Human Ear Lab Guide 2014-2016
... includes the Tympanic Membrane, Malleus, Incus, Stapes, and Oval window. If any of these structures do not vibrate normally, sound waves would not be amplified and the membrane covering the oval window would not vibrate sufficiently, resulting in impaired hearing. ...
... includes the Tympanic Membrane, Malleus, Incus, Stapes, and Oval window. If any of these structures do not vibrate normally, sound waves would not be amplified and the membrane covering the oval window would not vibrate sufficiently, resulting in impaired hearing. ...
TSM54 - The Auditory Pathway
... o 0 dB is the quietest sound detectible (arbitrary reference level) – 20 μPa pressure o 30 dB is roughly the level of a whisper o 60 dB is the level of normal conversation o 90 dB is the threshold for hearing damage o Sound above 140 dB is essentially perceived only as pain Conductive hearing loss i ...
... o 0 dB is the quietest sound detectible (arbitrary reference level) – 20 μPa pressure o 30 dB is roughly the level of a whisper o 60 dB is the level of normal conversation o 90 dB is the threshold for hearing damage o Sound above 140 dB is essentially perceived only as pain Conductive hearing loss i ...
Ch 15b Hearing and Equilibrium
... organ of Corti basilar membrane vibrates hair cells stereocilia stretch against tectorial membrane open K channels K+ (in endolymph) rushes into cell hair cells depolarize hair cells release NT ...
... organ of Corti basilar membrane vibrates hair cells stereocilia stretch against tectorial membrane open K channels K+ (in endolymph) rushes into cell hair cells depolarize hair cells release NT ...
Sound and Pitch (Ch 11)
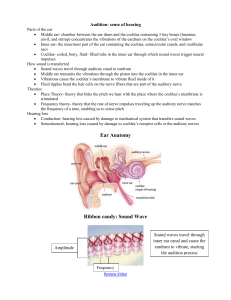
... The Cochlea – Fluid-filled snail-like structure set into vibration by the stapes – Divided into the scala vestibuli and scala tympani by the cochlear partition – Cochlear partition extends from the base (stapes end) to the apex (far end) – Organ of Corti contained by the cochlear partition ...
... The Cochlea – Fluid-filled snail-like structure set into vibration by the stapes – Divided into the scala vestibuli and scala tympani by the cochlear partition – Cochlear partition extends from the base (stapes end) to the apex (far end) – Organ of Corti contained by the cochlear partition ...
Auditory Pathways
... dB= 20 log [(pressure of sound)/(pressure of standard sound) 0 dB is the threshold for human hearing At 140 dB, sounds are both felt and heard ...
... dB= 20 log [(pressure of sound)/(pressure of standard sound) 0 dB is the threshold for human hearing At 140 dB, sounds are both felt and heard ...
Hearing: and Equilibrium
... •Auditory receptors of the inner ear operate in a fluid environment underwater sound receiver •Effective transfer of sound energy from air (lower acoustic resistance/impedance) to fluid (higher acoustic resistance/impedance) is due to amplification of the pressure by: olarge ratio btwn the areas o ...
... •Auditory receptors of the inner ear operate in a fluid environment underwater sound receiver •Effective transfer of sound energy from air (lower acoustic resistance/impedance) to fluid (higher acoustic resistance/impedance) is due to amplification of the pressure by: olarge ratio btwn the areas o ...
Chapter 13b Special Senses
... Airborne sound enters external auditory canal, strikes tympanic membrane and vibrates it with the same frequency. ...
... Airborne sound enters external auditory canal, strikes tympanic membrane and vibrates it with the same frequency. ...
THE AUDITORY SYSTEM (p.1) 1. The Sound Stimulus a waveform
... h.c.s near oval window – sensitive to high frequency waves; h.c.s near end of basilar membrane (apex) – sensitive to low frequency waves (“place theory” of hearing) auditory neurons, axons form C.N. VIII (“acoustic” branch) eustacean tube (between middle ear and throat) inner ear & semi-circular can ...
