AMBASSADOR SCHOOL DUBAI, UAE Sample paper SA – 1 2016
... eg. tapeworm IV. Phylum Nematoda – i. round unsegmented , elongated bodies. ii. no circulatory system. eg. Pinworm, roundworm V. Phylum Annelida i. Round, segmented bodies. ii. found in fresh and salt water, as well as damp land. eg earthworm, leech VI. Phylum Mollusca i. soft bodied animals. ii. fo ...
... eg. tapeworm IV. Phylum Nematoda – i. round unsegmented , elongated bodies. ii. no circulatory system. eg. Pinworm, roundworm V. Phylum Annelida i. Round, segmented bodies. ii. found in fresh and salt water, as well as damp land. eg earthworm, leech VI. Phylum Mollusca i. soft bodied animals. ii. fo ...
Sci_Ch_1_Notes_Lessons_2
... groups organisms are classified. After being classified into a kingdom, organisms are then put into smaller and smaller subgroups. The narrowest group is called species. ...
... groups organisms are classified. After being classified into a kingdom, organisms are then put into smaller and smaller subgroups. The narrowest group is called species. ...
Animals
... (hollow ball of cells) Blastopore – single opening to outside formed as blastula folds inward Protostome –organism in which blastopore becomes mouth Deuterostome –blastopore becomes anus ...
... (hollow ball of cells) Blastopore – single opening to outside formed as blastula folds inward Protostome –organism in which blastopore becomes mouth Deuterostome –blastopore becomes anus ...
Animalia NOTES
... Produced by body cells from metabolism of PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Removed by EXCRETORY SYSTEM AMMONIA-Most TOXIC; requires most water to dilute Excreted by aquatic organisms directly into water via gills or other organs UREA- Less toxic than ammonia; requires less water to dilute excreted by amphib ...
... Produced by body cells from metabolism of PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Removed by EXCRETORY SYSTEM AMMONIA-Most TOXIC; requires most water to dilute Excreted by aquatic organisms directly into water via gills or other organs UREA- Less toxic than ammonia; requires less water to dilute excreted by amphib ...
Animalia NOTES
... Produced by body cells from metabolism of PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Removed by EXCRETORY SYSTEM AMMONIA-Most TOXIC; requires most water to dilute Excreted by aquatic organisms directly into water via gills or other organs UREA- Less toxic than ammonia; requires less water to dilute excreted by amphib ...
... Produced by body cells from metabolism of PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Removed by EXCRETORY SYSTEM AMMONIA-Most TOXIC; requires most water to dilute Excreted by aquatic organisms directly into water via gills or other organs UREA- Less toxic than ammonia; requires less water to dilute excreted by amphib ...
Invertebrates and Vertebrates
... 9. Reproduction and development • Amphibians and some fish – larva hatches in water, develops into an adult organism • Reptiles, birds and mammals do not have larval stage • Embryo is protected by membranes • Eggs of reptiles, birds and some mammals have a shell ...
... 9. Reproduction and development • Amphibians and some fish – larva hatches in water, develops into an adult organism • Reptiles, birds and mammals do not have larval stage • Embryo is protected by membranes • Eggs of reptiles, birds and some mammals have a shell ...
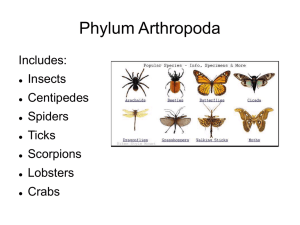
Arthropods are the largest grouping of animals all of
... Phylum Arthropoda includes animals that have been successful in colonizing terrestrial, aquatic, and aerialhabitats. This phylum is further classified into five subphyla: Trilobitomorpha (trilobites, all extinct), Hexapoda (insects and relatives), Myriapoda (millipedes, centipedes, and relatives), C ...
... Phylum Arthropoda includes animals that have been successful in colonizing terrestrial, aquatic, and aerialhabitats. This phylum is further classified into five subphyla: Trilobitomorpha (trilobites, all extinct), Hexapoda (insects and relatives), Myriapoda (millipedes, centipedes, and relatives), C ...
Invertebrates - Hartsville High School
... Marine worms • Bilateral symmetry- left and right are mirror ...
... Marine worms • Bilateral symmetry- left and right are mirror ...
Invertebrates - Cloudfront.net
... environment • The more surface area that is exposed to the environment, the greater the amount of gas exchange that can occur • In addition, gases diffuse most efficiently across a thin, moist membrane • Given these principles, all respiratory systems share two basic features: – Respiratory organs h ...
... environment • The more surface area that is exposed to the environment, the greater the amount of gas exchange that can occur • In addition, gases diffuse most efficiently across a thin, moist membrane • Given these principles, all respiratory systems share two basic features: – Respiratory organs h ...
Trainer 1 File
... Sponges: phylum Porifera What are tissues? There are many cell types, but they function essentially independently. An isolated cell is still functional. ...
... Sponges: phylum Porifera What are tissues? There are many cell types, but they function essentially independently. An isolated cell is still functional. ...
Introduction to Animals Notes
... •Small, transparent, wormlike or spherical animals •Bilaterally symmetrical •Pseudocoelomates •Almost all live in fresh water •Example: rotifers •About 1,750 species •Phylum Annelida •Bilaterally symmetrical •Serially segmented worms •Protostomes •Examples: earthworms, leeches •About 15,000 species ...
