ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... • Two phyla have been particularly successful • Nematoda (roundworms): pseudocoelomates • Arthropoda: coelomates • Insects, crustaceans, and others ...
... • Two phyla have been particularly successful • Nematoda (roundworms): pseudocoelomates • Arthropoda: coelomates • Insects, crustaceans, and others ...
Zoology
... 1. Arthropods have an exoskeleton, a segmented body (body in sections), and jointed appendages (limbs/legs/antennae in sections that can bend). 2. An exoskeleton is a rigid outer covering. 3. The process by which arthropods shed their exoskeleton as they grow is called molting. 4. Arthropods have an ...
... 1. Arthropods have an exoskeleton, a segmented body (body in sections), and jointed appendages (limbs/legs/antennae in sections that can bend). 2. An exoskeleton is a rigid outer covering. 3. The process by which arthropods shed their exoskeleton as they grow is called molting. 4. Arthropods have an ...
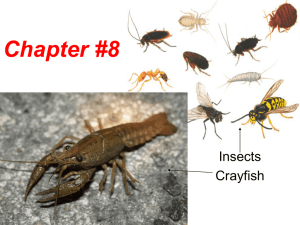
Notes Chapter #8
... • 2 pairs of legs per segment, no claws, eat plants. 5. Insects- are the only invertebrate that can fly!!! • 3 body parts, 2 compound eyes and 3 simple eyes, 1 pair antennae, 3 pairs of legs, 2 pairs of wings. ...
... • 2 pairs of legs per segment, no claws, eat plants. 5. Insects- are the only invertebrate that can fly!!! • 3 body parts, 2 compound eyes and 3 simple eyes, 1 pair antennae, 3 pairs of legs, 2 pairs of wings. ...
Kingdom Animalia Notes - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... Kingdom – Animalia Phylum – Chordata Subphylum – Vertebrata ...
... Kingdom – Animalia Phylum – Chordata Subphylum – Vertebrata ...
Chapter 6 Resource: Invertebrate Animals
... 1. thin layer of tissue that secretes a mollusk’s shell 3. an animal with a backbone 5. spiny-skinned invertebrate that lives on the ocean bottom 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14 ...
... 1. thin layer of tissue that secretes a mollusk’s shell 3. an animal with a backbone 5. spiny-skinned invertebrate that lives on the ocean bottom 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14 ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Embryonic Development Sponges have the cellular level of organization; they are multicellular, but lack true tissues and are therefore in a separate group called the parazoans. True tissues appear in eumatazoans as they undergo embryological development. Some animals have two germ layers (ectoderm a ...
... Embryonic Development Sponges have the cellular level of organization; they are multicellular, but lack true tissues and are therefore in a separate group called the parazoans. True tissues appear in eumatazoans as they undergo embryological development. Some animals have two germ layers (ectoderm a ...
File - PATRIOTS POINT
... together. There are seven groups of classification: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Scientists place organisms into a broad group, kingdom and then place them into more specific gro ...
... together. There are seven groups of classification: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Scientists place organisms into a broad group, kingdom and then place them into more specific gro ...
Invertebrate PowerPoint
... Main groups of mollusks 1. Gastropods (“stomach-footed”) 80% of mollusk a. Univalves: one shell, breathe with lungs; example: snail, slug b. Bivalves: two shells, breathe with gills; example: clam 2. Cephalopods (“head-footed”)-foot is modified into tentacles, breathe with gills; examples: octopus, ...
... Main groups of mollusks 1. Gastropods (“stomach-footed”) 80% of mollusk a. Univalves: one shell, breathe with lungs; example: snail, slug b. Bivalves: two shells, breathe with gills; example: clam 2. Cephalopods (“head-footed”)-foot is modified into tentacles, breathe with gills; examples: octopus, ...
Intro Invertebrates
... • What is an animal? – a multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls. ...
... • What is an animal? – a multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls. ...
