Answers to the Study Guide for C12 Molecular Genetics Labeled
... Deletion – when a base is taken out which also changes the reading frame. These two things are considered frameshift mutations and can be considered point mutations. 13. When a specific kind of protein is not continually used by a cell, the gene for that protein is usually repressible. 14. The lac o ...
... Deletion – when a base is taken out which also changes the reading frame. These two things are considered frameshift mutations and can be considered point mutations. 13. When a specific kind of protein is not continually used by a cell, the gene for that protein is usually repressible. 14. The lac o ...
Central Dogma
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
DNA - Hermantown
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
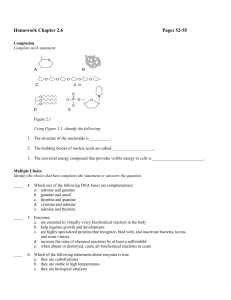
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... ____ 10. The nucleotide chains of DNA are held together by: a. carbon bonds b. hydrogen bonds c. ionic bonds d. nonpolar covalent bonds e. polar covalent bonds ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell ...
... ____ 10. The nucleotide chains of DNA are held together by: a. carbon bonds b. hydrogen bonds c. ionic bonds d. nonpolar covalent bonds e. polar covalent bonds ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... Who discovered/made a model of the double helix structure? What holds base pairs together? The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide seque ...
... Who discovered/made a model of the double helix structure? What holds base pairs together? The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide seque ...
Chap 3 - Workforce3One
... • RNA polymerase directs binding of ribonucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction • Movement of the polymerase along the DNA template causes the “bubble” of separated DNA strands to move also • As DNA transcription machinery passes, the two DNA strands reform the double helix ...
... • RNA polymerase directs binding of ribonucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction • Movement of the polymerase along the DNA template causes the “bubble” of separated DNA strands to move also • As DNA transcription machinery passes, the two DNA strands reform the double helix ...
Information Flow
... It is upstream from the gene. It is commonly rich in A and T bases: TATAAA A protein called sigma (σ) associates with the promoter and marks the site for RNA polymerase to associate. RNA polymerase polymerase, unwinds and reads the DNA as it synthesizes RNA. RNA synthesis is from 5’ to 3’. As mRNA i ...
... It is upstream from the gene. It is commonly rich in A and T bases: TATAAA A protein called sigma (σ) associates with the promoter and marks the site for RNA polymerase to associate. RNA polymerase polymerase, unwinds and reads the DNA as it synthesizes RNA. RNA synthesis is from 5’ to 3’. As mRNA i ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose ...
... nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose ...
Chapter 17: Gene Expression Gene Expression DNA houses all
... RNA Processing o pre-mRNA altered before leaving o 5’ cap on 5’ end when transcription starts Modified guanine added Helps protect from hydrolytic enzymes ‘Attach here’ signal for ribosome o Poly-A Tail on 3’ end right after released 50-250 adenines added Facilitates export from nucleus ...
... RNA Processing o pre-mRNA altered before leaving o 5’ cap on 5’ end when transcription starts Modified guanine added Helps protect from hydrolytic enzymes ‘Attach here’ signal for ribosome o Poly-A Tail on 3’ end right after released 50-250 adenines added Facilitates export from nucleus ...
Protein Synthesis
... ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
... ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
Unit Three “Cell Proliferation and Genetics”
... Categories of RNA • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – DNA serves as template for production of rRNA; formed in the nucleus of a cell; moves into the cytoplasm to bond with proteins; rRNA + proteins make up Ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – DNA serves as template for production of ...
... Categories of RNA • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – DNA serves as template for production of rRNA; formed in the nucleus of a cell; moves into the cytoplasm to bond with proteins; rRNA + proteins make up Ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – DNA serves as template for production of ...
Unfinished Material - Answer Key
... How does alternative splicing allow different proteins to be produced from the same gene? - When splicing occurs, selected exons are removed from the primary transcript along with the introns; however, the same primary RNA transcript can yield more than one kind of mature, processed mRNA, consisti ...
... How does alternative splicing allow different proteins to be produced from the same gene? - When splicing occurs, selected exons are removed from the primary transcript along with the introns; however, the same primary RNA transcript can yield more than one kind of mature, processed mRNA, consisti ...
LECT34 RNAproc
... PRO: mRNA contains no introns EU: mRNA contains intervening sequences (introns) that are removed during processing ...
... PRO: mRNA contains no introns EU: mRNA contains intervening sequences (introns) that are removed during processing ...
Pengaturan Ekspresi gen 1. Struktur gen prokaryot dan eukaryot
... alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mR ...
... alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mR ...
Chapter_17_answers
... o Initial site of RNA polymerase attachment o Includes start codon and several dozen nucleotide pairs “upstream” Transcription factors o Mediate binding of RNA polymerase and initiation of transcription o Transcription factors + RNA polymerase = transcription initiation complex TATA box o Transc ...
... o Initial site of RNA polymerase attachment o Includes start codon and several dozen nucleotide pairs “upstream” Transcription factors o Mediate binding of RNA polymerase and initiation of transcription o Transcription factors + RNA polymerase = transcription initiation complex TATA box o Transc ...
RNA
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...
Name__________________________ Date______ Period
... 7. Do some amino acids have more than one codon? Give an example. 8. Name the start codon. 9. Name the 3 stop codons. 10. Define translation. ...
... 7. Do some amino acids have more than one codon? Give an example. 8. Name the start codon. 9. Name the 3 stop codons. 10. Define translation. ...
Protein Synthesis
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
Dicer-Like
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
Central Dogma - Arkansas State University
... The Process of Transcription-2 • RNA synthesis continues (Elongation), only one DNA strand (template) is transcribed. • RNA nucleotides, complementary to bases on DNA strand, are connected to make mRNA • Termination: must be a stop sign, right? – In bacteria, hairpin loop followed by run of U’s in ...
... The Process of Transcription-2 • RNA synthesis continues (Elongation), only one DNA strand (template) is transcribed. • RNA nucleotides, complementary to bases on DNA strand, are connected to make mRNA • Termination: must be a stop sign, right? – In bacteria, hairpin loop followed by run of U’s in ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.