Ch. 18
... their opinions to agree with others. • B) most people changing their opinions to agree with others. • C) most everyone ignored what others said. • D) a small minority changed their opinions to agree with others. ...
... their opinions to agree with others. • B) most people changing their opinions to agree with others. • C) most everyone ignored what others said. • D) a small minority changed their opinions to agree with others. ...
File - Communities of Practice
... numerous factors. SSS6.a: Describe how and why societies change over time. SSS6.b: Examine various social influences that can lead to immediate and long-term changes. SSS6.c: Describe how collective behavior can influence and change society. SSS6.d: Examine how technological innovations and scientif ...
... numerous factors. SSS6.a: Describe how and why societies change over time. SSS6.b: Examine various social influences that can lead to immediate and long-term changes. SSS6.c: Describe how collective behavior can influence and change society. SSS6.d: Examine how technological innovations and scientif ...
Social Influence
... • Process whereby attitudes are influenced by the real or implied presence of other people (Hogg & Vaughan, 2005) • Changes mainly in behavior resulting from interpersonal interaction (Fiske, 2004) ...
... • Process whereby attitudes are influenced by the real or implied presence of other people (Hogg & Vaughan, 2005) • Changes mainly in behavior resulting from interpersonal interaction (Fiske, 2004) ...
Thinking/Influences Unit Guide
... behavior is against our morals or how we normally would behave. ...
... behavior is against our morals or how we normally would behave. ...
Exam revision - nclmoodle.org.uk
... …psychologists have looked at many factors involved in the process of forming relationships. Most research has looked at the formation of romantic relationships between monogamous heterosexual couples and so may not be representative of all types of relationship but the following factors are just so ...
... …psychologists have looked at many factors involved in the process of forming relationships. Most research has looked at the formation of romantic relationships between monogamous heterosexual couples and so may not be representative of all types of relationship but the following factors are just so ...
Social Psychology - Solon City Schools
... • Discomfort we feel when your thoughts are behaviors are inconsistent • People want to have consistent attitudes and behaviors….when they are not they experience ...
... • Discomfort we feel when your thoughts are behaviors are inconsistent • People want to have consistent attitudes and behaviors….when they are not they experience ...
Multi-step Cart-wheeling Problems
... 5. Year 6 are trusted to have groups up to 13 in number. 75 of the year 6 children want to cart-wheel. How many groups will this be? 6. The Governors are still concerned about safety and have said all children taking part in cart-wheeling must remove their shoes. The Headteacher has thus arranged fo ...
... 5. Year 6 are trusted to have groups up to 13 in number. 75 of the year 6 children want to cart-wheel. How many groups will this be? 6. The Governors are still concerned about safety and have said all children taking part in cart-wheeling must remove their shoes. The Headteacher has thus arranged fo ...
Social Psychology - Modules 56-59
... – People less likely to conform when not in the presence of authority – i.e., when instructions given in a different room/building ...
... – People less likely to conform when not in the presence of authority – i.e., when instructions given in a different room/building ...
AP Psychology Unit XIV * Social Psychology
... …then identify any and all commonalities within these conflicts. …with what methods/techniques might the conflicts be resolved? ...
... …then identify any and all commonalities within these conflicts. …with what methods/techniques might the conflicts be resolved? ...
SocialPsychology
... Social Influence Social Facilitation improved performance of some tasks in the presence of others occurs with simple or well-learned tasks but not with tasks that are difficult or not yet ...
... Social Influence Social Facilitation improved performance of some tasks in the presence of others occurs with simple or well-learned tasks but not with tasks that are difficult or not yet ...
Social Psychology
... What did you write down? Did you write down something that you wouldn’t have done if people knew it was you? ...
... What did you write down? Did you write down something that you wouldn’t have done if people knew it was you? ...
ppt_ch14
... how our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by our social interactions with others and the culture in which we live ...
... how our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by our social interactions with others and the culture in which we live ...
Document
... professions but some of their findings are relevant in medicine .Whether by standers intervene to help in an emergency is related into two factors; I. The number of people present II. The perceived cause of the problems. The more people present ,the less likely anyone intervenes.This may be because ...
... professions but some of their findings are relevant in medicine .Whether by standers intervene to help in an emergency is related into two factors; I. The number of people present II. The perceived cause of the problems. The more people present ,the less likely anyone intervenes.This may be because ...
SOCIOLOGY CHAPTER 4
... Families, couples in love, street gangs, social clubs Relationships that are face-to-face and personal term “primary group”--coined by Charles Cooley two or more people who have a significant amount of interaction with one another must know a lot about one another, and share strong, intimate emotion ...
