Evolution of bilateral symmetry
... Pseudocoelomates: Nematoda and Rotifera • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
... Pseudocoelomates: Nematoda and Rotifera • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
Phylum Arthropoda
... Adaptations of a Predator Shell filled with chambers of air for buoyancy Shells lost or small & internal = less weight Closed circulatory system = faster circulation for better delivery of oxygen to muscles Well developed eyes and brain = must be smarter than the food Foot converted to tenta ...
... Adaptations of a Predator Shell filled with chambers of air for buoyancy Shells lost or small & internal = less weight Closed circulatory system = faster circulation for better delivery of oxygen to muscles Well developed eyes and brain = must be smarter than the food Foot converted to tenta ...
Which of the following did NOT occur during the Cambrian Explosion?
... which is the liquid solution that surrounds the cells of an animal’s body. Explain why such a distinction is possible for animals with a closed circulatory system but not for animals with an open circulatory system. ...
... which is the liquid solution that surrounds the cells of an animal’s body. Explain why such a distinction is possible for animals with a closed circulatory system but not for animals with an open circulatory system. ...
organisms - Math/Science Nucleus
... Students have previously learned about large animals, and now we turn their attention to the smaller animals, or those called invertebrates. The animal kingdom is divided into two major groups according to the presence or absence of a spinal column (backbone). Animals with a backbone are called vert ...
... Students have previously learned about large animals, and now we turn their attention to the smaller animals, or those called invertebrates. The animal kingdom is divided into two major groups according to the presence or absence of a spinal column (backbone). Animals with a backbone are called vert ...
3.4 ANIMALS, Invertebrates
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites (named for the Greek god Hermes and goddess Aphrodite), meaning that each individual has both male and female sexual reproductive organs. Almost all sponges exhibit their hermaphroditism in sequence, functioning first as one sex and then as the other. Gametes (either ...
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites (named for the Greek god Hermes and goddess Aphrodite), meaning that each individual has both male and female sexual reproductive organs. Almost all sponges exhibit their hermaphroditism in sequence, functioning first as one sex and then as the other. Gametes (either ...
Energy Warm Ups 10 Weeks - 6th grade science weebly
... which water flows through a central cavity where I also eliminate waste. ___________ I have a soft body with a thick muscular foot for movement. ___________ I have a long tube-like body. ...
... which water flows through a central cavity where I also eliminate waste. ___________ I have a soft body with a thick muscular foot for movement. ___________ I have a long tube-like body. ...
Earthworms and the Environment
... Introduces more air into the soil. When they die they further increase the amount of organic matter ...
... Introduces more air into the soil. When they die they further increase the amount of organic matter ...
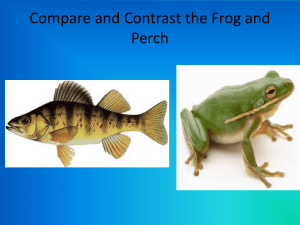
Bio II Chapter 32 - Marissa Junior/Senior High School
... All except fishes spend part or all of their life on land In order to adapt to life on land: Support of the body Conservation of water ...
... All except fishes spend part or all of their life on land In order to adapt to life on land: Support of the body Conservation of water ...
Introduction to Animals
... • Some animals like sponges and earthworms are hermaphrodites producing both eggs and sperm • Hermaphrodites may exchange sperm and NOT fertilize their own eggs ...
... • Some animals like sponges and earthworms are hermaphrodites producing both eggs and sperm • Hermaphrodites may exchange sperm and NOT fertilize their own eggs ...
Worms
... Roundworms have a digestive system that is like a tube, open at both ends. A one-way digestive system is efficient. Its like a conveyer belt; start where food enters, nutrients are absorbed, then remaining is wasted. This type of digestive system enables animal’s body to absorb a large amount of ...
... Roundworms have a digestive system that is like a tube, open at both ends. A one-way digestive system is efficient. Its like a conveyer belt; start where food enters, nutrients are absorbed, then remaining is wasted. This type of digestive system enables animal’s body to absorb a large amount of ...
