dhaval_sdcard_05282013
... different low-power modes, which can disable unneeded clocks and CPU. Additionally, the MSP430 is capable of wake-up times below 1 microsecond, allowing the microcontroller to stay in sleep mode longer, minimizing its ...
... different low-power modes, which can disable unneeded clocks and CPU. Additionally, the MSP430 is capable of wake-up times below 1 microsecond, allowing the microcontroller to stay in sleep mode longer, minimizing its ...
DS1135 3-in-1 High-Speed Silicon Delay Line FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT
... The DS1135 series is a low-power, +5-volt high-speed version of the popular DS1013 and DS1035. The DS1135 series of delay lines have three independent logic buffered delays in a single package. The device is Dallas Semiconductor’s fastest 3-in-1 delay line. It is available in a standard 8-pin DIP an ...
... The DS1135 series is a low-power, +5-volt high-speed version of the popular DS1013 and DS1035. The DS1135 series of delay lines have three independent logic buffered delays in a single package. The device is Dallas Semiconductor’s fastest 3-in-1 delay line. It is available in a standard 8-pin DIP an ...
High speed digital input current limiter
... Loss of VCC power supply The operation of the CLT01-38SQ7 is extended below the levels required in the IEC 611312 standard to allow the implementation of the under voltage alarm UVA as described the SPI control bit section. If there is no more power feeding on the VCC input, the CLT01-38SQ7 chip goe ...
... Loss of VCC power supply The operation of the CLT01-38SQ7 is extended below the levels required in the IEC 611312 standard to allow the implementation of the under voltage alarm UVA as described the SPI control bit section. If there is no more power feeding on the VCC input, the CLT01-38SQ7 chip goe ...
Craft Port™ Tiny RS-232 Transceiver for Portable Applications ADM101E
... charge pump draws current pulses from VCC, the VCC decoupling capacitor should also have low ESR. The VCC decoupling capacitor and V– reservoir capacitor should also have low ESR because they determine how effectively ESD pulses are clamped to VCC or V− by the on-chip clamp diodes. Tantalum or monol ...
... charge pump draws current pulses from VCC, the VCC decoupling capacitor should also have low ESR. The VCC decoupling capacitor and V– reservoir capacitor should also have low ESR because they determine how effectively ESD pulses are clamped to VCC or V− by the on-chip clamp diodes. Tantalum or monol ...
Synthesizer with VCO by Analog Devices
... Reference Input. This is a CMOS input with a nominal threshold of VDD/2 and a dc equivalent input resistance of 100 kΩ. See Figure 10. This input can be driven from a TTL or CMOS crystal oscillator or it can be ac-coupled. Serial Clock Input. This serial clock is used to clock in the serial data to ...
... Reference Input. This is a CMOS input with a nominal threshold of VDD/2 and a dc equivalent input resistance of 100 kΩ. See Figure 10. This input can be driven from a TTL or CMOS crystal oscillator or it can be ac-coupled. Serial Clock Input. This serial clock is used to clock in the serial data to ...
Electrical 2
... • Must calculate for BOTH output high and output low. Select the worst-case condition. (Disregard the negative in the ...
... • Must calculate for BOTH output high and output low. Select the worst-case condition. (Disregard the negative in the ...
Document
... To overcome the defect of low VTR in the MC, much research has been devoting to this problem. Different topology circuits have been introduced to improve VTR by adding extra switches and passive components, but the complexity was added. Another methods by adding extra switches in the input side ...
... To overcome the defect of low VTR in the MC, much research has been devoting to this problem. Different topology circuits have been introduced to improve VTR by adding extra switches and passive components, but the complexity was added. Another methods by adding extra switches in the input side ...
Diode :- Clamper
... The clamping network ‘clamp’ a signal to different dc level without altering the wave-shape. ...
... The clamping network ‘clamp’ a signal to different dc level without altering the wave-shape. ...
ppt
... IB+ sets up a voltage drop of RGIB+ across resistor RG and applies it to the (+) input. The differential input voltage of 0V, so the (-) input is also at RGIB+ Since there is 0 resistance in the feedback loop, V0 equals RGIB+. ...
... IB+ sets up a voltage drop of RGIB+ across resistor RG and applies it to the (+) input. The differential input voltage of 0V, so the (-) input is also at RGIB+ Since there is 0 resistance in the feedback loop, V0 equals RGIB+. ...
Lecture4 - UCSB ECE
... interconnects separate logic stages or when circuits have high fan-out load (use buffering). ...
... interconnects separate logic stages or when circuits have high fan-out load (use buffering). ...
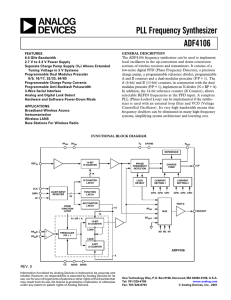
ADF4106
... 100 kΩ. See Figure 2. This input can be driven from a TTL or CMOS crystal oscillator or it can be ac coupled. Digital Ground Chip Enable. A logic low on this pin powers down the device and puts the charge pump output into three-state mode. Taking the pin high will power up the device depending on th ...
... 100 kΩ. See Figure 2. This input can be driven from a TTL or CMOS crystal oscillator or it can be ac coupled. Digital Ground Chip Enable. A logic low on this pin powers down the device and puts the charge pump output into three-state mode. Taking the pin high will power up the device depending on th ...
The Technology in the Parasound Halo CD 1
... The CD 1 uses a single AD1853 DAC in stereo mode, rather than a separate DAC for each channel. The choice of a single DAC was not budgetary, but rather because a single DAC is inherently free of any inter-DAC delays. The delay between multiple DACs working in parallel can measure up to 10 nanosecond ...
... The CD 1 uses a single AD1853 DAC in stereo mode, rather than a separate DAC for each channel. The choice of a single DAC was not budgetary, but rather because a single DAC is inherently free of any inter-DAC delays. The delay between multiple DACs working in parallel can measure up to 10 nanosecond ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.