Classification Intro - LaPazColegio2014-2015
... Flatworms are bilaterally symmetrical and belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes Many species are parasites, organisms that live in or on the body of another organism Non-parasitic, free-living flatworms inhabit aquatic, marine, and moist terrestrial habitats Flatworms can reproduce both sexuall ...
... Flatworms are bilaterally symmetrical and belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes Many species are parasites, organisms that live in or on the body of another organism Non-parasitic, free-living flatworms inhabit aquatic, marine, and moist terrestrial habitats Flatworms can reproduce both sexuall ...
Comparative Anatomy: Animal Body Systems: RESPIRATORY
... ◦ If require diffusion they must be moist. ...
... ◦ If require diffusion they must be moist. ...
Reynolds School District
... Animals are multicellular heterotrophic organisms that lack cell walls. Most members of the animal kingdom share other important characteristics, including: – sexual reproduction – movement Vertebrates have a backbone. Invertebrates do not have a backbone. – Invertebrates account for more than 95 pe ...
... Animals are multicellular heterotrophic organisms that lack cell walls. Most members of the animal kingdom share other important characteristics, including: – sexual reproduction – movement Vertebrates have a backbone. Invertebrates do not have a backbone. – Invertebrates account for more than 95 pe ...
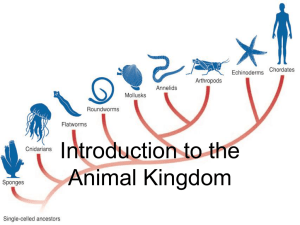
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... Animal Evolution • Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
... Animal Evolution • Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
Kingdom Animalia
... evolution of supporting organ systems and a means for distributing materials • The body cavity – a space surrounded by ...
... evolution of supporting organ systems and a means for distributing materials • The body cavity – a space surrounded by ...
What is the difference between Vertebrates and Invertebrates?
... either bony or cartilaginous. Among members of the Chordates, they are the largest group including Birds, Mammals, Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles. Their spinal cord runs along the body between cranial and caudal regions with a hollow tube of nervous tissue called spinal cord. Vertebrates have a bila ...
... either bony or cartilaginous. Among members of the Chordates, they are the largest group including Birds, Mammals, Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles. Their spinal cord runs along the body between cranial and caudal regions with a hollow tube of nervous tissue called spinal cord. Vertebrates have a bila ...
animals, invertebrates
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites (named for the Greek god Hermes and goddess Aphrodite), meaning that each individual has both male and female sexual reproductive organs. Almost all sponges exhibit their hermaphroditism in sequence, functioning first as one sex and then as the other. Gametes (either ...
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites (named for the Greek god Hermes and goddess Aphrodite), meaning that each individual has both male and female sexual reproductive organs. Almost all sponges exhibit their hermaphroditism in sequence, functioning first as one sex and then as the other. Gametes (either ...
Invertebrate Notes
... movement and give more area for gas exchange. Polychaetes often live commensally with sponges, mollusks, echinoderms, and crustaceans. Sexes are separate with external fertilization. ...
... movement and give more area for gas exchange. Polychaetes often live commensally with sponges, mollusks, echinoderms, and crustaceans. Sexes are separate with external fertilization. ...
Zoology – Arthropod Unit
... Reproduction Sensory/Motor response Any special features unique to the phylum 3. Identify derived characteristics that contribute to the phylogeny of phylum Arthropoda ...
... Reproduction Sensory/Motor response Any special features unique to the phylum 3. Identify derived characteristics that contribute to the phylogeny of phylum Arthropoda ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Kingdom Animalia The animal kingdom is divided into two realms – vertebrates (animals that have backbones) and invertebrates (animals that do not have a backbone). Each of these groups are comprised of different phylums based on similarities and differences. ...
... Kingdom Animalia The animal kingdom is divided into two realms – vertebrates (animals that have backbones) and invertebrates (animals that do not have a backbone). Each of these groups are comprised of different phylums based on similarities and differences. ...
document
... sheds its old cuticle and secretes a new, larger one have a complete digestive tract and use the fluid in their pseudocoelom to transport nutrients since they lack a circulatory system engage in sexual reproduction. play a major role in decomposition and nutrient recycling. The soil nematode, C. ...
... sheds its old cuticle and secretes a new, larger one have a complete digestive tract and use the fluid in their pseudocoelom to transport nutrients since they lack a circulatory system engage in sexual reproduction. play a major role in decomposition and nutrient recycling. The soil nematode, C. ...
PHYLUM ANNELIDA The Segmented Worms. There are
... 13. The segmented worms are hermaphroditic or with separate sexes. Fertilization is external and many produce trochophore larvae. ...
... 13. The segmented worms are hermaphroditic or with separate sexes. Fertilization is external and many produce trochophore larvae. ...
