Slide 1
... • Louis de Broglie suggested that e- in fixed orbitals (like Bohr suggested) behave with wave like properties. • He hypothesized that electrons also have dual particle-wave nature. ...
... • Louis de Broglie suggested that e- in fixed orbitals (like Bohr suggested) behave with wave like properties. • He hypothesized that electrons also have dual particle-wave nature. ...
Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons
... Quantum Mechanics and its Linear Algebra Influence By: Mandy Switzer Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, and photons. With quantum mechanics, one can more easily and more correctly see how and why particles behave a certain way, which was very difficu ...
... Quantum Mechanics and its Linear Algebra Influence By: Mandy Switzer Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, and photons. With quantum mechanics, one can more easily and more correctly see how and why particles behave a certain way, which was very difficu ...
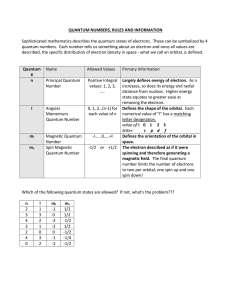
Quantum Number Table
... Sophisticated mathematics describes the quantum states of electrons. These can be symbolized by 4 quantum numbers. Each number tells us something about an electron and once all values are described, the specific distribution of electron density in space - what we call an orbital, is defined. ...
... Sophisticated mathematics describes the quantum states of electrons. These can be symbolized by 4 quantum numbers. Each number tells us something about an electron and once all values are described, the specific distribution of electron density in space - what we call an orbital, is defined. ...
Universal turning point behavior for Gaussian
... 具⌬2典共t兲 is assumed to be dominated by the t4 term, then the ⬀ 兩T2兩 / dependence in the autocorrelation estimate 共5兲 is recovered. Delocalization in the classical limit is again demonstrated to be slow relative to the orbital period, as a consequence of the large ratio 兩T2兩 / 兩T1兩. Equation 共10兲 ...
... 具⌬2典共t兲 is assumed to be dominated by the t4 term, then the ⬀ 兩T2兩 / dependence in the autocorrelation estimate 共5兲 is recovered. Delocalization in the classical limit is again demonstrated to be slow relative to the orbital period, as a consequence of the large ratio 兩T2兩 / 兩T1兩. Equation 共10兲 ...
Quantum Memories at Room-Temperature Supervisors: Dr Dylan
... the scaling of experiments to a regime where large numbers of photons can be prepared in quantum-correlated states. Here at the Ultrafast Quantum Optics Group (UFQO) at the University of Oxford we have been exploring the use of twophoton interactions in warm Alkali vapours as a potential solution to ...
... the scaling of experiments to a regime where large numbers of photons can be prepared in quantum-correlated states. Here at the Ultrafast Quantum Optics Group (UFQO) at the University of Oxford we have been exploring the use of twophoton interactions in warm Alkali vapours as a potential solution to ...
Localization and the Semiclassical Limit in Quantum Field Theories
... For each t, it is a Gaussian centered at x0 cos(ω0 t), reproducing the classical motion of the harmonic oscillator. ...
... For each t, it is a Gaussian centered at x0 cos(ω0 t), reproducing the classical motion of the harmonic oscillator. ...
planck , s law and the light quantum hypothesis
... been developed during the past twenty years and has yielded rich harvests in all fields of physics. Since its publication in the year 1901 many types of derivations of this law have been suggested. It is acknowledged that the fundamental assumptions of the quantum theory are inconsistent with the la ...
... been developed during the past twenty years and has yielded rich harvests in all fields of physics. Since its publication in the year 1901 many types of derivations of this law have been suggested. It is acknowledged that the fundamental assumptions of the quantum theory are inconsistent with the la ...
7.2.4. Normal Ordering
... Finally, we mention that some neutral particles are identical to their anti-particles. Notable examples are photons and neutral pions. Since one can call any given photon a particle as well as anti-particle, the net number of “particles” is always conserved as long as the total number of photons pr ...
