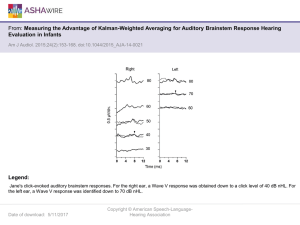
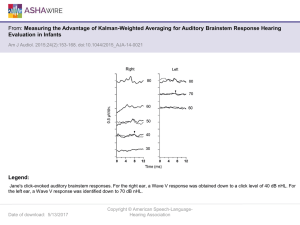
Hearing Vocabulary List
... 4. malleus – A hammer-shaped bone, the outermost of three small bones in the middle ear that transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. 5. incus - A small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear of mammals between the malleus and stapes bones. 6. stapes – A small stirrup-shaped bone in the ...
... 4. malleus – A hammer-shaped bone, the outermost of three small bones in the middle ear that transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. 5. incus - A small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear of mammals between the malleus and stapes bones. 6. stapes – A small stirrup-shaped bone in the ...
The Ear and Hearing - Bishop Amat Memorial High School
... creating a fluid motion. The fluid movement within the cochlea causes membranes in the Organ of Corti to shear against the hair cells. This creates an electrical signal which is sent via the Auditory Nerve to the brain, where sound is ...
... creating a fluid motion. The fluid movement within the cochlea causes membranes in the Organ of Corti to shear against the hair cells. This creates an electrical signal which is sent via the Auditory Nerve to the brain, where sound is ...
The Ear: Hearing and Balance
... this pathway: – Outer ear – pinna, auditory canal, eardrum – Middle ear – malleus, incus, and stapes to the oval window – Inner ear – scalas vestibuli and tympani to the cochlear duct • Stimulation of the organ of Corti • Generation of impulses in the cochlear nerve ...
... this pathway: – Outer ear – pinna, auditory canal, eardrum – Middle ear – malleus, incus, and stapes to the oval window – Inner ear – scalas vestibuli and tympani to the cochlear duct • Stimulation of the organ of Corti • Generation of impulses in the cochlear nerve ...
Vocabulary
... 2) The waves get transmitted through the middle ear through three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the cochlea in the middle ear. From there on, the vibrations vibrate the cochlea’s membrane that makes the fluids in its tube jostle that then ripples the basilar membrane and bends the hair ...
... 2) The waves get transmitted through the middle ear through three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the cochlea in the middle ear. From there on, the vibrations vibrate the cochlea’s membrane that makes the fluids in its tube jostle that then ripples the basilar membrane and bends the hair ...
Slide 1
... human body. The eardrum vibrates, and this vibrates the hammer, than the anvil and the stirrup one after another The stirrup then vibrates the Oval Window COCHLEA- This is a spirally coiled tube containing fluid and the actual organ of hearing (the Organ of Corti). Each Organ of Corti contains thous ...
... human body. The eardrum vibrates, and this vibrates the hammer, than the anvil and the stirrup one after another The stirrup then vibrates the Oval Window COCHLEA- This is a spirally coiled tube containing fluid and the actual organ of hearing (the Organ of Corti). Each Organ of Corti contains thous ...
pdf compact
... countries, on the basis of one member per country, with a Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, that coordinates the system. • Because "International Organization for Standardization" would have different abbreviations in different languages ("IOS" in English, "OIN" in French for Organisation ...
... countries, on the basis of one member per country, with a Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, that coordinates the system. • Because "International Organization for Standardization" would have different abbreviations in different languages ("IOS" in English, "OIN" in French for Organisation ...
Senses - Raleigh Charter High School
... ___________________ is involved in hearing, whereas the ______________________ are involved in balance. Inside the cochlea, there is a membrane (called the _________________ membrane) covered in tiny _________________________. Amplified sound waves cause these to bend, which opens ion channels and s ...
... ___________________ is involved in hearing, whereas the ______________________ are involved in balance. Inside the cochlea, there is a membrane (called the _________________ membrane) covered in tiny _________________________. Amplified sound waves cause these to bend, which opens ion channels and s ...
Neuro-Compensator
... • Compensate for loss of outer and inner hair cells • Learn optimal compensation parameters for a specific individual’s pattern of hearing loss ...
... • Compensate for loss of outer and inner hair cells • Learn optimal compensation parameters for a specific individual’s pattern of hearing loss ...
Training
... perilymph moves through helicotrema to round window, calls movement of endolymph of cochlear duct and tectorial membrane which irritates hair cells. Dendrites of spiral ganglion cells take impulse. ...
... perilymph moves through helicotrema to round window, calls movement of endolymph of cochlear duct and tectorial membrane which irritates hair cells. Dendrites of spiral ganglion cells take impulse. ...
The Ear: Hearing and Balance The three parts of the ear are the
... – Represented by a sine wave in wavelength, frequency, and amplitude • Frequency – the number of waves that pass a given point in a given time • Pitch – perception of different frequencies (we hear from 20–20,000 Hz) • Amplitude – intensity of a sound measured in decibels (dB) • Loudness – subjectiv ...
... – Represented by a sine wave in wavelength, frequency, and amplitude • Frequency – the number of waves that pass a given point in a given time • Pitch – perception of different frequencies (we hear from 20–20,000 Hz) • Amplitude – intensity of a sound measured in decibels (dB) • Loudness – subjectiv ...
Slides from Lecture 11/24/2004 (Pascal Wallisch)
... • Filled with fluid • Contains the Organ of Corti, which contains the transducers that transduce mechanical pressure waves into action potentials. • The cochlea is tonotopically organized. Frequencies map orderly along the length of the cochlea. • Hair cells near the Apex respond best to low frequen ...
... • Filled with fluid • Contains the Organ of Corti, which contains the transducers that transduce mechanical pressure waves into action potentials. • The cochlea is tonotopically organized. Frequencies map orderly along the length of the cochlea. • Hair cells near the Apex respond best to low frequen ...
Study guide for exam 2
... canal to communicate with the fluid in the tympanic canal. 20. This material is a fatty substance that coats the fibers of some but not all neurons. Fibers that contain this substance transmit neural signals more rapidly than uncoated fibers. 21. Give an example that illustrates the difference betwe ...
... canal to communicate with the fluid in the tympanic canal. 20. This material is a fatty substance that coats the fibers of some but not all neurons. Fibers that contain this substance transmit neural signals more rapidly than uncoated fibers. 21. Give an example that illustrates the difference betwe ...
Cellular Neuroscience - How Your Brain Works
... • Many physical objects emit sounds when they are “excited” (e.g. hit or rubbed). • Sounds are just pressure waves rippling through the air, but they carry a lot of information about the objects that emitted them. (Example: what are these two objects? Which one is heavier, object A or object B ...
... • Many physical objects emit sounds when they are “excited” (e.g. hit or rubbed). • Sounds are just pressure waves rippling through the air, but they carry a lot of information about the objects that emitted them. (Example: what are these two objects? Which one is heavier, object A or object B ...
AudVest8
... B. Brainstem nuclei and their Projections 2. Auditory nuclei: 3 major auditory relay nuclei of the brainstem: A. cochlear nuclei (same side from cn VIII) (medulla). B. superior olivary nuclear complex (integration from both sides) (pons). C. inferior colliculus (midbrain). [2 major divisions we not ...
... B. Brainstem nuclei and their Projections 2. Auditory nuclei: 3 major auditory relay nuclei of the brainstem: A. cochlear nuclei (same side from cn VIII) (medulla). B. superior olivary nuclear complex (integration from both sides) (pons). C. inferior colliculus (midbrain). [2 major divisions we not ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.