... h.c.s near oval window – sensitive to high frequency waves; h.c.s near end of basilar membrane (apex) – sensitive to low frequency waves (“place theory” of hearing) auditory neurons, axons form C.N. VIII (“acoustic” branch) eustacean tube (between middle ear and throat) inner ear & semi-circular can ...
Neuro Objectives 24
... side. Since there is no stiffening of the ossicular chain (quieting effect), sounds will sound unusually loud in the damaged side. ...
... side. Since there is no stiffening of the ossicular chain (quieting effect), sounds will sound unusually loud in the damaged side. ...
Hearing_notes
... Tonotopic mapping (different frequencies excite neurons in different places) is found at multiple levels of processing, from organ of Corti to cochlear nucleus to primary auditory cortex. Auditory processing Pitch perception: Based on which hair cells are activated. Basal end fibers (close to ov ...
... Tonotopic mapping (different frequencies excite neurons in different places) is found at multiple levels of processing, from organ of Corti to cochlear nucleus to primary auditory cortex. Auditory processing Pitch perception: Based on which hair cells are activated. Basal end fibers (close to ov ...
TheEar
... (1) auditory nerve to temporal lobes (cochlear nerve to medulla to midbrain to thalamus to auditory cortex in temporal lobes) (2) some fibers cross over to other side (not all); so impulses are interpreted by both sides of brain ...
... (1) auditory nerve to temporal lobes (cochlear nerve to medulla to midbrain to thalamus to auditory cortex in temporal lobes) (2) some fibers cross over to other side (not all); so impulses are interpreted by both sides of brain ...
760spring2012
... Auditory Nerve SPRING BREAK!!! Cochlear Nucleus (multiple cell types) Superior Olive Complex and Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus (Localization) Thalamus—Medial Geniculate Body (include multi-sensory cells) Auditory Cortex Auditory Cortex Final Projects Due ...
... Auditory Nerve SPRING BREAK!!! Cochlear Nucleus (multiple cell types) Superior Olive Complex and Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus (Localization) Thalamus—Medial Geniculate Body (include multi-sensory cells) Auditory Cortex Auditory Cortex Final Projects Due ...
The Ears: Hearing and Balance
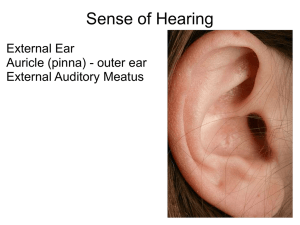
... External earoPinna (auricle) and acoustic meatus (ear canal) funnel sound to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) ...
... External earoPinna (auricle) and acoustic meatus (ear canal) funnel sound to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) ...
Module - Mount Sinai Hospital
... consists of the tympanic membrane (eardrum), the ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes), and the Eustachian tube. The inner ear consists of the cochlea, the vestibular system, and the auditory nerve. The auricle collects sound waves, which are funneled by the external auditory canal to the tympanic me ...
... consists of the tympanic membrane (eardrum), the ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes), and the Eustachian tube. The inner ear consists of the cochlea, the vestibular system, and the auditory nerve. The auricle collects sound waves, which are funneled by the external auditory canal to the tympanic me ...
Anatomy of the Ear
... 3. Tympanic membrane 4. Malleus 5. Incus 6. Stapes 7. Oval window 8. Organ of Corti in Cochlea 9. Hairs cells ...
... 3. Tympanic membrane 4. Malleus 5. Incus 6. Stapes 7. Oval window 8. Organ of Corti in Cochlea 9. Hairs cells ...
Hearing
... • Then the cochlea vibrates. • The cochlea is lined with mucus called basilar membrane. • In basilar membrane there are hair cells. • When hair cells vibrate they turn vibrations into neural impulses. • Sent then to thalamus up auditory nerve. ...
... • Then the cochlea vibrates. • The cochlea is lined with mucus called basilar membrane. • In basilar membrane there are hair cells. • When hair cells vibrate they turn vibrations into neural impulses. • Sent then to thalamus up auditory nerve. ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.