Features on Nucleic Acid Sequences, Gene Features and Coding
... sequence, you must locate specific features on that sequence. The relationship of features to sequences via locations requires the use of more than one table. Simple examples include a promoter, or a repeat region, or a UTR on an NA Sequence. In each case, there is a sequence, there is a feature loc ...
... sequence, you must locate specific features on that sequence. The relationship of features to sequences via locations requires the use of more than one table. Simple examples include a promoter, or a repeat region, or a UTR on an NA Sequence. In each case, there is a sequence, there is a feature loc ...
dna - Kowenscience.com
... • Unlike a newly formed DNA strand, the RNA strand does not remain hydrogenbonded to the DNA template strand. Instead, just behind the region where the ribonucleotides are being added, the RNA chain is displaced and the DNA helix re-forms. • Thus, the RNA molecules produced by transcription are rel ...
... • Unlike a newly formed DNA strand, the RNA strand does not remain hydrogenbonded to the DNA template strand. Instead, just behind the region where the ribonucleotides are being added, the RNA chain is displaced and the DNA helix re-forms. • Thus, the RNA molecules produced by transcription are rel ...
Biology - Edexcel
... answer began to emerge. In the early 1980s, Tijan discovered a protein called SP1 in human cells, and Rockefeller’s Robert Roeder found a protein called TFIIIA in frogs’ eggs. Both these proteins helped RNA polymerase but they could also activate specific genes. Now there was a plausible model for g ...
... answer began to emerge. In the early 1980s, Tijan discovered a protein called SP1 in human cells, and Rockefeller’s Robert Roeder found a protein called TFIIIA in frogs’ eggs. Both these proteins helped RNA polymerase but they could also activate specific genes. Now there was a plausible model for g ...
S2DTimes - Science4Kids.com
... the mutant gene. By correcting the splicing error, a normal mRNA was made from a faulty pre-mRNA transcript. In addition, Krainer and Cartegni used their technology on a defective form of the SM2gene, which is associated with the neurodegenerative disease spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The designer ...
... the mutant gene. By correcting the splicing error, a normal mRNA was made from a faulty pre-mRNA transcript. In addition, Krainer and Cartegni used their technology on a defective form of the SM2gene, which is associated with the neurodegenerative disease spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The designer ...
Biol 101 Study Guide Exam 5
... E) uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand. 49) If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be 49) ______ A) CGGTAC. B) GCCATG. C) GCCAUC. D) GCCTAG. E) TAACGT. 50) The copying mechanism of DNA is most like 50) ______ A) using a photograph ...
... E) uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand. 49) If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be 49) ______ A) CGGTAC. B) GCCATG. C) GCCAUC. D) GCCTAG. E) TAACGT. 50) The copying mechanism of DNA is most like 50) ______ A) using a photograph ...
C2006/F2402 `10
... Explanation for 7A-1 & A-2 (FYI – no explanation required for this part): The nucleolus is inside the nucleus. The nucleolus has no membrane, but the nuclear envelope surrounding the nucleus (including the nucleolus) consists of two bilayers. Material passes in and out of the nucleus through the nuc ...
... Explanation for 7A-1 & A-2 (FYI – no explanation required for this part): The nucleolus is inside the nucleus. The nucleolus has no membrane, but the nuclear envelope surrounding the nucleus (including the nucleolus) consists of two bilayers. Material passes in and out of the nucleus through the nuc ...
2008 LASKER AWARDS for MEDICAL RESEARCH
... extra copies of cells ordinarily produced only at early stages. These observations suggested that normal lin-4 allows immature worms to advance past a particular developmental stage; animals with the defective version cannot overcome that hurdle. Ambros discovered that worms lacking a different ...
... extra copies of cells ordinarily produced only at early stages. These observations suggested that normal lin-4 allows immature worms to advance past a particular developmental stage; animals with the defective version cannot overcome that hurdle. Ambros discovered that worms lacking a different ...
Some Biology that Computer Scientists Need for
... • Only certain genes are “turned on” at any particular time. • When a gene is transcribed (copied to mRNA), it is said to be expressed. • The mRNA in a cell can be isolated. Its contents give a snapshot of the genes currently being expressed. • Correlating gene expressions with conditions gives hint ...
