Our Ears Hear - Or Do They?
... of hearing from 20Hz (very low bass) to 20,000Hz (very high pitch). Everyday conversation generally falls in the frequency range of 250Hz to 8000Hz. Equally important is how we hear Since childhood, we have been taught that we hear with our ears, but that is only partially correct. The ears are mere ...
... of hearing from 20Hz (very low bass) to 20,000Hz (very high pitch). Everyday conversation generally falls in the frequency range of 250Hz to 8000Hz. Equally important is how we hear Since childhood, we have been taught that we hear with our ears, but that is only partially correct. The ears are mere ...
noise in army aviation
... B. Mechanism of noise induced hearing loss. The magnitude of sound wave transmitted by the tympanic membrane causes a corresponding deformation of the hair cell. When the magnitude of the sound is too great (approximately 140 decibels), the deformation of the hair cell tends to become permanent and ...
... B. Mechanism of noise induced hearing loss. The magnitude of sound wave transmitted by the tympanic membrane causes a corresponding deformation of the hair cell. When the magnitude of the sound is too great (approximately 140 decibels), the deformation of the hair cell tends to become permanent and ...
HUMAN EAR & SIMPLE TESTS OF HEARING
... If examiner hears longer you have a diminished schwabach which is consistent with a sensorineural loss. If patient hears tone longer you have a prolonged schwabach consistent with a conductive loss. ...
... If examiner hears longer you have a diminished schwabach which is consistent with a sensorineural loss. If patient hears tone longer you have a prolonged schwabach consistent with a conductive loss. ...
Can you hear me now?
... than were women, men underestimate their hearing difficulties compared to women, “ men don’t hear as well as women do, but most men are blissfully unaware of the fact”. ...
... than were women, men underestimate their hearing difficulties compared to women, “ men don’t hear as well as women do, but most men are blissfully unaware of the fact”. ...
PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL AUDITORY ASSESSMENT Ravi
... Ascending series of presentation Excellent speech discrimination in conductive hearing loss patients Poor speech discrimination in cochlear hearing loss patients Poorest speech discrimination in retrocochlear hearing loss patients ...
... Ascending series of presentation Excellent speech discrimination in conductive hearing loss patients Poor speech discrimination in cochlear hearing loss patients Poorest speech discrimination in retrocochlear hearing loss patients ...
Can you hear me now?
... than were women, men underestimate their hearing difficulties compared to women, “ men don’t hear as well as women do, but most men are blissfully unaware of the fact”. ...
... than were women, men underestimate their hearing difficulties compared to women, “ men don’t hear as well as women do, but most men are blissfully unaware of the fact”. ...
The inner ear The inner ear can be divided into
... The inner ear can be divided into three parts: the semicircular canals, vestibule and the cochlea all of which are located in the temporal bone of the skull. Vibrations from the ossicles are transmitted to the cochlea via the stapes bone. The inner ear changes mechanical vibrations from the middle e ...
... The inner ear can be divided into three parts: the semicircular canals, vestibule and the cochlea all of which are located in the temporal bone of the skull. Vibrations from the ossicles are transmitted to the cochlea via the stapes bone. The inner ear changes mechanical vibrations from the middle e ...
Table 2.Delay progressive factors
... Table 2. Factors associated with delayed diagnosis of hearing loss and contributing to late intervention for infants who pass newborn hearing screening. Adapted from Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007). _______________________________________________________________ ...
... Table 2. Factors associated with delayed diagnosis of hearing loss and contributing to late intervention for infants who pass newborn hearing screening. Adapted from Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007). _______________________________________________________________ ...
A.P. Psychology 4 (D)
... Links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated Different frequencies vibrate in different places of the cochlea Problem: low-pitched sounds not localized ...
... Links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated Different frequencies vibrate in different places of the cochlea Problem: low-pitched sounds not localized ...
Theory of Mind - Listening and Spoken Language Knowledge Center
... Tries to do it using gestures and single words. Tries to show what happened by acting it out. Does it by responding to questions. Gives a coherent version of the story. Doesn’t identify events and characters sufficiently for you to understand. Sequence is jumbled ©The Ear Foundation 2012 ...
... Tries to do it using gestures and single words. Tries to show what happened by acting it out. Does it by responding to questions. Gives a coherent version of the story. Doesn’t identify events and characters sufficiently for you to understand. Sequence is jumbled ©The Ear Foundation 2012 ...
AAPC MEETING TUESDAY, JUNE 19, 2012
... incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The footplate of the stapes fits into the oval window, which is outermost boundary of the inner ear. The movement of the footplate causes fluid in the inner ear to move. The bones provide a mechanical advantage which moves the fluid. Without that mechanical advan ...
... incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The footplate of the stapes fits into the oval window, which is outermost boundary of the inner ear. The movement of the footplate causes fluid in the inner ear to move. The bones provide a mechanical advantage which moves the fluid. Without that mechanical advan ...
Discharge - Otolaryngology online
... Rinne test • All three frequencies can be used • + Rinne (Air conduction better than bone conduction) • -ve Rinne (Bone conduction better than air conduction) • False positive Rinne (occurs in unilateral total hearing loss due to opposite ear hearing) ...
... Rinne test • All three frequencies can be used • + Rinne (Air conduction better than bone conduction) • -ve Rinne (Bone conduction better than air conduction) • False positive Rinne (occurs in unilateral total hearing loss due to opposite ear hearing) ...
Clinical Otology - Otolaryngology presentation
... Rinne test • All three frequencies can be used • + Rinne (Air conduction better than bone conduction) • -ve Rinne (Bone conduction better than air conduction) • False positive Rinne (occurs in unilateral total hearing loss due to opposite ear hearing) ...
... Rinne test • All three frequencies can be used • + Rinne (Air conduction better than bone conduction) • -ve Rinne (Bone conduction better than air conduction) • False positive Rinne (occurs in unilateral total hearing loss due to opposite ear hearing) ...
Lecture notes
... Carries sound to the stapes. c) stapes or stirrup passes sound energy into the inner ear. • It rests on a membrane covered opening called the oval window which allows vibrations to enter the inner ear. ...
... Carries sound to the stapes. c) stapes or stirrup passes sound energy into the inner ear. • It rests on a membrane covered opening called the oval window which allows vibrations to enter the inner ear. ...
THE HUMAN EAR: READING AND QUESTIONS
... of the inner ear is a spiral tube, coiled two and a half times, which resembles a snail’s shell. If you could stretch it out into a straight line, it would consist of three canals separated by thin membranes. The cochlea is the structure most responsible for the highly developed sense of hearing fou ...
... of the inner ear is a spiral tube, coiled two and a half times, which resembles a snail’s shell. If you could stretch it out into a straight line, it would consist of three canals separated by thin membranes. The cochlea is the structure most responsible for the highly developed sense of hearing fou ...
External Ear
... with adipose tissue.Instead, it is a wedge of adipose tissue covered by skin. – Tears of the earlobe can be generally repaired with good results. Since there is no cartilage, there is not the risk of deformity from a blood clot or pressure injury to the ear lobe. Other injuries causing major deformi ...
... with adipose tissue.Instead, it is a wedge of adipose tissue covered by skin. – Tears of the earlobe can be generally repaired with good results. Since there is no cartilage, there is not the risk of deformity from a blood clot or pressure injury to the ear lobe. Other injuries causing major deformi ...
Genetic Bases of Music Related Hearing Loss
... Brass major Woodwind major String major Keyboard major ...
... Brass major Woodwind major String major Keyboard major ...
13ear Final
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
SPECIAL SENSES
... 1. Accessory structures – includes the eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and lacrimal apparatus. a. The lacrimal apparatus includes the following structures: i. The lacrimal glands – secrete lacrimal fluid (tears). ii. The excretory lacrimal ducts – empty tears from the lacrimal glands onto the surface o ...
... 1. Accessory structures – includes the eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and lacrimal apparatus. a. The lacrimal apparatus includes the following structures: i. The lacrimal glands – secrete lacrimal fluid (tears). ii. The excretory lacrimal ducts – empty tears from the lacrimal glands onto the surface o ...
9-Ear Final (2o15-16)
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
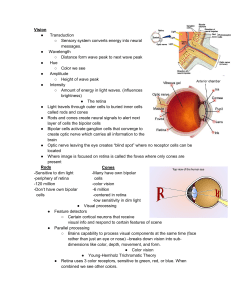
Vision Transduction Sensory system converts energy into neural
... ● Remarkable memory for certain smells ● Smell plays an integral role in the finer sense of taste Hearing ● Converts objective stimuli of vibrating airwaves into sounds ● Amplitude of waves determine loudness ● Frequency of waves determine pitch ...
... ● Remarkable memory for certain smells ● Smell plays an integral role in the finer sense of taste Hearing ● Converts objective stimuli of vibrating airwaves into sounds ● Amplitude of waves determine loudness ● Frequency of waves determine pitch ...
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers
... Specific combinations of temporal lobe activity occur as people look at shoes, faces, chairs and ...
... Specific combinations of temporal lobe activity occur as people look at shoes, faces, chairs and ...
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system.Often the entire organ is considered the ear, though it may also be considered just the visible portion. In most mammals, the visible ear is a flap of tissue that is also called the pinna (or auricle in humans) and is the first of many steps in hearing. Vertebrates have a pair of ears placed somewhat symmetrically on opposite sides of the head. This arrangement aids in the ability to localize sound sources.