HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... 14) Complete the following table for the functions of the various types of RNA / RNA complexes in a eukaryotic cell. Type of RNA Function Messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... 14) Complete the following table for the functions of the various types of RNA / RNA complexes in a eukaryotic cell. Type of RNA Function Messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
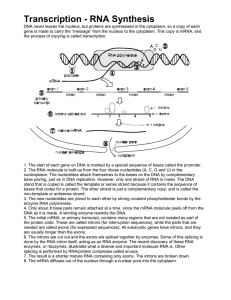
... strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
... strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
Document
... 2. How is information about making proteins transmitted from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis? ...
... 2. How is information about making proteins transmitted from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis? ...
CentralDogmaNotes
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
Lecture #7 Date ______
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
word
... 3’ cleavage and polyadenylation: a conserved polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA) lies 10-30 nucleotides upstream from a poly(A) site a) A GU- or U-rich site sequence downstream contributes to efficiency of cleavage ...
... 3’ cleavage and polyadenylation: a conserved polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA) lies 10-30 nucleotides upstream from a poly(A) site a) A GU- or U-rich site sequence downstream contributes to efficiency of cleavage ...
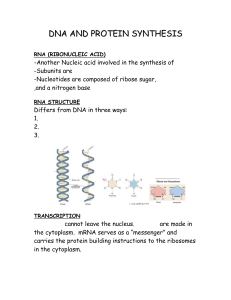
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
LEQ: How does RNA help to make a protein?
... The type of RNA that carriers the genetic information/message from DNA and coveys it to ribosomes where the information is translated into amino acid sequences ...
... The type of RNA that carriers the genetic information/message from DNA and coveys it to ribosomes where the information is translated into amino acid sequences ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
Worksheet 6 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
MTC19: transcription and gene expression 02/10/07
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
Glossary
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
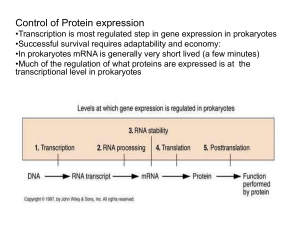
control of gene expression
... • Promotor sequence and how conserved it is (affects RNA polymerase binding) • -10 and –35 sequences and how conserved • Sigma factors • Whether or not a repressor protein is present • Enhancer/activator sequences • Once the transcript has been produced there is the opportunity for anti sense RNAs t ...
... • Promotor sequence and how conserved it is (affects RNA polymerase binding) • -10 and –35 sequences and how conserved • Sigma factors • Whether or not a repressor protein is present • Enhancer/activator sequences • Once the transcript has been produced there is the opportunity for anti sense RNAs t ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... Problem 7: Features of nuclear RNA processing Which of the following is not part of RNA processing in eukaryotes? A. splicing of exons B. reverse transcription C. addition of a 5' cap D. addition of a poly A tail E. intron removal ...
... Problem 7: Features of nuclear RNA processing Which of the following is not part of RNA processing in eukaryotes? A. splicing of exons B. reverse transcription C. addition of a 5' cap D. addition of a poly A tail E. intron removal ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.