... • Only certain genes are “turned on” at any particular time. • When a gene is transcribed (copied to mRNA), it is said to be expressed. • The mRNA in a cell can be isolated. Its contents give a snapshot of the genes currently being expressed. • Correlating gene expressions with conditions gives hint ...
Chapter 27
... 4. Triploid: having 1 extra of every homologous pair (69) chromosomes) 5. Polyploidy- sometimes all 22 chromosomal pairs fail to separate. The resulting 2n gamete fuses with the normal n gamete, producing a 3n zygote. This is common in plants but rare in humans ...
... 4. Triploid: having 1 extra of every homologous pair (69) chromosomes) 5. Polyploidy- sometimes all 22 chromosomal pairs fail to separate. The resulting 2n gamete fuses with the normal n gamete, producing a 3n zygote. This is common in plants but rare in humans ...
Protein Synthesis 2
... RF-1 = recognizes UAA and UAG RF-2 = recognizes UAA and UGA RF-3 = G-protein; helps trigger hydrolysis (by the 23S rRNA) RRF = liberates ribosome/release factors ...
... RF-1 = recognizes UAA and UAG RF-2 = recognizes UAA and UGA RF-3 = G-protein; helps trigger hydrolysis (by the 23S rRNA) RRF = liberates ribosome/release factors ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... complementary bases of triplet anticodon of tRNA 6. tRNA moves sequentially through the three binding sites from A, to P, to E site 7. Growing polypeptide chain exits the ribosome through a tunnel in the large subunit ...
... complementary bases of triplet anticodon of tRNA 6. tRNA moves sequentially through the three binding sites from A, to P, to E site 7. Growing polypeptide chain exits the ribosome through a tunnel in the large subunit ...
Exam #3 Part of Ch. 13, Ch.14-17 and Ch. 20 Supplement to notes
... RNA polymerase 5’ to 3’ direction-no need of primer can start from scratch, promoter region, terminator region, transcription unit, transcription factors, transcription initiation complex, TATA box, pre-mRNA Fig. 17.7 the stages of transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination Fig. 17.8 The ...
... RNA polymerase 5’ to 3’ direction-no need of primer can start from scratch, promoter region, terminator region, transcription unit, transcription factors, transcription initiation complex, TATA box, pre-mRNA Fig. 17.7 the stages of transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination Fig. 17.8 The ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 18 8thed
... A given gene may have multiple enhancers, each active at a different time or in a different cell type or location in the organism. Interactions between enhancers and specific transcription factors called activators or repressors are important in controlling gene expression. An activator is a p ...
... A given gene may have multiple enhancers, each active at a different time or in a different cell type or location in the organism. Interactions between enhancers and specific transcription factors called activators or repressors are important in controlling gene expression. An activator is a p ...
bio 30 ch 18 molecular genetics review
... 2. DNA replication copies the entire DNA code. Transcription makes a short section of the DNA. 3. DNA nucleotides include thymines, while RNA contains uracil 6. If mRNA can not be produced, proteins can not be synthesized. Functional proteins serve a variety of essential body functions and include h ...
... 2. DNA replication copies the entire DNA code. Transcription makes a short section of the DNA. 3. DNA nucleotides include thymines, while RNA contains uracil 6. If mRNA can not be produced, proteins can not be synthesized. Functional proteins serve a variety of essential body functions and include h ...
Image PowerPoint
... spark. Condensers cooled any gases, causing molecular products to collect in the water. From this water, samples were taken over the next week and analyzed. Among the organic molecules formed were amino acids, basic building blocks of protein. Subsequent follow-up trials, by many other biologists, u ...
... spark. Condensers cooled any gases, causing molecular products to collect in the water. From this water, samples were taken over the next week and analyzed. Among the organic molecules formed were amino acids, basic building blocks of protein. Subsequent follow-up trials, by many other biologists, u ...
chapter 19 the organization and control of eukaryotic
... By using regulatory mechanisms that operate after transcription, a cell can rapidly fine-tune gene expression in response to environmental changes without altering its transcriptional patterns. RNA processing in the nucleus and the export of mRNA to the cytoplasm provide opportunities for gene r ...