Five Kingdoms of Living Things Created by Stella Thalluri 2014 www.beaconmedia.com.au
... a. the act of placing objects in groups based on characteristics 3. Scientists use both of these to organize living organisms. 4. The largest group living things are placed in is a kingdom (there are 5). 5. The smallest classification group is the species. The second smallest is the genus. ...
... a. the act of placing objects in groups based on characteristics 3. Scientists use both of these to organize living organisms. 4. The largest group living things are placed in is a kingdom (there are 5). 5. The smallest classification group is the species. The second smallest is the genus. ...
7D Grade Descriptors File
... Identify similarities and differences between organisms of the same species e.g. Poodle and Alsatian Classify organisms into plants and animals Recognize that a vertebrate has a backbone and an invertebrate does not. Recognize that animals are not just mammals. Level 4 Recognize that invertebrates a ...
... Identify similarities and differences between organisms of the same species e.g. Poodle and Alsatian Classify organisms into plants and animals Recognize that a vertebrate has a backbone and an invertebrate does not. Recognize that animals are not just mammals. Level 4 Recognize that invertebrates a ...
Mollusks and Echinoderm PowerPoint
... • A characteristic unique to echinoderms • Allows them to move, exchange CO2 and O2, capture food, and release wastes • It is a network of water-filled canals with thousands of tube feet connected to it. • Tube feet—hollow, thin walled tubes that ends in a suction cup. – As pressure in the tube feet ...
... • A characteristic unique to echinoderms • Allows them to move, exchange CO2 and O2, capture food, and release wastes • It is a network of water-filled canals with thousands of tube feet connected to it. • Tube feet—hollow, thin walled tubes that ends in a suction cup. – As pressure in the tube feet ...
SUB: BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII ANIMAL CLASSIFICATION
... - These are small, soft, flattened, unsegmented worms, without body cavity - Alimentary canal has only one opening, the mouth - Most of them live as parasites, few are free, living in fresh water or sea - Examples : Parasites --- Liverfluke, Tapeworm ...
... - These are small, soft, flattened, unsegmented worms, without body cavity - Alimentary canal has only one opening, the mouth - Most of them live as parasites, few are free, living in fresh water or sea - Examples : Parasites --- Liverfluke, Tapeworm ...
biology final exam 2007
... 35. Which type of symmetry does each of the following animals display? ...
... 35. Which type of symmetry does each of the following animals display? ...
The Animal Kingdom PowerPoint
... –Scorpions are found in tropical areas and hunt insects and spiders. –Ticks are external parasites that feed on the blood of a host. Some transmit Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. –Mites are found mostly in dust and are ...
... –Scorpions are found in tropical areas and hunt insects and spiders. –Ticks are external parasites that feed on the blood of a host. Some transmit Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. –Mites are found mostly in dust and are ...
Classifying Animals Part 2 Vertebrates
... 6.3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals). ...
... 6.3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals). ...
Review_Animals
... Diploblasts vs. triploblasts. Which have a mesoderm? Which group contains animals with bilateral symmetry? With cephalization? Triploblastic animals can be further categorized based on whether they are acoelomates, pseudocoelomates, or true coelomates. What is the importance of a coelom? Give ex ...
... Diploblasts vs. triploblasts. Which have a mesoderm? Which group contains animals with bilateral symmetry? With cephalization? Triploblastic animals can be further categorized based on whether they are acoelomates, pseudocoelomates, or true coelomates. What is the importance of a coelom? Give ex ...
Unit 4 : Simple Animals
... modified into a sucker with which it forms a temporary attachment to the shark. When the shark feeds, the remora picks up scraps. The shark makes no attempt to prey on the remora. ...
... modified into a sucker with which it forms a temporary attachment to the shark. When the shark feeds, the remora picks up scraps. The shark makes no attempt to prey on the remora. ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... a. The body of a mollusk is soft and does not have bones, but some mollusks have a hard outer shell that protects them from being eaten. b. This phylum includes snails, slugs, clams, and squid that get oxygen by using gills or absorb oxygen through their skin. Worms a. Flat worms are very flat and t ...
... a. The body of a mollusk is soft and does not have bones, but some mollusks have a hard outer shell that protects them from being eaten. b. This phylum includes snails, slugs, clams, and squid that get oxygen by using gills or absorb oxygen through their skin. Worms a. Flat worms are very flat and t ...
Simple Invertebrates
... • Special cells, collar cells, filter food particles and microorganisms from the water • The rest of the water flows into a central cavity and out a hole in the top of the sponge – the osculum ...
... • Special cells, collar cells, filter food particles and microorganisms from the water • The rest of the water flows into a central cavity and out a hole in the top of the sponge – the osculum ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.