failed, that is, explain how sound depends on the motion of the inner ear, yet you don't hear ...
... back and forth to test the hypothesis that hearing depends on the motion of your inner ear. You do not hear anything even though they are trying really hard to shake you up. Explain why your experiment has failed, that is, explain how sound depends on the motion of the inner ear, yet you don't hear ...
Auditory, Tactile, and Vestibular Systems
... Pinna – collects sound, helps localization (Holds up glasses) Tympanic Membrane (ear drum)– at end of ear canal, vibrates to sound pressure (like a drum head) Ossicles – bones of middle ear that convert sound to mechanical energy. – Malleus (hammer) is the largest bone and receives vibration from ea ...
... Pinna – collects sound, helps localization (Holds up glasses) Tympanic Membrane (ear drum)– at end of ear canal, vibrates to sound pressure (like a drum head) Ossicles – bones of middle ear that convert sound to mechanical energy. – Malleus (hammer) is the largest bone and receives vibration from ea ...
Do You Hear What I Hear?
... Extra Credit: Label as many parts of the ear as you can. Each correct answer is worth 1 bonus ...
... Extra Credit: Label as many parts of the ear as you can. Each correct answer is worth 1 bonus ...
handout_2
... The Stapedius muscle is the smallest muscle with an average length of 6.3 mm, while the Tensor Tympani is 25 mm. The Stapedius muscle emerges from a bony projection (pyramid) in the posterior wall and attaches to the neck of the Stapes. Upon contraction it pulls the Stapes posteriorly and it i ...
... The Stapedius muscle is the smallest muscle with an average length of 6.3 mm, while the Tensor Tympani is 25 mm. The Stapedius muscle emerges from a bony projection (pyramid) in the posterior wall and attaches to the neck of the Stapes. Upon contraction it pulls the Stapes posteriorly and it i ...
Congenital Temporal Bone Anomalies: An
... bone shows bilateral fusion of the lateral semicircular canals and vestibule (black arrows). The posterior (yellow arrows) and superior semicircular canals as well as the cochlea was normal bilaterally. The lateral SCC is the last to develop and therefore is the most commonly malformed canal. Isolat ...
... bone shows bilateral fusion of the lateral semicircular canals and vestibule (black arrows). The posterior (yellow arrows) and superior semicircular canals as well as the cochlea was normal bilaterally. The lateral SCC is the last to develop and therefore is the most commonly malformed canal. Isolat ...
Implementation of a Medical Device for Testing the Functionality of
... This project attempts to annul the aforementioned problems associated with DPOAE measurement devices by implementing a clinically viable prototype. The gap between data collection and data processing will be bridged using the MATLAB data acquisition toolbox. The problem associated with complex compu ...
... This project attempts to annul the aforementioned problems associated with DPOAE measurement devices by implementing a clinically viable prototype. The gap between data collection and data processing will be bridged using the MATLAB data acquisition toolbox. The problem associated with complex compu ...
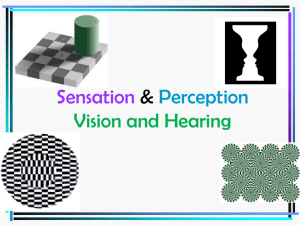
Sensation and Perception - Weebly
... the air outside and allows the bones of the middle ear to vibrate properly. When you "pop" your ears as you change altitude (going up a mountain or in an airplane), you are equalizing the air pressure in your middle ear. ...
... the air outside and allows the bones of the middle ear to vibrate properly. When you "pop" your ears as you change altitude (going up a mountain or in an airplane), you are equalizing the air pressure in your middle ear. ...
UNIT 11 Special Senses: Eyes and Ears Pathological Conditions
... Suppurative OM is a common affliction in infants and young children, due to the horizontal orientation and small diameter of the eustachian tube in such patients, which predisposes them to infection. If left untreated, ...
... Suppurative OM is a common affliction in infants and young children, due to the horizontal orientation and small diameter of the eustachian tube in such patients, which predisposes them to infection. If left untreated, ...
DATA INFORMATION
... Noise exposures that are loud enough and last long enough could damage the nerves in the inner ear complex system that will result in permanent and irreversible hearing loss. Repeated exposure to noise levels above 85dBA or one exposure to 140dBA could results in hearing loss. The hearing disability ...
... Noise exposures that are loud enough and last long enough could damage the nerves in the inner ear complex system that will result in permanent and irreversible hearing loss. Repeated exposure to noise levels above 85dBA or one exposure to 140dBA could results in hearing loss. The hearing disability ...
Introduction
... III-The inner ear The inner ear it is called labyrinth and it is made of two parts one within the other the bony labyrinth is encased in the hardest bone of the body, the petrous bone. Within this ivory hard bone, there is a membranous labyrinth is surrounded by perilymph, which by itself contains a ...
... III-The inner ear The inner ear it is called labyrinth and it is made of two parts one within the other the bony labyrinth is encased in the hardest bone of the body, the petrous bone. Within this ivory hard bone, there is a membranous labyrinth is surrounded by perilymph, which by itself contains a ...
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system.Often the entire organ is considered the ear, though it may also be considered just the visible portion. In most mammals, the visible ear is a flap of tissue that is also called the pinna (or auricle in humans) and is the first of many steps in hearing. Vertebrates have a pair of ears placed somewhat symmetrically on opposite sides of the head. This arrangement aids in the ability to localize sound sources.