31.1 Animals are multicellular heterotrophs without cell walls. Some
... Bivalvia (bivalves), and class Cephalopoda (octopuses, squids, and nautiluses). (pp. ...
... Bivalvia (bivalves), and class Cephalopoda (octopuses, squids, and nautiluses). (pp. ...
Introduction to Animals
... During gastrulation, an indentation occurs. A multi-layer embryo is formed with 3 germ layers Blastopore – opening of indentation ...
... During gastrulation, an indentation occurs. A multi-layer embryo is formed with 3 germ layers Blastopore – opening of indentation ...
Invertebrate Phylae
... All cells require a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients and the cells must remove the wastes. Simpler animals do this by diffusion More complex animals use one or more hearts and an open or closed circulatory system. ...
... All cells require a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients and the cells must remove the wastes. Simpler animals do this by diffusion More complex animals use one or more hearts and an open or closed circulatory system. ...
notes
... or female), have internal fertilization (inside the body); shed their exoskeletons as they grow (molting) More species of arthropods than all other animals combined! Five classes of arthropods: crustaceans, arachnids, centipedes, millipedes, and insects. Crustaceans (Crustacea) Two or three bo ...
... or female), have internal fertilization (inside the body); shed their exoskeletons as they grow (molting) More species of arthropods than all other animals combined! Five classes of arthropods: crustaceans, arachnids, centipedes, millipedes, and insects. Crustaceans (Crustacea) Two or three bo ...
Bacteria protist fungi insect mammal
... In humans, travels to liver (dormant), then infects blood cells causing blood cells to rupture and ...
... In humans, travels to liver (dormant), then infects blood cells causing blood cells to rupture and ...
Invertebrates- Mollusks, Arthropods, Echinoderms By: Isaiah
... Use a network of specialized cells (neurons) that serve as an info highway ...
... Use a network of specialized cells (neurons) that serve as an info highway ...
The Notes
... 6-3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals). EQ: What characteristics do scientists use to classify invertebrates? _____________ ...
... 6-3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals). EQ: What characteristics do scientists use to classify invertebrates? _____________ ...
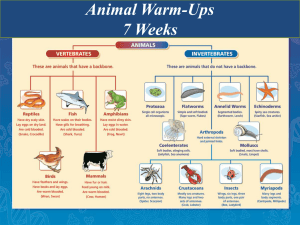
Vertebrates and Invertebrates
... Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals with backbones. These can be made into smaller groups. These are Mammals, Reptiles, Amphibians, Birds and Fish ...
... Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals with backbones. These can be made into smaller groups. These are Mammals, Reptiles, Amphibians, Birds and Fish ...
Chapter 3, Section 1 – Protists
... c. bilateral symmetry d. have head and tail ends e. all have tissues, organs, and body systems ...
... c. bilateral symmetry d. have head and tail ends e. all have tissues, organs, and body systems ...
Body Cavities
... surrounded by a funnel-shaped contractile collar, very similar to choanocyte feeding cells of sponges ...
... surrounded by a funnel-shaped contractile collar, very similar to choanocyte feeding cells of sponges ...
Marine Invertebrates
... species is only found in the Atlantic Ocean. Condylactis anemones are hermaphroditic and can also reproduce by division, furrowing to create two genetically identical anemones. They should be provided with compact fluorescent lighting to aid in the photosynthesis of their symbiotic algae. • Cassiope ...
... species is only found in the Atlantic Ocean. Condylactis anemones are hermaphroditic and can also reproduce by division, furrowing to create two genetically identical anemones. They should be provided with compact fluorescent lighting to aid in the photosynthesis of their symbiotic algae. • Cassiope ...
What is an Animal?
... • Carbon dioxide and ammonia are toxic and must be excreted and eliminated from the body • Many animals remove CO2 with their respiratory system. More complex animals have a specialized organs system for eliminating waste called the excretory system • Before wastes can be eliminated they need to be ...
... • Carbon dioxide and ammonia are toxic and must be excreted and eliminated from the body • Many animals remove CO2 with their respiratory system. More complex animals have a specialized organs system for eliminating waste called the excretory system • Before wastes can be eliminated they need to be ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.