ppt
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
e-the-quantum-numberssv-2
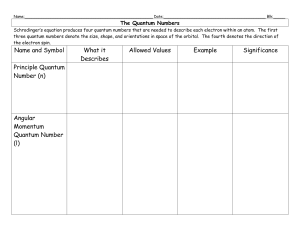
... Name:______________________________________________________ Date:___________________________________________ Blk:_____ ...
... Name:______________________________________________________ Date:___________________________________________ Blk:_____ ...
Coherence, Decoherence and Incoherence in Natural Light
... But incoherent light can be composed of unrelated fs pulses— hence fs pulsed Initial dynamics is relevant to incoherent case. ...
... But incoherent light can be composed of unrelated fs pulses— hence fs pulsed Initial dynamics is relevant to incoherent case. ...
in-class worksheet
... QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Contributors to the quantum mechanical model in mid-1920s: Louis deBroglie Erwin Schrödinger Werner Heisenberg Schrödinger – treat e– as a wave Schrödinger equation: Ĥ = E solve to get wave functions, which predict locations of electrons wave function = ORBITAL ...
... QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Contributors to the quantum mechanical model in mid-1920s: Louis deBroglie Erwin Schrödinger Werner Heisenberg Schrödinger – treat e– as a wave Schrödinger equation: Ĥ = E solve to get wave functions, which predict locations of electrons wave function = ORBITAL ...
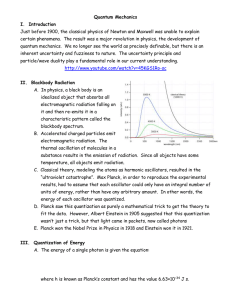
Quantum Mechanics I. Introduction Just before 1900, the classical
... it and then re-emits it in a characteristic pattern called the blackbody spectrum. B. Accelerated charged particles emit electromagnetic radiation. The thermal oscillation of molecules in a substance results in the emission of radiation. Since all objects have some temperature, all objects emit radi ...
... it and then re-emits it in a characteristic pattern called the blackbody spectrum. B. Accelerated charged particles emit electromagnetic radiation. The thermal oscillation of molecules in a substance results in the emission of radiation. Since all objects have some temperature, all objects emit radi ...
Postulate 1 of Quantum Mechanics (wave function)
... • The wavefunction must be single-valued, continuous, finite (not infinite over a finite range), and normalized (the probability of find it somewhere is 1). ...
... • The wavefunction must be single-valued, continuous, finite (not infinite over a finite range), and normalized (the probability of find it somewhere is 1). ...
Equilibrium and non-equilibrium dynamics in the quantum regime
... principle and the second law of thermodynamics in the quantum regime and claimed their breaking. If true, these results would have powerful and unlikely consequences for both, thermodynamics and information theory. I will review the original discussion on the model of a quantum brownian oscillator a ...
... principle and the second law of thermodynamics in the quantum regime and claimed their breaking. If true, these results would have powerful and unlikely consequences for both, thermodynamics and information theory. I will review the original discussion on the model of a quantum brownian oscillator a ...
Lecture #3
... A moving “particle” is described by a superposition of a great many sin and cos waves which constructively interfere to give a Gaussian probability near a certain point but destructively interfere everywhere else. The Gaussian “wave packet” moves according to the kinetic energy given by the average ...
... A moving “particle” is described by a superposition of a great many sin and cos waves which constructively interfere to give a Gaussian probability near a certain point but destructively interfere everywhere else. The Gaussian “wave packet” moves according to the kinetic energy given by the average ...
HWU4-21 QUESTION: The principal quantum number, n, describes
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
(Quantum Mechanics) 1. State basic concepts (or postulates) of
... 4. One of the uncertainty relations is expressed as = , where ∆ is the uncertainty in the position and ∆ , that in the momentum . (a) Using the uncertainty relation, estimate the ground state energy and radius of the hydrogen atom. (b) Similary, estimate the ground state energy of one-d ...
... 4. One of the uncertainty relations is expressed as = , where ∆ is the uncertainty in the position and ∆ , that in the momentum . (a) Using the uncertainty relation, estimate the ground state energy and radius of the hydrogen atom. (b) Similary, estimate the ground state energy of one-d ...
Quantum coherence: myth or fact?
... language is invalid [1]. A resolution to this debate is urgent not only in consideration of the last forty years of experimental achievements but also to provide a precise interpretation of present and future experimental results. The representation of a state and its associated interpretation are f ...
... language is invalid [1]. A resolution to this debate is urgent not only in consideration of the last forty years of experimental achievements but also to provide a precise interpretation of present and future experimental results. The representation of a state and its associated interpretation are f ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14.a.Find the energy eigen values of a particle of mass ‘m’ confined to a box of side ‘L’ (4) b.Three electrons are confined to a box of side 0.5Au. Find the lowest possible energy of the system if electron mass is 9.1 x 10-31kg and Planck’s constant h= 6.63x10-34Js (3.5) 15. Obtain the expression f ...
... 14.a.Find the energy eigen values of a particle of mass ‘m’ confined to a box of side ‘L’ (4) b.Three electrons are confined to a box of side 0.5Au. Find the lowest possible energy of the system if electron mass is 9.1 x 10-31kg and Planck’s constant h= 6.63x10-34Js (3.5) 15. Obtain the expression f ...
Many-body Quantum Mechanics
... the method of using annihilation and creation operators acting on a Fock space as ”second quantization”. As should be clear from the above, this terminology is misleading in the sense that ψ̂ is not a once more quantized version of the wave function, but an object which is directly (or via a Fourier ...
... the method of using annihilation and creation operators acting on a Fock space as ”second quantization”. As should be clear from the above, this terminology is misleading in the sense that ψ̂ is not a once more quantized version of the wave function, but an object which is directly (or via a Fourier ...
Modern Physics Guide
... Double slit interference: quantum must pass through both slits to produce interference. Interference pattern is a probability distribution for finding the quantum at the screen. Making a measurement collapses the wave function to that for the result. Uncertainty principle: ΔpΔx≥ħ ; ΔEΔt≥ħ due to the ...
... Double slit interference: quantum must pass through both slits to produce interference. Interference pattern is a probability distribution for finding the quantum at the screen. Making a measurement collapses the wave function to that for the result. Uncertainty principle: ΔpΔx≥ħ ; ΔEΔt≥ħ due to the ...