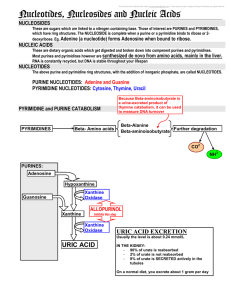
DNA Transcription / Translation
... B. RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter sequence. C. Transcription is always initiated at the start codon. D. The 3’ end of the RNA molecule is produced first. ...
... B. RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter sequence. C. Transcription is always initiated at the start codon. D. The 3’ end of the RNA molecule is produced first. ...
Building Proteins - Marblehead High School
... promoter region on the DNA Promoters – nucleotide sequence that signals the RNA polymerase to bind to them 2) RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands ...
... promoter region on the DNA Promoters – nucleotide sequence that signals the RNA polymerase to bind to them 2) RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands ...
Chapter 13
... - RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base Uracil instead of Thymine - Adenine will pair with Uracil (Uracil is a pyrimidine) ...
... - RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base Uracil instead of Thymine - Adenine will pair with Uracil (Uracil is a pyrimidine) ...
RNA
... • according to base-pairing rules the mRNA base triplets are called codons • shared by the simplest bacteria after the most complex plants and animals ...
... • according to base-pairing rules the mRNA base triplets are called codons • shared by the simplest bacteria after the most complex plants and animals ...
Part B - Modeling Transcription: How is RNA modified? Name:
... molecule that is initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to ...
... molecule that is initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
... another tRNA binds to next codon; continues until polypeptide / protein formed to stop codon; stop codon has no corresponding tRNA/amino acid / causes release of polypeptide; [8 max] ...
... another tRNA binds to next codon; continues until polypeptide / protein formed to stop codon; stop codon has no corresponding tRNA/amino acid / causes release of polypeptide; [8 max] ...
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA - Tenafly Public Schools
... AUG is called the start or initiation codon (codes for methionine, which is usually the first amino acid in a protein) The three stop or termination codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA ...
... AUG is called the start or initiation codon (codes for methionine, which is usually the first amino acid in a protein) The three stop or termination codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
BioIIch17notesRNAfilled.p pt
... -A site: holds tRNA carrying the next amino acid -E site: discharges tRNAs after they deliver the amino acid -act like a vise and holds the tRNA and mRNA close together and positions the new amino acid for addition to the growing protein ...
... -A site: holds tRNA carrying the next amino acid -E site: discharges tRNAs after they deliver the amino acid -act like a vise and holds the tRNA and mRNA close together and positions the new amino acid for addition to the growing protein ...
Review Topics for Final Part 1
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
Protein Synthesis
... 1 – Transcription is the transfer of the information from DNA to RNA Step 2- Translation is the process of reading the information on DNA and converting it into the amino acid sequences of the protein The specific sequence of genes (bases) on DNA directly determine the sequence of RNA, and there ...
... 1 – Transcription is the transfer of the information from DNA to RNA Step 2- Translation is the process of reading the information on DNA and converting it into the amino acid sequences of the protein The specific sequence of genes (bases) on DNA directly determine the sequence of RNA, and there ...
12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
SPECIFIKÁCIÓS TÁBLÁZAT Vegyszer neve Specifikáció Kiszerelés
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
Nucleic acid chemistry lecture 3
... Differentiate between different types of RNA List differences between DNA and RNA Mention free nucleotides of biological impotances ...
... Differentiate between different types of RNA List differences between DNA and RNA Mention free nucleotides of biological impotances ...
overview rna, transcription, translation
... itself to leave the nucleus, enzymes cut out and remove the introns. The remaining exons are spliced back together again by a different enzyme. This modified m RNA is what comes to the ribosome to be translated into polypeptides. ...
... itself to leave the nucleus, enzymes cut out and remove the introns. The remaining exons are spliced back together again by a different enzyme. This modified m RNA is what comes to the ribosome to be translated into polypeptides. ...
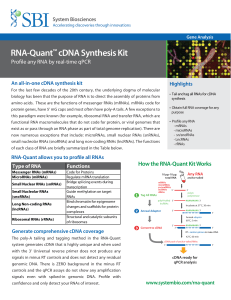
RNA-Quant™ cDNA Synthesis Kit
... biology has been that the purpose of RNA is to direct the assembly of proteins from amino acids. These are the functions of messenger RNAs (mRNAs). mRNAs code for ...
... biology has been that the purpose of RNA is to direct the assembly of proteins from amino acids. These are the functions of messenger RNAs (mRNAs). mRNAs code for ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.