... By using regulatory mechanisms that operate after transcription, a cell can rapidly fine-tune gene expression in response to environmental changes without altering its transcriptional patterns. RNA processing in the nucleus and the export of mRNA to the cytoplasm provide opportunities for gene r ...
Molecular Genetics
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Associates with proteins to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm Transfer RNA (tRNA) Smaller segments of RNA nucleotides that transport amino acids to the ribosome ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Associates with proteins to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm Transfer RNA (tRNA) Smaller segments of RNA nucleotides that transport amino acids to the ribosome ...
Reverse Transcriptase and cDNA Synthesis
... purified enzyme, it was shown that this enzyme also catalyzes DNA synthesis using DNA as a template. Retroviruses contain a dimeric RNA genome in each infectious virion and produce viral DNA by reverse transcription. In addition to reverse transcriptase activity, ribonuclease H activity as well as D ...
... purified enzyme, it was shown that this enzyme also catalyzes DNA synthesis using DNA as a template. Retroviruses contain a dimeric RNA genome in each infectious virion and produce viral DNA by reverse transcription. In addition to reverse transcriptase activity, ribonuclease H activity as well as D ...
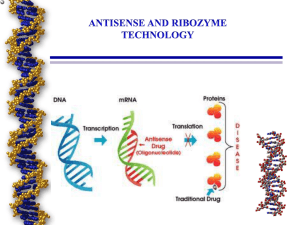
Gene Therapy and Transgenic Animals
... Antisense Oligonucleotides are unmodified or chemically modified ssDNA, RNA or their analogs. They are 13-25 nucleotides long and are specifically designed to hybridize to the corresponding RNA by Watson-Crick binding ...
... Antisense Oligonucleotides are unmodified or chemically modified ssDNA, RNA or their analogs. They are 13-25 nucleotides long and are specifically designed to hybridize to the corresponding RNA by Watson-Crick binding ...
An artifact in studies of gene regulation using β
... level. To test this hypothesis, semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) experiments were performed as described previously [11] using template RNA prepared from E. coli BL21(DE3) either with or without these plasmids. Results show that the expression of lacZ RNA is ...
... level. To test this hypothesis, semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) experiments were performed as described previously [11] using template RNA prepared from E. coli BL21(DE3) either with or without these plasmids. Results show that the expression of lacZ RNA is ...
Fe2+ is absorbed from the lumen of the gut (in the small intestine) by
... part of 16a). The part of 16a between the 3’ end of 16 and the 3’end of 16a is part of an intron in one case and an exon in another. It all depends on where the 5’ (donor) end of intron 16 is – at the end of exon 16 or the end of exon 16a. The 3’ (acceptor) end of the intron 16 is always the same – ...
... part of 16a). The part of 16a between the 3’ end of 16 and the 3’end of 16a is part of an intron in one case and an exon in another. It all depends on where the 5’ (donor) end of intron 16 is – at the end of exon 16 or the end of exon 16a. The 3’ (acceptor) end of the intron 16 is always the same – ...
The Gene Concept - bioinf.uni
... What is a gene? “I can’t tell but I recognize a gene when I see one.” a biologist “Something is a gene when a biologist says it is one.” a bioinformatician “A gene is a database entry with an Ensembl gene ID.” a computer scientist “A gene is what Wikipedia says it is.” a student “A gene is a locata ...
... What is a gene? “I can’t tell but I recognize a gene when I see one.” a biologist “Something is a gene when a biologist says it is one.” a bioinformatician “A gene is a database entry with an Ensembl gene ID.” a computer scientist “A gene is what Wikipedia says it is.” a student “A gene is a locata ...
Lesson Overview
... You can think of an RNA molecule, as a disposable copy of a segment of DNA, a working copy of a single gene. RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis only. RNA controls the assembly of amino acids into proteins. ...
... You can think of an RNA molecule, as a disposable copy of a segment of DNA, a working copy of a single gene. RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis only. RNA controls the assembly of amino acids into proteins. ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.