middle ear
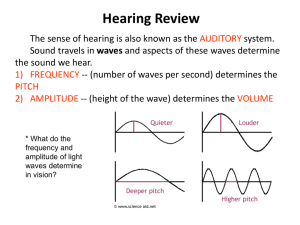
... the sound waves; sound waves of higher frequency cause more FREQUENT action potentials which the brain interprets as a HIGHER pitch. Problem – we can hear pitches of frequencies higher than the membrane can move. • PLACE theory – high-frequency sounds vibrate most near the OPENING of the cochlea, wh ...
... the sound waves; sound waves of higher frequency cause more FREQUENT action potentials which the brain interprets as a HIGHER pitch. Problem – we can hear pitches of frequencies higher than the membrane can move. • PLACE theory – high-frequency sounds vibrate most near the OPENING of the cochlea, wh ...
Sound, the Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
... This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 559 Nathan Abbott Way, Stanford, California 94305, USA. ...
... This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 559 Nathan Abbott Way, Stanford, California 94305, USA. ...
Lect15
... • Compression of oval window vibrates the basilar membrane • Shear forces between basilar membrane and tectorial membrane deflect stereocilia of hair cells ...
... • Compression of oval window vibrates the basilar membrane • Shear forces between basilar membrane and tectorial membrane deflect stereocilia of hair cells ...
Physiology of Hearing Talk
... – Sound energy transmitted through gaseous/liquid/solid medium – Vibration of medium’s molecules – Sound wave • ↑ amplitude: ↑ loudness • ↑ vibration: ↑ pitch • 1000-4000 Hz ...
... – Sound energy transmitted through gaseous/liquid/solid medium – Vibration of medium’s molecules – Sound wave • ↑ amplitude: ↑ loudness • ↑ vibration: ↑ pitch • 1000-4000 Hz ...
Evolution of brain and behaviour
... Measuring sound intensity • We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities, so a logarithmic scale works well • intensity in dB=20 x log (P1/P2) – where P2 is 0.0002 dynes2/cm2 ...
... Measuring sound intensity • We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities, so a logarithmic scale works well • intensity in dB=20 x log (P1/P2) – where P2 is 0.0002 dynes2/cm2 ...
Auditory System - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... 4. Vibration of the basilar membrane causes bending of the hair cells. This causes inner hair cell depolarization due to cation (mainly K+) influx (generator potential), followed by Ca2+ influx (due to opening of voltage-dependent Ca channels), leading to release of excitatory transmitter, causing a ...
... 4. Vibration of the basilar membrane causes bending of the hair cells. This causes inner hair cell depolarization due to cation (mainly K+) influx (generator potential), followed by Ca2+ influx (due to opening of voltage-dependent Ca channels), leading to release of excitatory transmitter, causing a ...
Otoacoustic Emissions
... Transient and Distortion-Product OAEs Rationale: quick, relatively inexpensive, possibly catching losses in a broader frequency range than ABR NIH (1994) recommended two-stage protocol combining OAEs and ABR ...
... Transient and Distortion-Product OAEs Rationale: quick, relatively inexpensive, possibly catching losses in a broader frequency range than ABR NIH (1994) recommended two-stage protocol combining OAEs and ABR ...
The Auditory System
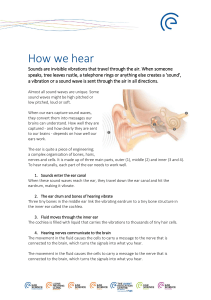
... 3. Tympanic membrane (eardrum): vibrations strike the tympanic membrane causing it to vibrate at roughly the same frequency as the sound waves that strike it. ...
... 3. Tympanic membrane (eardrum): vibrations strike the tympanic membrane causing it to vibrate at roughly the same frequency as the sound waves that strike it. ...
PSY 342: Review for Exam 3 Chapter 11: Sound and the Auditory
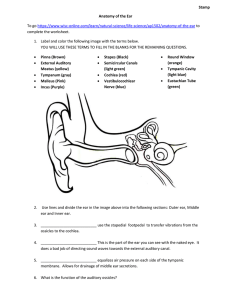
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
File
... know the components of the external, middle, and internal ear know the muscles in the middle ear and their innervations and functions know the path of auditory vibrations know the spaces within the cochlea and the membranes which separate them know the locations of the endolymph and perilymph know t ...
... know the components of the external, middle, and internal ear know the muscles in the middle ear and their innervations and functions know the path of auditory vibrations know the spaces within the cochlea and the membranes which separate them know the locations of the endolymph and perilymph know t ...
Document
... auditory system – not as well studied as responses in the auditory nerve • Some neurons in the auditory cortex only respond to complex stimuli, or to stimuli with time varying characteristics ...
... auditory system – not as well studied as responses in the auditory nerve • Some neurons in the auditory cortex only respond to complex stimuli, or to stimuli with time varying characteristics ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.