... •Small, transparent, wormlike or spherical animals •Bilaterally symmetrical •Pseudocoelomates •Almost all live in fresh water •Example: rotifers •About 1,750 species •Phylum Annelida •Bilaterally symmetrical •Serially segmented worms •Protostomes •Examples: earthworms, leeches •About 15,000 species ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... C Their body plan has two main tissue layers. D They have a digestive system with two openings. ____ 20 Based on embryological evidence, echinoderms are most closely related to A rotifers. B annelids. C chordates. D arthropods. ____ 21 Earthworms are in the phylum A Annelida. B Nematoda. C Arthropod ...
... C Their body plan has two main tissue layers. D They have a digestive system with two openings. ____ 20 Based on embryological evidence, echinoderms are most closely related to A rotifers. B annelids. C chordates. D arthropods. ____ 21 Earthworms are in the phylum A Annelida. B Nematoda. C Arthropod ...
ch. 23 practice exam
... An animal whose body parts are arranged around a central point, like spokes around the hub of a wheel, has ____________________ symmetry. A(n) ____________________ ____________________ is a term used to describe an animal’s shape, symmetry, and internal organization. Animals with ___________________ ...
... An animal whose body parts are arranged around a central point, like spokes around the hub of a wheel, has ____________________ symmetry. A(n) ____________________ ____________________ is a term used to describe an animal’s shape, symmetry, and internal organization. Animals with ___________________ ...
ZOOLOGY - Benchmark 2 Study Guide 1. Approximately what
... 68. Annelids are ____________________ worms found in _________________. 69. External segments correspond to internal segments called _______________. 70. Give two ways that segmentation is an advantage for an organism. 71. Annelids have a tube within a tube body plan called the ___________________ w ...
... 68. Annelids are ____________________ worms found in _________________. 69. External segments correspond to internal segments called _______________. 70. Give two ways that segmentation is an advantage for an organism. 71. Annelids have a tube within a tube body plan called the ___________________ w ...
Invertebrate Notes - Parkway C-2
... About 97% of all animals are invertebrates. Invertebrates are animals which do not have a backbone. There are nine phyla of invertebrates: Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Rotifera, Mollusca, Annelida, Arthropoda, & Echinodermata. ...
... About 97% of all animals are invertebrates. Invertebrates are animals which do not have a backbone. There are nine phyla of invertebrates: Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Rotifera, Mollusca, Annelida, Arthropoda, & Echinodermata. ...
BIOL212StudyGuide2MAY2012
... Ecdysozoans are the most species rich animal group. - Ecdysis – molting process of emerging from an old exoskeleton. Echinoderms and chordates are deuterostomes. So what is a protostome? What is a deuterostome? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryo ...
... Ecdysozoans are the most species rich animal group. - Ecdysis – molting process of emerging from an old exoskeleton. Echinoderms and chordates are deuterostomes. So what is a protostome? What is a deuterostome? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryo ...
Introduction to animals
... but the eggs develop without being fertilized! ● New offspring will be all female ...
... but the eggs develop without being fertilized! ● New offspring will be all female ...
CH32IntroCharacteristicsPart2
... • An animal's skeleton provides a framework that supports the animal's body and is vital to an animal's movement. • Many soft-bodied invertebrates, such as jellyfish, have a hydrostatic skeleton, which is a water-filled cavity that is under pressure. (Balloon) • An exoskeleton is a rigid external sk ...
... • An animal's skeleton provides a framework that supports the animal's body and is vital to an animal's movement. • Many soft-bodied invertebrates, such as jellyfish, have a hydrostatic skeleton, which is a water-filled cavity that is under pressure. (Balloon) • An exoskeleton is a rigid external sk ...
Chapter 23
... 19. List three structural characteristics typical of flatworms. a. Triplobastic—three cell layers b. no coelom c. bilaterally symmetrical d. one opening to the digestive cavity e. flat body form f. many are parasites—Cestoda and Trematoda 20. Describe the life cycle of a fluke. The adult form of the ...
... 19. List three structural characteristics typical of flatworms. a. Triplobastic—three cell layers b. no coelom c. bilaterally symmetrical d. one opening to the digestive cavity e. flat body form f. many are parasites—Cestoda and Trematoda 20. Describe the life cycle of a fluke. The adult form of the ...
Chapter 6 – Vertebrates ()
... 1. They are a subphylum under the Phylum Chordata. This means they possess a dorsal nerve cord, notochord, and gill slits at the embryo stage. 2. Vertebrates are the most numerous (95%) and most complex of all chordates. 3. Possess a backbone which replaces the notochord and protects the nerve c ...
... 1. They are a subphylum under the Phylum Chordata. This means they possess a dorsal nerve cord, notochord, and gill slits at the embryo stage. 2. Vertebrates are the most numerous (95%) and most complex of all chordates. 3. Possess a backbone which replaces the notochord and protects the nerve c ...
1 Animals
... Dogs are truly amazing. They also give us their company and affection. A dog is truly man’s best friend! ...
... Dogs are truly amazing. They also give us their company and affection. A dog is truly man’s best friend! ...
Animal Kingdom Test Study Guide
... 8. Contrast the following characteristics and give examples of animals that have each adaptation. Closed Circulatory System Open Circulatory System Definition System in blood is contained within a System in which blood is not always network of blood vessels contained within a network of blood vesse ...
... 8. Contrast the following characteristics and give examples of animals that have each adaptation. Closed Circulatory System Open Circulatory System Definition System in blood is contained within a System in which blood is not always network of blood vessels contained within a network of blood vesse ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.