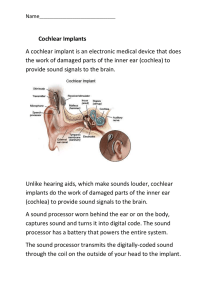
Cochlear Implants
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
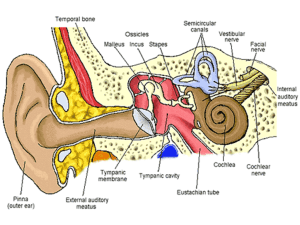
The Ear - Downey Unified School District
... • Carries the signal into the brainstem and synapses in the cochlear nucleus • From there the auditory information splits into motion and form procession • Auditory nerve fibers going to the ventral cochlear nucleus synapse on their target cells with giant, hand like terminals • Two streams: • Cell ...
... • Carries the signal into the brainstem and synapses in the cochlear nucleus • From there the auditory information splits into motion and form procession • Auditory nerve fibers going to the ventral cochlear nucleus synapse on their target cells with giant, hand like terminals • Two streams: • Cell ...
HEARING
... The COCHLEA is a snail-shell shaped, membrane-bound, fluid-filled receptor for sound of the inner ear. When viewed in cross-section , the cochlea is divided into upper and lower halves by the BASILAR MEMBRANE. Angling into the upper half is another membrane called the TECTORIAL MEMBRANE. Resting on ...
... The COCHLEA is a snail-shell shaped, membrane-bound, fluid-filled receptor for sound of the inner ear. When viewed in cross-section , the cochlea is divided into upper and lower halves by the BASILAR MEMBRANE. Angling into the upper half is another membrane called the TECTORIAL MEMBRANE. Resting on ...
The Special Senses
... Between the scala tympani and the scala media/cochlear duct is the complex receptor system: the spiral organ of Corti Sensory Hair Cells stand on the basilar membrane and their processes are attached to the Tectorial ...
... Between the scala tympani and the scala media/cochlear duct is the complex receptor system: the spiral organ of Corti Sensory Hair Cells stand on the basilar membrane and their processes are attached to the Tectorial ...
The EAR
... The frequency of sound that reaches our ears changes when the sound source is moving. The change in perceived pitch due to movement is known as the Doppler shift. ...
... The frequency of sound that reaches our ears changes when the sound source is moving. The change in perceived pitch due to movement is known as the Doppler shift. ...
Cell Bio 14- Auditory Pathways All 3 parts necessary to hear
... High tones produce greatest crests where the membrane is tight, low tones where the wall is slack The position of this crest is important because it determines which nerve fibers will send signals to the brain High frequency tones cause the crest to occur at the base of the cochlea and the lower f ...
... High tones produce greatest crests where the membrane is tight, low tones where the wall is slack The position of this crest is important because it determines which nerve fibers will send signals to the brain High frequency tones cause the crest to occur at the base of the cochlea and the lower f ...
Document
... perilymph to vibrate; the hair cells here transmit this vibration. • Therefore the HAIR CELLS in this region are for damaged HEARING. As you receptors age, hair cells become (loud music can speed this process along). Older people usually can’t hear frequencies that younger people can hear. Try the h ...
... perilymph to vibrate; the hair cells here transmit this vibration. • Therefore the HAIR CELLS in this region are for damaged HEARING. As you receptors age, hair cells become (loud music can speed this process along). Older people usually can’t hear frequencies that younger people can hear. Try the h ...
File
... 5. What’s the 2 factors which affect the sensitivity of the skin? 6. What’s function of the sweat glands in the skin? 7. What is mucus? 8. How can a common cold decrease our sense of ...
... 5. What’s the 2 factors which affect the sensitivity of the skin? 6. What’s function of the sweat glands in the skin? 7. What is mucus? 8. How can a common cold decrease our sense of ...
Slide 1
... – Response where onset of loud sound causes tensor tympani and stapedius muscle contraction – Function: Adapt ear to loud sounds, understand speech better ...
... – Response where onset of loud sound causes tensor tympani and stapedius muscle contraction – Function: Adapt ear to loud sounds, understand speech better ...
Hearing Module 14 - Clayton Valley Charter High School
... Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window. ...
... Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window. ...
Ear
... Inner Ear Cochlea • Movements of the stapes bone hitting the ear drum are transmitted to the oval window (start of cochlea) • Vibrations move through the fluid in the cochlea • Organ of Corti in the cochlea is the sensory organ for hearing • Contain hairs that are triggered as sound vibrations pass ...
... Inner Ear Cochlea • Movements of the stapes bone hitting the ear drum are transmitted to the oval window (start of cochlea) • Vibrations move through the fluid in the cochlea • Organ of Corti in the cochlea is the sensory organ for hearing • Contain hairs that are triggered as sound vibrations pass ...
Sense of Hearing
... the Organ of Corti, the sensory epithelium, a cellular layer on the basilar membrane, powered by the potential difference between the perilymph and the endolymph hair cells, sensory cells in the Organ of Corti, topped with hair-like structures called stereocilia ...
... the Organ of Corti, the sensory epithelium, a cellular layer on the basilar membrane, powered by the potential difference between the perilymph and the endolymph hair cells, sensory cells in the Organ of Corti, topped with hair-like structures called stereocilia ...
Structure and Function of the Inner Ear
... The inner ear is entirely enclosed within the temporal bone. It has two separate regions, the cochlea and vestibule, which are responsible for hearing and balance, respectively. The neural signals from the two regions of the inner ear are relayed to the brainstem through separate fiber bundles, but ...
... The inner ear is entirely enclosed within the temporal bone. It has two separate regions, the cochlea and vestibule, which are responsible for hearing and balance, respectively. The neural signals from the two regions of the inner ear are relayed to the brainstem through separate fiber bundles, but ...
03/12 PPT
... The frequency of sound that reaches our ears changes when the sound source is moving. The change in perceived pitch due to movement is known as the Doppler shift. ...
... The frequency of sound that reaches our ears changes when the sound source is moving. The change in perceived pitch due to movement is known as the Doppler shift. ...
The Inner Ear
... • __________- Converting acousticalmechanical energy into electro-chemical energy. • ___________- Breaking sound up into its component frequencies ...
... • __________- Converting acousticalmechanical energy into electro-chemical energy. • ___________- Breaking sound up into its component frequencies ...
Exam 3 Sample 2003
... b. change in pressure over time. c. change in pitch at each frequency. d. number of harmonics in the tone. The unit for loudness is the a. decibel. b. Hertz. c. mel. d. sound pressure level. The middle ear contains the a. auditory canal. b. cochlea. c. organ of Corti. d. ossicles. The bones of the m ...
... b. change in pressure over time. c. change in pitch at each frequency. d. number of harmonics in the tone. The unit for loudness is the a. decibel. b. Hertz. c. mel. d. sound pressure level. The middle ear contains the a. auditory canal. b. cochlea. c. organ of Corti. d. ossicles. The bones of the m ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.