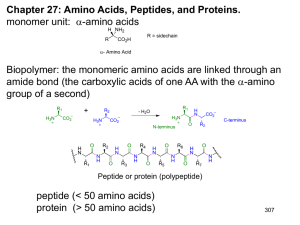
Amino Acids
... The intracellular pH is also near 7, so about half the imidazole groups will be protonated. In other words, the imidazole groups can easily abstract a proton or give one up, as is required for catalysis, and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. It is more likely that the pK of these groups i ...
... The intracellular pH is also near 7, so about half the imidazole groups will be protonated. In other words, the imidazole groups can easily abstract a proton or give one up, as is required for catalysis, and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. It is more likely that the pK of these groups i ...
exam2_2011_key
... iii) Which of the three diagrams (A, B, C) best represents the distribution of bound ligands (shaded circles) for this protein? Briefly justify your answer (3 pts). In the case of negative cooperativity, it is more likely for ligands to bind to un-occupied trimers, since the first binding event will ...
... iii) Which of the three diagrams (A, B, C) best represents the distribution of bound ligands (shaded circles) for this protein? Briefly justify your answer (3 pts). In the case of negative cooperativity, it is more likely for ligands to bind to un-occupied trimers, since the first binding event will ...
... iii) Which of the three diagrams (A, B, C) best represents the distribution of bound ligands (shaded circles) for this protein? Briefly justify your answer (3 pts). In the case of negative cooperativity, it is more likely for ligands to bind to un-occupied trimers, since the first binding event will ...
Mistranslation and its control by tRNA synthetases
... to discriminate against amino acids that are closely similar to the cognate one [12–14]. An example is isoleucyltRNA synthetase (IleRS), which misactivates valine at a frequency of roughly 1/200 [15]. Isoleucine can only be recognized by hydrophobic interactions and valine, which lacks one methylene ...
... to discriminate against amino acids that are closely similar to the cognate one [12–14]. An example is isoleucyltRNA synthetase (IleRS), which misactivates valine at a frequency of roughly 1/200 [15]. Isoleucine can only be recognized by hydrophobic interactions and valine, which lacks one methylene ...
Teaching Active Transport At the Turn of the Twenty
... This is very close to the experimentally observed value, and is consistent with the independently observed stoichiometry of 1 Ca2+ transported versus 1 H+ countertransported. The experimental parameters considered for this analysis should be actual rates of net transport and countertransport rather ...
... This is very close to the experimentally observed value, and is consistent with the independently observed stoichiometry of 1 Ca2+ transported versus 1 H+ countertransported. The experimental parameters considered for this analysis should be actual rates of net transport and countertransport rather ...
amino acid 1
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
a-Aminoadipate aminotransferase from an extremely
... To characterize the lysN gene product, we expressed the gene in E. coli and obtained a purified preparation of LysN by using a T7 promoter expression system. LysN was accumulated as insoluble inclusion bodies when the E. coli cells carrying pETLysN7 were cultured in the presence of 1 mM IPTG at 37 u ...
... To characterize the lysN gene product, we expressed the gene in E. coli and obtained a purified preparation of LysN by using a T7 promoter expression system. LysN was accumulated as insoluble inclusion bodies when the E. coli cells carrying pETLysN7 were cultured in the presence of 1 mM IPTG at 37 u ...
... production as well. Amino acid analysis is a good indicator to measure the quality of protein which may vary according to different species and environmental factors. Therefore, the objectives of the present study is to characterization of Pisum sativum varieties grown in Central Europe by evaluatin ...
R-C-SCoA (acyl CoA) O
... The identity of the products–in this case AMP plus Ppi-has a significance. The carboxyl group of an organic acid (e.g. acetate) is an unactivated, low-energy, resonance-stabilized anion that is not easily attacked by a nucleophile (e.g. CoAS-); it is extremely difficult to remove one of the two carb ...
... The identity of the products–in this case AMP plus Ppi-has a significance. The carboxyl group of an organic acid (e.g. acetate) is an unactivated, low-energy, resonance-stabilized anion that is not easily attacked by a nucleophile (e.g. CoAS-); it is extremely difficult to remove one of the two carb ...
Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of
... and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, combined with pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pr ...
... and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, combined with pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pr ...
4. AMINO ACIDS
... b) Based on the groups present in the side chain: • Based on the groups present in the side chain ‘R’ amino acids are classified as ...
... b) Based on the groups present in the side chain: • Based on the groups present in the side chain ‘R’ amino acids are classified as ...
ppt - Vanderbilt University
... Globular. Proteins that fold into a “spherical” conformation . Hydrophobic effect. Proteins will fold so that hydrophobic amino acids are on the inside (shielded from water) and hydrophilic amino acids are on the outside (exposed to water). ...
... Globular. Proteins that fold into a “spherical” conformation . Hydrophobic effect. Proteins will fold so that hydrophobic amino acids are on the inside (shielded from water) and hydrophilic amino acids are on the outside (exposed to water). ...
Three-dimensional Structure of Goose
... of the structure. The explanation for this difference may be found in Go's (1983) analysis of the relationship between the module structure and the functional elements of the HEWL structure. No residue in module 1 of HEWL plays an obvious role in substrate binding or in the catalytic mechanism. The ...
... of the structure. The explanation for this difference may be found in Go's (1983) analysis of the relationship between the module structure and the functional elements of the HEWL structure. No residue in module 1 of HEWL plays an obvious role in substrate binding or in the catalytic mechanism. The ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.