Fatty acid synthesis
... •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot cross mitochondrial membrane Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate to form Citrate Citrate enters into the cytoplasm and gets cleaved by citrate lyase. ...
... •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot cross mitochondrial membrane Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate to form Citrate Citrate enters into the cytoplasm and gets cleaved by citrate lyase. ...
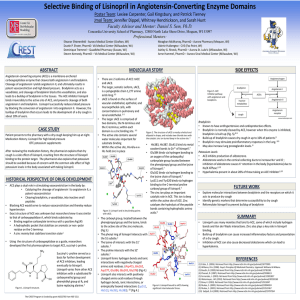
Selective Binding of Lisinopril in Angiotensin
... Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a membrane-anchored carboxypeptidase enzyme that cleaves both angiotensin I and bradykinin. Cleavage of angiotensin I yields angiotensin II, and ultimately results in potent vasoconstriction and high blood pressure. Bradykinin acts as a vasodilator, and cleavag ...
... Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a membrane-anchored carboxypeptidase enzyme that cleaves both angiotensin I and bradykinin. Cleavage of angiotensin I yields angiotensin II, and ultimately results in potent vasoconstriction and high blood pressure. Bradykinin acts as a vasodilator, and cleavag ...
Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of
... Now this amino acids are playing a very important role as far as the mechanism the cell functionality is concerned and that is the reason this amino acids has been classified or symbolized with either three letter digit or with one letter digit say for example, now glycine if we considered glycine a ...
... Now this amino acids are playing a very important role as far as the mechanism the cell functionality is concerned and that is the reason this amino acids has been classified or symbolized with either three letter digit or with one letter digit say for example, now glycine if we considered glycine a ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and
... To accomplish these general steps we protect and deprotect NH2 groups and activate CO2 H groups. One way chemists protect NH2 groups is with tertbutyloxycarbonyl (t-Boc) groups from tert-butyloxycarbonyl chloride (tBocCl). [graphic 22.14] Trifluoroacetic acid in methylene chloride deprotects NH2 gro ...
... To accomplish these general steps we protect and deprotect NH2 groups and activate CO2 H groups. One way chemists protect NH2 groups is with tertbutyloxycarbonyl (t-Boc) groups from tert-butyloxycarbonyl chloride (tBocCl). [graphic 22.14] Trifluoroacetic acid in methylene chloride deprotects NH2 gro ...
Irreversible Inhibitors of Serine, Cysteine, and Threonine Proteases
... of four heptameric rings. The subunits range from 22 to 30 kDa, giving a total molecular weight of 700750 kDa.25 The proteasome was initially described as a multicatalytic protease by Orlowski due to several different catalytic activities (chymotrypsinlike, trypsin-like, and peptidylglutamyl peptide ...
... of four heptameric rings. The subunits range from 22 to 30 kDa, giving a total molecular weight of 700750 kDa.25 The proteasome was initially described as a multicatalytic protease by Orlowski due to several different catalytic activities (chymotrypsinlike, trypsin-like, and peptidylglutamyl peptide ...
Lab 5
... All biochemical reactions occur under conditions of strict control over the concentration of hydrogen ions. Life cannot exist when there are large fluctuations of the hydrogen ion also known as H+ or proton. Changes in pH, the measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions, will affect the struct ...
... All biochemical reactions occur under conditions of strict control over the concentration of hydrogen ions. Life cannot exist when there are large fluctuations of the hydrogen ion also known as H+ or proton. Changes in pH, the measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions, will affect the struct ...
Document
... Acid-Base Properties of Glycine The zwitterionic structure of glycine also follows from considering its acid-base properties. A good way to think about this is to start with the structure of glycine in strongly acidic solution, say pH = 1. At pH = 1, glycine exists in its protonated form (a monocat ...
... Acid-Base Properties of Glycine The zwitterionic structure of glycine also follows from considering its acid-base properties. A good way to think about this is to start with the structure of glycine in strongly acidic solution, say pH = 1. At pH = 1, glycine exists in its protonated form (a monocat ...
MCAD - MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling
... Intermolecular Interactions Modeled in MCAD, FAD and ETF MCAD Active Site: Glu376, Glu199, Leu103, Ser142, Met249, Asp253, Arg388 Folding of MCAD: 2 Dimers Combine: Arg28:A and Glu86:D Tetramer: Lys304, Glu300, Gln342, Asp346, Arg383 ...
... Intermolecular Interactions Modeled in MCAD, FAD and ETF MCAD Active Site: Glu376, Glu199, Leu103, Ser142, Met249, Asp253, Arg388 Folding of MCAD: 2 Dimers Combine: Arg28:A and Glu86:D Tetramer: Lys304, Glu300, Gln342, Asp346, Arg383 ...
Carbohydrate metabolism File
... number of reactive sites in the molecule increases, speeding up both glycogenesis and glycogenolysis. ...
... number of reactive sites in the molecule increases, speeding up both glycogenesis and glycogenolysis. ...
Effects of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature, pH
... In this work, there were four different parameters studied which were enzyme concentrations, temperature, pH and time of incubation. Only one parameter was varied at one time as to see its effect alone not considering interactions with other parameters. James et al. (2005) reported that enzyme conce ...
... In this work, there were four different parameters studied which were enzyme concentrations, temperature, pH and time of incubation. Only one parameter was varied at one time as to see its effect alone not considering interactions with other parameters. James et al. (2005) reported that enzyme conce ...
AminoAcidMetabolismFIN2011
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
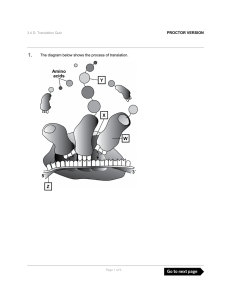
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that most deletions result in a frameshift where all codons that follow the deletion are no longer functional, but does not understand that this particular deletion of a triplet is an exception and does not cause a frameshift beca ...
... Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that most deletions result in a frameshift where all codons that follow the deletion are no longer functional, but does not understand that this particular deletion of a triplet is an exception and does not cause a frameshift beca ...
CHEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 • Alanine ( ala) and lysine (lys) are
... Consequence for structure: This rigidity and the charge on the oxygen are ideal for the formation of α-helices and β -pleated sheets via H-bonding. Consequence for chemistry: The involvement of the N lone pair in resonance, means that the N is unavailable for protonation and is non-basic. The peptid ...
... Consequence for structure: This rigidity and the charge on the oxygen are ideal for the formation of α-helices and β -pleated sheets via H-bonding. Consequence for chemistry: The involvement of the N lone pair in resonance, means that the N is unavailable for protonation and is non-basic. The peptid ...
Amino Acids
... D,L Monosaccharides • According to the conventions proposed by Fischer: – D-monosaccharide: A monosaccharide that has the same configuration at its penultimate carbon as Dglyceraldehyde; that is, its -OH is on the right when written as a Fischer projection. – L-monosaccharide: A monosaccharide that ...
... D,L Monosaccharides • According to the conventions proposed by Fischer: – D-monosaccharide: A monosaccharide that has the same configuration at its penultimate carbon as Dglyceraldehyde; that is, its -OH is on the right when written as a Fischer projection. – L-monosaccharide: A monosaccharide that ...
Amino acids
... • The precise amino acid content, and the sequence of those amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not ...
... • The precise amino acid content, and the sequence of those amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.