Concept 1: sponges are basal animals that lack true tissues
... They were named after their feeding appendages called chelicerae, and they are divided into two main body parts: posterior abdomen and interior cephalothorax, and most of them have simple eyes. The earliest members of this clade are eurypterids (water scorpions) which can reach to 3 meters in le ...
... They were named after their feeding appendages called chelicerae, and they are divided into two main body parts: posterior abdomen and interior cephalothorax, and most of them have simple eyes. The earliest members of this clade are eurypterids (water scorpions) which can reach to 3 meters in le ...
Kingdom Animalia
... ▫ Larva: immature form of an animal that looks different from the adult forms and usually eats different food ▫ Larva undergoes metamorphosis to become an adult ...
... ▫ Larva: immature form of an animal that looks different from the adult forms and usually eats different food ▫ Larva undergoes metamorphosis to become an adult ...
Classifying Living Organisms Unit 10.4.16
... • Corals get nutrients from algae's photosynthesis ...
... • Corals get nutrients from algae's photosynthesis ...
Classification
... Have hair or fur and females produce milk to suckle young Give birth to live well developed offspring (no eggs) Warm blooded Mouth contains a variety of teeth for varied diets ...
... Have hair or fur and females produce milk to suckle young Give birth to live well developed offspring (no eggs) Warm blooded Mouth contains a variety of teeth for varied diets ...
Classification - rosedale11universitybiology
... The three main types of symmetry are: Bilateral – can be cut into two mirror images through a central line. Radial – body is organized around a central axis. They are symmetrical around any central cut. Asymmetry – no distinctive symmetry ...
... The three main types of symmetry are: Bilateral – can be cut into two mirror images through a central line. Radial – body is organized around a central axis. They are symmetrical around any central cut. Asymmetry – no distinctive symmetry ...
Chapters 16-19: Diversity of Life 1. Taxonomic Classification The Classification of Organisms
... Invertebrate animals • NO backbone or “vertebral” column • > 97% of known animal species • any “non-vertebrate” animal ...
... Invertebrate animals • NO backbone or “vertebral” column • > 97% of known animal species • any “non-vertebrate” animal ...
Create an Invertebrate
... head of many invertebrates. *Examples: praying mantis, butterfly, ladybug. bilateral symmetry: A form or shape that has two identical parts on either side of an axis. *Examples: flatworm, lobster, centipede bioluminescent: Light that is produced by living organisms. *Examples: fireflies, dinoflagell ...
... head of many invertebrates. *Examples: praying mantis, butterfly, ladybug. bilateral symmetry: A form or shape that has two identical parts on either side of an axis. *Examples: flatworm, lobster, centipede bioluminescent: Light that is produced by living organisms. *Examples: fireflies, dinoflagell ...
Warm Up Question: - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... • Examples-Shellfish, squids, snails • Mollusks have a soft body (their name is derived from the Latin word mollus, meaning "soft”) ...
... • Examples-Shellfish, squids, snails • Mollusks have a soft body (their name is derived from the Latin word mollus, meaning "soft”) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - nvertebrates
... • This shell grows within their body and is formed by the ____________ ...
... • This shell grows within their body and is formed by the ____________ ...
Section 29
... 11. As larger and more complex animals evolved, in what ways did specialized cells join together? Specialized cells joined together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions. ...
... 11. As larger and more complex animals evolved, in what ways did specialized cells join together? Specialized cells joined together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions. ...
Classifying Animals Voc.and Notes Aug.29
... muscle tissues, stinger cells, and a mouth. Worms: There are three main groups of worms: flatworms, roundworms, and segmented worms. All worms have bilateral symmetry. Flatworms have a flat body and head with simple eyes and a mouth. Flatworms have only one body opening, undigested food leaves its b ...
... muscle tissues, stinger cells, and a mouth. Worms: There are three main groups of worms: flatworms, roundworms, and segmented worms. All worms have bilateral symmetry. Flatworms have a flat body and head with simple eyes and a mouth. Flatworms have only one body opening, undigested food leaves its b ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.