... Families, couples in love, street gangs, social clubs Relationships that are face-to-face and personal term “primary group”--coined by Charles Cooley two or more people who have a significant amount of interaction with one another must know a lot about one another, and share strong, intimate emotion ...
Social Psychology
... think about other people, interact in relationships and groups, and are influenced by others Scientific study of how people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior are impacted by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others The study of social situations, with special attention to how we view ...
... think about other people, interact in relationships and groups, and are influenced by others Scientific study of how people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior are impacted by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others The study of social situations, with special attention to how we view ...
Unit XIV Test Review
... Prejudice and stereotype Prejudice is an unjustifiable (usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members. Prejudice is often directed towards different cultural, ethnic, or gender groups and is often based on a stereotype or false belief about that group. Example: Irish are hot tempered an ...
... Prejudice and stereotype Prejudice is an unjustifiable (usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members. Prejudice is often directed towards different cultural, ethnic, or gender groups and is often based on a stereotype or false belief about that group. Example: Irish are hot tempered an ...
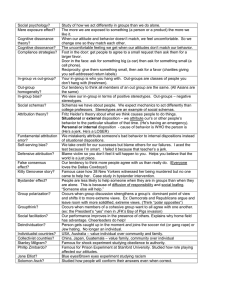
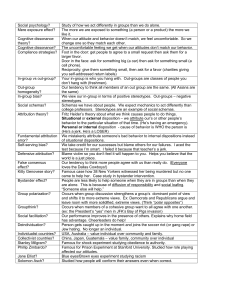
Unit 13 Study Guide (chapter 18)
... C) social exchange theory. D) evolutionary psychology. E) two-factor theory. ____ 8. According to cognitive dissonance theory, dissonance is most likely to occur when: A) a person's behavior is not based on strongly held attitudes. B) two people have conflicting attitudes and find themselves in disa ...
... C) social exchange theory. D) evolutionary psychology. E) two-factor theory. ____ 8. According to cognitive dissonance theory, dissonance is most likely to occur when: A) a person's behavior is not based on strongly held attitudes. B) two people have conflicting attitudes and find themselves in disa ...
Social Psych notes
... test because I’m smart. I failed it because that teacher’s a jerk. Blame victim so you don’t feel it will happen to you. Helps you believe that the world is a just place. Our tendency to think more people agree with us than really do. (Everyone loves the Dallas Cowboys!) Famous case how 38 New Yorke ...
... test because I’m smart. I failed it because that teacher’s a jerk. Blame victim so you don’t feel it will happen to you. Helps you believe that the world is a just place. Our tendency to think more people agree with us than really do. (Everyone loves the Dallas Cowboys!) Famous case how 38 New Yorke ...
Social psychology? Study of how we act differently in groups than
... test because I’m smart. I failed it because that teacher’s a jerk. Blame victim so you don’t feel it will happen to you. Helps you believe that the world is a just place. Our tendency to think more people agree with us than really do. (Everyone loves the Dallas Cowboys!) Famous case how 38 New Yorke ...
... test because I’m smart. I failed it because that teacher’s a jerk. Blame victim so you don’t feel it will happen to you. Helps you believe that the world is a just place. Our tendency to think more people agree with us than really do. (Everyone loves the Dallas Cowboys!) Famous case how 38 New Yorke ...
11-7 Adolescent Psychosocial Development
... • From where do teens learn about sex? • Peers: “Don’t trust adults. I mean, they don’t know what we’re going through. Just want to scare you from having sex, like you’ll die if you do. Gotta ask your friends for advice on how to do it,” (Archibald, Jacoby, Davies, 2010) ...
... • From where do teens learn about sex? • Peers: “Don’t trust adults. I mean, they don’t know what we’re going through. Just want to scare you from having sex, like you’ll die if you do. Gotta ask your friends for advice on how to do it,” (Archibald, Jacoby, Davies, 2010) ...
The Consumer and Conformity
... Individuals or groups that select use and dispose of products services or experiences to satisfy needs and desires ...
... Individuals or groups that select use and dispose of products services or experiences to satisfy needs and desires ...
Social Psychology
... O When confederates gave incorrect responses that contradicted what the participants knew to be true, the participant went along with the incorrect response abt 30% of the time. O Less than 1 in 4 chances that the participant would act independently and disagree with the group. ...
... O When confederates gave incorrect responses that contradicted what the participants knew to be true, the participant went along with the incorrect response abt 30% of the time. O Less than 1 in 4 chances that the participant would act independently and disagree with the group. ...