Nonlincourse13
... nonlinear. The generator of the transformation is determined up to a diagonal ("resonant") term. This procedure can be carried out to higher orders, but the results do not change in nature. The classical limit is obtained by computing the transition energy between two adjacent states, |n> and |n+1>, ...
... nonlinear. The generator of the transformation is determined up to a diagonal ("resonant") term. This procedure can be carried out to higher orders, but the results do not change in nature. The classical limit is obtained by computing the transition energy between two adjacent states, |n> and |n+1>, ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
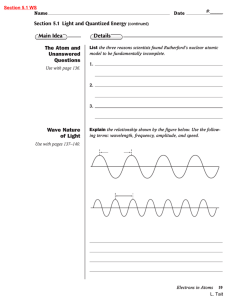
... The quantum concept concludes that matter can gain or lose only in small, specific amounts called ...
... The quantum concept concludes that matter can gain or lose only in small, specific amounts called ...
Characterizing Atom Sources with Quantum Coherence
... viewed by a wave or particle picture, by using quantum optics as an analogy. For example, first-order coherence measures amplitude fluctuations related to fringe visibility in an interferometer. Secondorder coherence measures intensity variations as manifested in laser light speckle. Hanbury Brown a ...
... viewed by a wave or particle picture, by using quantum optics as an analogy. For example, first-order coherence measures amplitude fluctuations related to fringe visibility in an interferometer. Secondorder coherence measures intensity variations as manifested in laser light speckle. Hanbury Brown a ...
Quantum phase transition - Condensed Matter Theory and Quantum
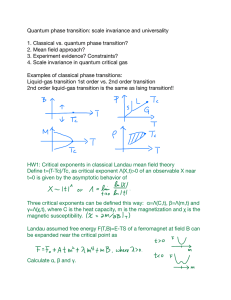
... Three critical exponents can be defined this way: α=Λ(C,t), β=Λ(m,t) and γ=Λ(χ,t), where C is the heat capacity, m is the magnetization and χ is the magnetic susceptibility. ...
... Three critical exponents can be defined this way: α=Λ(C,t), β=Λ(m,t) and γ=Λ(χ,t), where C is the heat capacity, m is the magnetization and χ is the magnetic susceptibility. ...
슬라이드 1
... Schrödinger Cat (Measurement and Superposition) Schrödinger wrote (1935): One can even set up quite ridiculous cases. A cat is penned up in a steel chamber, along with the following device (which must be secured against direct interference by the cat): in a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of rad ...
... Schrödinger Cat (Measurement and Superposition) Schrödinger wrote (1935): One can even set up quite ridiculous cases. A cat is penned up in a steel chamber, along with the following device (which must be secured against direct interference by the cat): in a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of rad ...
Physics 411: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... Homework assignments will be handed out once per week and must be turned it one week later, same day. We typically have ten homework assignments per semester. Homework is graded on a scale from 1 (= poor) to 3 (very good or excellent). Midterms will be split into a take home problem and a test in cl ...
... Homework assignments will be handed out once per week and must be turned it one week later, same day. We typically have ten homework assignments per semester. Homework is graded on a scale from 1 (= poor) to 3 (very good or excellent). Midterms will be split into a take home problem and a test in cl ...
Anmeldeformular für Email
... Abstract: Since classical physics is described in phase space and quantum mechanics in Hilbert space a unified picture is desired. This is provided, for instance, by the so called Wigner function (WF), which has remarkable properties: It transform s the wave function of a quantum mechanical particle ...
... Abstract: Since classical physics is described in phase space and quantum mechanics in Hilbert space a unified picture is desired. This is provided, for instance, by the so called Wigner function (WF), which has remarkable properties: It transform s the wave function of a quantum mechanical particle ...
Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography Sigma Pi Sigma INDUCTION
... fuzzy. We can no longer make predictions with certainty. Nature is intrinsically probabilistic. Objects have no clear position unless we look at them. Despite its strangeness, the theory of quantum mechanics has been passing all experimental tests and has been confirming various bizarre predictions. ...
... fuzzy. We can no longer make predictions with certainty. Nature is intrinsically probabilistic. Objects have no clear position unless we look at them. Despite its strangeness, the theory of quantum mechanics has been passing all experimental tests and has been confirming various bizarre predictions. ...
Coherent states
... Obtain a differential equation for the function v(t) and show that its real and imaginary parts correspond to the classical Hamilton equations dq/dt = p,dp/dt = F(t). ...
... Obtain a differential equation for the function v(t) and show that its real and imaginary parts correspond to the classical Hamilton equations dq/dt = p,dp/dt = F(t). ...
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 5: Solutions
... (e) Assuming that the spin-orbit interaction lifts the degeneracy of the states with different j, how many distinct energy levels make up the fine-structure of the (3p)2 state? The allowed j values are j = 0, 1, 2, so there would be 3 fine-structure levels. (f) Which j levels would shift if a contac ...
... (e) Assuming that the spin-orbit interaction lifts the degeneracy of the states with different j, how many distinct energy levels make up the fine-structure of the (3p)2 state? The allowed j values are j = 0, 1, 2, so there would be 3 fine-structure levels. (f) Which j levels would shift if a contac ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
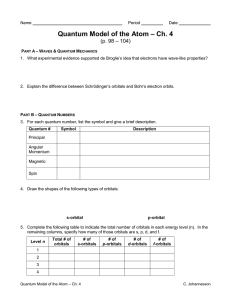
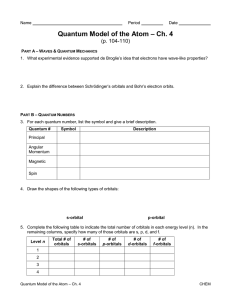
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and velocity of an electron, or any particle. 4. wave mechanics looks to suggest the locations of electr ...
... 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and velocity of an electron, or any particle. 4. wave mechanics looks to suggest the locations of electr ...
CONJECTURING THE MATHEMATICAL AXIOM THAT
... been ignored, but it has been neglected. In quantum physics, it has been unjustly neglected. One usually considers situations that are too idealized, and one investigates problems for which the directedness of time and for which irreversibility do not play a prominent role. An example is classical m ...
... been ignored, but it has been neglected. In quantum physics, it has been unjustly neglected. One usually considers situations that are too idealized, and one investigates problems for which the directedness of time and for which irreversibility do not play a prominent role. An example is classical m ...
Planck`s Law and Light Quantum Hypothesis.
... that is, the relation between the radiation density and the mean energy of an oscillator, and they make assumptions about the number of degrees of freedom of the ether, which appear in the above formula (the first factor on the right– hand side). This factor, however, can be derived only from classi ...
... that is, the relation between the radiation density and the mean energy of an oscillator, and they make assumptions about the number of degrees of freedom of the ether, which appear in the above formula (the first factor on the right– hand side). This factor, however, can be derived only from classi ...
CLASSICAL-QUANTUM CORRESPONDENCE AND WAVE PACKET SOLUTIONS OF THE DIRAC
... Abstract. The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with a ...
... Abstract. The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with a ...