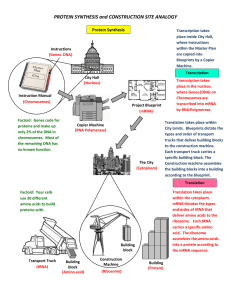
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
Protein Synthesis-Part Two - Halton District School Board
... • Each sequence of nucleotides has a correct reading frame, or grouping of codons. This means that knowing where to start transcription and translation is essential. • There is no mechanism for re-setting transcription or translation if they do not start at the right place. ...
... • Each sequence of nucleotides has a correct reading frame, or grouping of codons. This means that knowing where to start transcription and translation is essential. • There is no mechanism for re-setting transcription or translation if they do not start at the right place. ...
4.13 notes
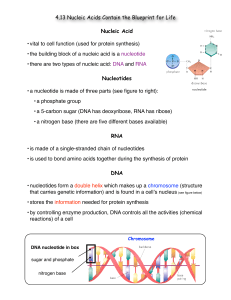
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... mRNA shortly after transcription begins - Protects the growing mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes - Helps small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end 2) Poly-A Tail = Sequence of about 50-100 adenine (A) nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits the ...
... mRNA shortly after transcription begins - Protects the growing mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes - Helps small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end 2) Poly-A Tail = Sequence of about 50-100 adenine (A) nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits the ...
From Gene to Protein
... 5ʹ′ end receives a modified nucleotide 5ʹ′ cap. The 3ʹ′ end gets a poly-A tail. ...
... 5ʹ′ end receives a modified nucleotide 5ʹ′ cap. The 3ʹ′ end gets a poly-A tail. ...
Slide 1
... Protein TRANSLATION from mRNA The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG ( ...
... Protein TRANSLATION from mRNA The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG ( ...
AP Protein synthesis
... RNA Polymerase II, and Transcription factors all combined and ready to start transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase II, and Transcription factors all combined and ready to start transcription. ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
Indezine Template
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
RNA interference 1. The central dogma 3. The RNAi mechanism
... 3. The RNAi mechanism RNA interference (RNAi) is an important biological mechanism in the regulation of gene expression. ...
... 3. The RNAi mechanism RNA interference (RNAi) is an important biological mechanism in the regulation of gene expression. ...
The four types of nucleotides in DNA are Adenine, Thymine
... Carrying information for protein synthesis to the cytoplasm Storing genetic information while the cell is replicating Carrying genetic information between cells Indicating the transcription start site ...
... Carrying information for protein synthesis to the cytoplasm Storing genetic information while the cell is replicating Carrying genetic information between cells Indicating the transcription start site ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
Document
... Further mechanism to mark Exon and Intron difference CBC: capping binding complex hnRNP: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, binding to introns SR: rich in serine and arginines, binding to exons ...
... Further mechanism to mark Exon and Intron difference CBC: capping binding complex hnRNP: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, binding to introns SR: rich in serine and arginines, binding to exons ...
258927_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 15. In this example, what occurs during translation? 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of ou ...
... 15. In this example, what occurs during translation? 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of ou ...
Name:
... 15. In this example, what occurs during translation? 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of ou ...
... 15. In this example, what occurs during translation? 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of ou ...
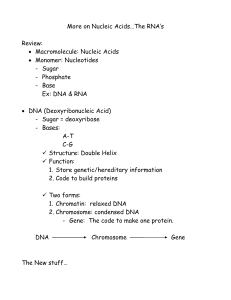
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... Structure: Double Helix Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... Structure: Double Helix Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.