Sensory systems: II. Auditory
... vestibuli shown in red; scala media in dark blue. Scala tympani and scala vestibuli are filled with perilymph; scala media is filled with endolymph. ...
... vestibuli shown in red; scala media in dark blue. Scala tympani and scala vestibuli are filled with perilymph; scala media is filled with endolymph. ...
Chapter Summary The Auditory Stimulus Sound waves can be
... 5. The phase angle of a sound wave is measured in degrees; it indicates the position of a wave in its cycle. The Auditory System 1. The outer ear consists of the pinna, the external auditory canal, and the tympanic membrane. 2. The middle ear contains three bones—the malleus, the incus, and the stap ...
... 5. The phase angle of a sound wave is measured in degrees; it indicates the position of a wave in its cycle. The Auditory System 1. The outer ear consists of the pinna, the external auditory canal, and the tympanic membrane. 2. The middle ear contains three bones—the malleus, the incus, and the stap ...
The Auditory Sense: Hearing
... • A loud sound has a higher amplitude • The further the distance between the peak and baseline, the louder the sound (amplitude) • We can measure how loud a sound is in decibels (db) ...
... • A loud sound has a higher amplitude • The further the distance between the peak and baseline, the louder the sound (amplitude) • We can measure how loud a sound is in decibels (db) ...
The Ear and Hearing 1. Outer Ear
... (measured in decibels) to the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate. B. Vibration of the tympanic membrane causes vibrations in the middle ear ossicles(tiny bones)malleus, incus and stapes, which vibrates the oval window of the cochlea. C. Vibration of the oval window sets up a traveling wave of ...
... (measured in decibels) to the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate. B. Vibration of the tympanic membrane causes vibrations in the middle ear ossicles(tiny bones)malleus, incus and stapes, which vibrates the oval window of the cochlea. C. Vibration of the oval window sets up a traveling wave of ...
Audition Outline - Villanova University
... • Many sound features are encoded before the signal reaches the cortex - Cochlear nucleus segregates sound information - Signals from each ear converge on the superior olivary complex important for sound localization - Inferior colliculus is sensitive to location, absolute intensity, rates of intens ...
... • Many sound features are encoded before the signal reaches the cortex - Cochlear nucleus segregates sound information - Signals from each ear converge on the superior olivary complex important for sound localization - Inferior colliculus is sensitive to location, absolute intensity, rates of intens ...
Vibration of the stapes at the oval window causes the perilymph in
... • Cats are able to move their pinna (which collect and concentrate sound) toward the source making them able to hear even when facing a different direction. • Humans do not have this ability, yet the three muscles that turn the pinna in the cat are still found surrounding the human pinna. • Evolutio ...
... • Cats are able to move their pinna (which collect and concentrate sound) toward the source making them able to hear even when facing a different direction. • Humans do not have this ability, yet the three muscles that turn the pinna in the cat are still found surrounding the human pinna. • Evolutio ...
File
... 2. Inside the auditory canal are ceruminous glands, which secrete a waxy yellow substance, called earwax, or cerumen. 3. Sound waves eventually hit the tympanic membrane or eardrum, and cause it to vibrate. The middle ear: 1.) The middle ear is also referred to as the tympanic cavity. It is a small, ...
... 2. Inside the auditory canal are ceruminous glands, which secrete a waxy yellow substance, called earwax, or cerumen. 3. Sound waves eventually hit the tympanic membrane or eardrum, and cause it to vibrate. The middle ear: 1.) The middle ear is also referred to as the tympanic cavity. It is a small, ...
anatomy and physiology of the ear
... to skull cavity and brain stem Carry signals from cochlea to primary auditory cortex, with continuous processing along the way ...
... to skull cavity and brain stem Carry signals from cochlea to primary auditory cortex, with continuous processing along the way ...
1145010Module Hearing 08JS
... Amplitude (strength) determines loudness Frequency the number of wavelengths determines Pitch - a tone’s highness or lowness ...
... Amplitude (strength) determines loudness Frequency the number of wavelengths determines Pitch - a tone’s highness or lowness ...
The Auditory and Vestibular Systems
... source. I discussed each of these characteristics in lecture in detail. You should know how each of these characteristics is coded by the nervous system. The anatomy of the ear was reviewed (see Fig. 11.3 for the basic structures). You will be expected to know the three divisions of the ear (the out ...
... source. I discussed each of these characteristics in lecture in detail. You should know how each of these characteristics is coded by the nervous system. The anatomy of the ear was reviewed (see Fig. 11.3 for the basic structures). You will be expected to know the three divisions of the ear (the out ...
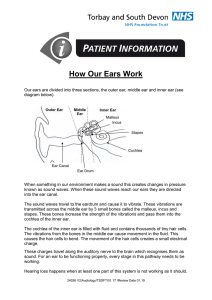
How our ears work information leaflet
... cochlea of the inner ear. The cochlea of the inner ear is filled with fluid and contains thousands of tiny hair cells. The vibrations from the bones in the middle ear cause movement in the fluid. This causes the hair cells to bend. The movement of the hair cells creates a small electrical ...
... cochlea of the inner ear. The cochlea of the inner ear is filled with fluid and contains thousands of tiny hair cells. The vibrations from the bones in the middle ear cause movement in the fluid. This causes the hair cells to bend. The movement of the hair cells creates a small electrical ...
CHAPTER 7 Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
... about 5% of the innervation of the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. Inner Hair Cells – There is one row of approximately 3500 inner hair cells. These cells receive about 95% of the innervation from the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. These cells hav ...
... about 5% of the innervation of the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. Inner Hair Cells – There is one row of approximately 3500 inner hair cells. These cells receive about 95% of the innervation from the nerve fibers from the acoustic portion of the VIII nerve. These cells hav ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.