ADS901 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... to place the reference ladder of the ADS901 between the supply rails, as shown in Figure 5. Two additional resistors (RT, RB) are necessary to set the correct current through the ladder. However depending on the desired full-scale swing and supply voltage different resistor values might be selected. ...
... to place the reference ladder of the ADS901 between the supply rails, as shown in Figure 5. Two additional resistors (RT, RB) are necessary to set the correct current through the ladder. However depending on the desired full-scale swing and supply voltage different resistor values might be selected. ...
MAX1011 Low-Power, 90Msps, 6-Bit ADC General Description Features
... Note 2: A typical application will AC couple the analog input to the DC bias level present at the analog inputs (typically 2.35V). However, it is also possible to DC couple the analog input (using differential or single-ended drive) within this commonmode input range (Figures 4 and 5). Note 3: PSRR ...
... Note 2: A typical application will AC couple the analog input to the DC bias level present at the analog inputs (typically 2.35V). However, it is also possible to DC couple the analog input (using differential or single-ended drive) within this commonmode input range (Figures 4 and 5). Note 3: PSRR ...
Are you violating your op amp`s input- common-mode range?
... (Figure 5). VIN further increases to 4.2V p-p to clearly exceed VICMR. As the input peak exceeds the limit near the positive rail, the signal at VOUT rails out as it jumps up to the positive rail, 5V, and stays there until VIN returns to an acceptable range (Figure 6). As the input drops below the l ...
... (Figure 5). VIN further increases to 4.2V p-p to clearly exceed VICMR. As the input peak exceeds the limit near the positive rail, the signal at VOUT rails out as it jumps up to the positive rail, 5V, and stays there until VIN returns to an acceptable range (Figure 6). As the input drops below the l ...
Preliminary User`s Manual
... electro-optical VCA principle. This method - controlling the gain by the means of a light dependent resistor - is not as fast as the varimu method, but much more subtle sonically. This principle is known from e.g. the classic Universal audio LA2, LA3 and LA4 compressors, although we use a considerab ...
... electro-optical VCA principle. This method - controlling the gain by the means of a light dependent resistor - is not as fast as the varimu method, but much more subtle sonically. This principle is known from e.g. the classic Universal audio LA2, LA3 and LA4 compressors, although we use a considerab ...
Technical Info CMRR (Common Mode Rejection Ratio)
... diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input terminal of the differential amplifier with exactly the same voltage value, and there is no degradation o ...
... diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input terminal of the differential amplifier with exactly the same voltage value, and there is no degradation o ...
Project 4
... You will need to design a logic circuit (much as you did in Project 3) to implement these equations. Your inputs and outputs are active high. (If active low inputs are desired, you can exchange the + and – inputs in Figure 2.) 7-Segment Decoder and Display Decoding binary data for 7-segment displays ...
... You will need to design a logic circuit (much as you did in Project 3) to implement these equations. Your inputs and outputs are active high. (If active low inputs are desired, you can exchange the + and – inputs in Figure 2.) 7-Segment Decoder and Display Decoding binary data for 7-segment displays ...
Product Specification - The UK Mirror Service
... memory or an I/O device. The addressed I/O device or memory should use this signal to gate data onto the CPU data bus. Tri-state output, active low. WR indicates that the CPU data bus holds valid data to be stored in the addressed memory or I/O device. ...
... memory or an I/O device. The addressed I/O device or memory should use this signal to gate data onto the CPU data bus. Tri-state output, active low. WR indicates that the CPU data bus holds valid data to be stored in the addressed memory or I/O device. ...
TRANSPAK T752 ™ Potentiometer Input Isolating, Field
... The T752 is useful in any application requiring isolation of a 2-wire loop current from a 3-wire potentiometer. Typical applications include tank level data acquisition and position sensor conditioning. The output of the T752 can be used to drive a digital meter for direct display or interface with ...
... The T752 is useful in any application requiring isolation of a 2-wire loop current from a 3-wire potentiometer. Typical applications include tank level data acquisition and position sensor conditioning. The output of the T752 can be used to drive a digital meter for direct display or interface with ...
MAX7375 3-Pin Silicon Oscillator General Description Features
... The MAX7375 operates with power-supply voltages in the 2.7V to 5.5V range. Good power-supply decoupling is needed to maintain the power-supply rejection performance of the MAX7375. Use a 0.1µF surface-mount ceramic capacitor connected between V+ and GND and mounted as close to the device as possible ...
... The MAX7375 operates with power-supply voltages in the 2.7V to 5.5V range. Good power-supply decoupling is needed to maintain the power-supply rejection performance of the MAX7375. Use a 0.1µF surface-mount ceramic capacitor connected between V+ and GND and mounted as close to the device as possible ...
