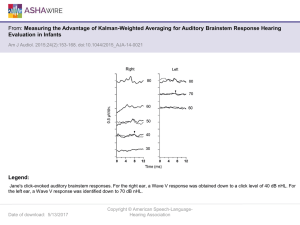
Hearing
... – Pitch is determined by frequency hair cells produce action potentials – If the frequency of the sound is 100 waves per second then the neuron fires at 100 pulses per second. – But we can hear frequencies above 1000 waves per second but can’t fire neurons faster than 1000 pulses per second. – Volle ...
... – Pitch is determined by frequency hair cells produce action potentials – If the frequency of the sound is 100 waves per second then the neuron fires at 100 pulses per second. – But we can hear frequencies above 1000 waves per second but can’t fire neurons faster than 1000 pulses per second. – Volle ...
Slide ()
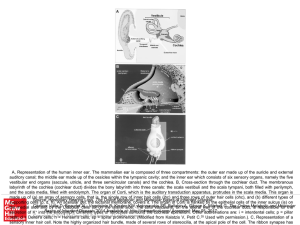
... A, Representation of the human inner ear. The mammalian ear is composed of three compartments: the outer ear made up of the auricle and external auditory canal; the middle ear made up of the ossicles within the tympanic cavity; and the inner ear which consists of six sensory organs, namely the five ...
... A, Representation of the human inner ear. The mammalian ear is composed of three compartments: the outer ear made up of the auricle and external auditory canal; the middle ear made up of the ossicles within the tympanic cavity; and the inner ear which consists of six sensory organs, namely the five ...
THE EXTERNAL EAR
... BLOOD SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR: branches of external carotid artery Venous drainage: to posterior auricular & superficial temporal veins Lymphatic drainage: to pre-auricular, infra-auricular & mastoid lymph nodes. ...
... BLOOD SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR: branches of external carotid artery Venous drainage: to posterior auricular & superficial temporal veins Lymphatic drainage: to pre-auricular, infra-auricular & mastoid lymph nodes. ...
BIOLOGY 2423: Special Senses Assignment
... Use the figures, tables, and text from Chapter 22 in Tortora to correctly complete this assignment. Be as complete and specific as possible in finding the locations and functions of these special senses structures, since this material will surface on Exam 3. ...
... Use the figures, tables, and text from Chapter 22 in Tortora to correctly complete this assignment. Be as complete and specific as possible in finding the locations and functions of these special senses structures, since this material will surface on Exam 3. ...
Anatomy of the Ear
... Otitis externa is an inflammation of the external ear, usually from moisture in the canal leading to bacterial or fungal infection (swimmer’s ear) or to an infected hair follicle (boil). The condition can be painful because of tightness of the skin lining the canal that is abundantly innervated. Inc ...
... Otitis externa is an inflammation of the external ear, usually from moisture in the canal leading to bacterial or fungal infection (swimmer’s ear) or to an infected hair follicle (boil). The condition can be painful because of tightness of the skin lining the canal that is abundantly innervated. Inc ...
The Ear: Hearing and Balance
... Each of these bones has 2 names apiece: _________________ or malleus _______________ or incus _________________ or stapes ...
... Each of these bones has 2 names apiece: _________________ or malleus _______________ or incus _________________ or stapes ...
Special Sensory Reception
... Anatomy of the Ear • Three parts of the ear: 1. External (outer) ear • Includes the auricle (pinna) which surroundes the entrance to the external acoustic meatus (ear canal) – The auricle protects the ear canal and collects and funnels sound into the ear canal ...
... Anatomy of the Ear • Three parts of the ear: 1. External (outer) ear • Includes the auricle (pinna) which surroundes the entrance to the external acoustic meatus (ear canal) – The auricle protects the ear canal and collects and funnels sound into the ear canal ...
parts of the ear combined act as a transducer
... All parts of the ear combined act as a transducer, changing acoustic ...
... All parts of the ear combined act as a transducer, changing acoustic ...
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs122.org
... the second part is the middle ear-a cavity in the petrous part of the temporal bone bounded laterally, and separated from the external canal, by a membrane and connected internally to the pharynx by a narrow tube; the third part is the internal ear consisting of a series of cavities within the petro ...
... the second part is the middle ear-a cavity in the petrous part of the temporal bone bounded laterally, and separated from the external canal, by a membrane and connected internally to the pharynx by a narrow tube; the third part is the internal ear consisting of a series of cavities within the petro ...
outline ear and senses - Social Circle City Schools
... 15. What part of the brain then interprets the sound as hearing? ...
... 15. What part of the brain then interprets the sound as hearing? ...
Advanced Human Anatomy Score: ____/10
... 13. Visible portion of the ear located outside of the head; funnels sound waves 16. Sheet of connective tissue that vibrates in responses to sound waves; ear drum 20. Light sensitive layer of the eye ...
... 13. Visible portion of the ear located outside of the head; funnels sound waves 16. Sheet of connective tissue that vibrates in responses to sound waves; ear drum 20. Light sensitive layer of the eye ...
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system.Often the entire organ is considered the ear, though it may also be considered just the visible portion. In most mammals, the visible ear is a flap of tissue that is also called the pinna (or auricle in humans) and is the first of many steps in hearing. Vertebrates have a pair of ears placed somewhat symmetrically on opposite sides of the head. This arrangement aids in the ability to localize sound sources.