... Finally, we mention that some neutral particles are identical to their anti-particles. Notable examples are photons and neutral pions. Since one can call any given photon a particle as well as anti-particle, the net number of “particles” is always conserved as long as the total number of photons pr ...
ppt - HEP Educational Outreach
... down to a single-photon (i.e. - there’s never more than a single photon in the apparatus at a time), what should we see? ...
... down to a single-photon (i.e. - there’s never more than a single photon in the apparatus at a time), what should we see? ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #5
... (d) Confirm that you get the same result by using grade-school quantum mechanics and matching right and left going waves on the left with a right going wave on the right at x = 0. You’ll need to integrate the Schrödinger equation across x = 0 to match the derivatives. (e) We showed last semester th ...
... (d) Confirm that you get the same result by using grade-school quantum mechanics and matching right and left going waves on the left with a right going wave on the right at x = 0. You’ll need to integrate the Schrödinger equation across x = 0 to match the derivatives. (e) We showed last semester th ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 15. Explain the use of perturbation theory for the case of a 2-d harmonic oscillator. PART C ( 4 X 12.5 = 50 MARKS ) ANSWER ANY FOUR QUESTIONS. EACH QUESTION CARRIES 12.5 MARKS. 16. Describe Compton effect and derive an expression for the shift in wavelength of the scattered beam. 17.Consider a squa ...
... 15. Explain the use of perturbation theory for the case of a 2-d harmonic oscillator. PART C ( 4 X 12.5 = 50 MARKS ) ANSWER ANY FOUR QUESTIONS. EACH QUESTION CARRIES 12.5 MARKS. 16. Describe Compton effect and derive an expression for the shift in wavelength of the scattered beam. 17.Consider a squa ...
DOC - 嘉義大學
... (d) If the cutoff frequency is 1.041015 Hz, Find the stopping voltage for Zn if photoelectrons are produced by the wavelength 233.5 nm. 3. (a) Explain why you observe two different types of diffraction patterns in the following two figures. (b) What does the observed spots or rings indicate? Explai ...
... (d) If the cutoff frequency is 1.041015 Hz, Find the stopping voltage for Zn if photoelectrons are produced by the wavelength 233.5 nm. 3. (a) Explain why you observe two different types of diffraction patterns in the following two figures. (b) What does the observed spots or rings indicate? Explai ...
Homework 2
... 2.2 The simple harmonic oscillator, ie, the parabolic potential from part 1, has equally spaced eigenvalues that look like (n+1/2) ħ where is the angular frequency of the oscillator. Consider now the half-oscillator shown below, whose potential equals a regular oscillator for x > 0 and equals in ...
... 2.2 The simple harmonic oscillator, ie, the parabolic potential from part 1, has equally spaced eigenvalues that look like (n+1/2) ħ where is the angular frequency of the oscillator. Consider now the half-oscillator shown below, whose potential equals a regular oscillator for x > 0 and equals in ...
Group and phase velocity
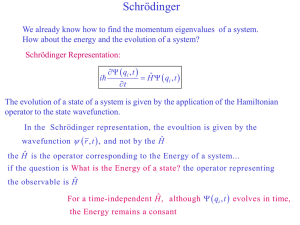
... We already know how to find the momentum eigenvalues of a system. How about the energy and the evolution of a system? Schrödinger Representation: ...
... We already know how to find the momentum eigenvalues of a system. How about the energy and the evolution of a system? Schrödinger Representation: ...
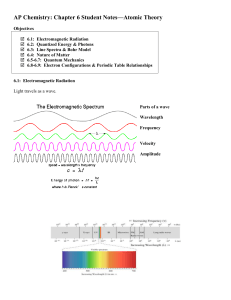
Sec 4-1 Chapter 4 Notes
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that travels through space. All electromagnetic radiation (or waves) travel at 3.0 x 108 m/s. This is called the speed of light. ...
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that travels through space. All electromagnetic radiation (or waves) travel at 3.0 x 108 m/s. This is called the speed of light. ...