8-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converters With Serial
... 1. CS is brought low. To minimize errors caused by noise at CS, the internal circuitry waits for two rising edges and then a falling edge of the internal system clock after a CS↓ before the transition is recognized. However, upon a CS rising edge, DATA OUT goes to a high-impedance state within the s ...
... 1. CS is brought low. To minimize errors caused by noise at CS, the internal circuitry waits for two rising edges and then a falling edge of the internal system clock after a CS↓ before the transition is recognized. However, upon a CS rising edge, DATA OUT goes to a high-impedance state within the s ...
Ch 10
... • The intersection point is called the “3dB point” since at that frequency ACL will be down by 3dB. ...
... • The intersection point is called the “3dB point” since at that frequency ACL will be down by 3dB. ...
HSTL16918 9-bit to 18-bit HSTL-to-LVTTL
... Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so at th ...
... Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so at th ...
Digital Examination2 - Philadelphia University Jordan
... 50- Schottky devices reduce the storage time delay (ts) by: Allowing the transistor to go deeply in saturation. Not allowing the transistor to go deeply in saturation. Allowing the transistor to go very fast to cutoff. 51- The number of transistors needed to build n inputs of dynamics NMOS gat ...
... 50- Schottky devices reduce the storage time delay (ts) by: Allowing the transistor to go deeply in saturation. Not allowing the transistor to go deeply in saturation. Allowing the transistor to go very fast to cutoff. 51- The number of transistors needed to build n inputs of dynamics NMOS gat ...
Complementry II DIGITAL ELECTRONICS For BSc Computer
... 1. The minimum term in a Boolean function 2. A prime implicant 3. Always smaller than a maxterm 4. A square on a karnaugh map ...
... 1. The minimum term in a Boolean function 2. A prime implicant 3. Always smaller than a maxterm 4. A square on a karnaugh map ...
03 Circuit Analyze, Signals, Timing Diagrams
... Clock is a periodic signal. Clock usually hasn’t beginning or end. It exists all the time while power is on and is used for synchronization of circuits. For the period when the signal has high level sometime we say “The signal exists” or “There is a signal”. For the period when the signal ha ...
... Clock is a periodic signal. Clock usually hasn’t beginning or end. It exists all the time while power is on and is used for synchronization of circuits. For the period when the signal has high level sometime we say “The signal exists” or “There is a signal”. For the period when the signal ha ...
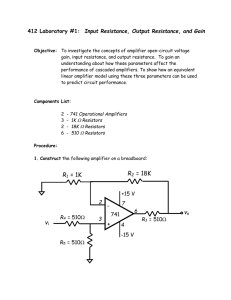
Experiment 1-4
... amplifier. You should find that the output amplitude is twice the input amplitude. Verify that this relationship holds true as you vary the input voltage and frequency. ...
... amplifier. You should find that the output amplitude is twice the input amplitude. Verify that this relationship holds true as you vary the input voltage and frequency. ...
EET425 Lab 1 - Portal UniMAP
... (1) 24kΩ resistor (1) Voltmeter Introduction Digital circuits function by using signals that are at one of two distinct voltage levels. The other classification of electronic circuits is analog. These devices function by operating with signals that vary anywhere between the low and high extreme volt ...
... (1) 24kΩ resistor (1) Voltmeter Introduction Digital circuits function by using signals that are at one of two distinct voltage levels. The other classification of electronic circuits is analog. These devices function by operating with signals that vary anywhere between the low and high extreme volt ...
NAND Gate is a Universal Gate
... sensitive sequential circuits have this problem). Before the enable input changes state from HIGH to LOW (assuming HIGH is ON and LOW is OFF state), if inputs changes, then another state transition occurs for the same enable pulse. This sort of multiple transition problem is called racing. If we mak ...
... sensitive sequential circuits have this problem). Before the enable input changes state from HIGH to LOW (assuming HIGH is ON and LOW is OFF state), if inputs changes, then another state transition occurs for the same enable pulse. This sort of multiple transition problem is called racing. If we mak ...
DVM with the ICL7106
... The control signals necessary for auto-ranging are overrange, under-range, and clock. The over-range and underrange inputs control the direction of a scale shift, becoming active at the completion of an invalid conversion and remaining active until a valid conversion occurs. The clock input controls ...
... The control signals necessary for auto-ranging are overrange, under-range, and clock. The over-range and underrange inputs control the direction of a scale shift, becoming active at the completion of an invalid conversion and remaining active until a valid conversion occurs. The clock input controls ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.