Invertebrates Animal Kingdom Characteristics Body Plans
... - Invertebrates- animals without backbones - sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, worms, echinoderms, arthropods ...
... - Invertebrates- animals without backbones - sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, worms, echinoderms, arthropods ...
Inverterates - Grafton School District
... - Invertebrates- animals without backbones - sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, worms, echinoderms, arthropods ...
... - Invertebrates- animals without backbones - sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, worms, echinoderms, arthropods ...
Chapter 29
... 1. They are bivalved like mollusk bivalves, but the symmetry is opposite C. Phylum Phoronida includes only 12 extant species, although they may locally be abundant 1. They live in tubes formed by sand D. Phylum Bryozoa, also known as "moss animals," form sessile colonies by asexual budding E. Rotife ...
... 1. They are bivalved like mollusk bivalves, but the symmetry is opposite C. Phylum Phoronida includes only 12 extant species, although they may locally be abundant 1. They live in tubes formed by sand D. Phylum Bryozoa, also known as "moss animals," form sessile colonies by asexual budding E. Rotife ...
Unit 4 Part 2 Outline Animal Diversity
... Animals are extremely diverse, but in general they are heterotrophic, typically have the power of movement or locomotion by means of muscle fibers, are multicellular, have a life cycle in which the adult is typically diploid, and undergo sexual reproduction and produce an embryo that goes through de ...
... Animals are extremely diverse, but in general they are heterotrophic, typically have the power of movement or locomotion by means of muscle fibers, are multicellular, have a life cycle in which the adult is typically diploid, and undergo sexual reproduction and produce an embryo that goes through de ...
CHAPTER 33
... All brachiopods are marine. Most live attached to the substratum by a stalk, opening their shell slightly to allow water to flow over the lophophore. The living brachiopods are remnants of a richer past. ...
... All brachiopods are marine. Most live attached to the substratum by a stalk, opening their shell slightly to allow water to flow over the lophophore. The living brachiopods are remnants of a richer past. ...
cnidaria - Sakshieducation.com
... a.ventral central nervous system—leech b. no pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo-Chaemeleon c.ventral heart- scorpion d.post anal tail—Octopus ...
... a.ventral central nervous system—leech b. no pharyngeal gill slits in the embryo-Chaemeleon c.ventral heart- scorpion d.post anal tail—Octopus ...
sensory neurons
... Provide watertight coverings that enable some arthropods to live in Earth’s driest places Can provide physical protection against ...
... Provide watertight coverings that enable some arthropods to live in Earth’s driest places Can provide physical protection against ...
A Brief Survey of Animals
... Arthropods have developed a rigid and jointed external skeleton made of a waterproof material known as Chitin. The skeleton provides many advantages including a site for muscle attachment and protection of bodily tissues. Because Arthropods do grow and because their exoskeletons cannot expands, they ...
... Arthropods have developed a rigid and jointed external skeleton made of a waterproof material known as Chitin. The skeleton provides many advantages including a site for muscle attachment and protection of bodily tissues. Because Arthropods do grow and because their exoskeletons cannot expands, they ...
D. Protostomia: Ecdysozoa
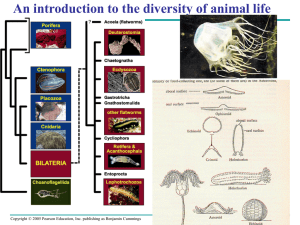
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. Animals are grouped into about 35 phyla. Animals inhabit nearly all environments on Earth, but most phyla consist mainly of aquatic species. Most live in the s ...
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. Animals are grouped into about 35 phyla. Animals inhabit nearly all environments on Earth, but most phyla consist mainly of aquatic species. Most live in the s ...
Unit 11 Animal Evolution Chp 33 Invertebrates Notes
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. ...
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. ...
Animal Notes - WordPress.com
... through a central axis, into equal halves. Animal has bilateral symmetry if it can be _____________________________________ into similar right and left halves forming mirror images of each other. Not all animals have a skeleton but some have: ...
... through a central axis, into equal halves. Animal has bilateral symmetry if it can be _____________________________________ into similar right and left halves forming mirror images of each other. Not all animals have a skeleton but some have: ...
video slide
... exoskeleton supporting a complex system of tube feet used for slow locomotion. Any fossil – if it is pentagonal, it’s an echinoderm! Classes Asteroidea - starfish Echinoidea - sea urchins Ophiuroidea - brittle stars Holothuridae - sea cucumbers Crinoidea - feather stars Starfish are predators, echin ...
... exoskeleton supporting a complex system of tube feet used for slow locomotion. Any fossil – if it is pentagonal, it’s an echinoderm! Classes Asteroidea - starfish Echinoidea - sea urchins Ophiuroidea - brittle stars Holothuridae - sea cucumbers Crinoidea - feather stars Starfish are predators, echin ...
5.5 CLASSIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
... Seeds are enclosed in fruits.( ovules form seeds and ovary forms fruit) ...
... Seeds are enclosed in fruits.( ovules form seeds and ovary forms fruit) ...
Skeletal System
... ~offspring produced rapidly ~individuals don’t have to find a mate ~species can’t change quickly with a changing environment ~types include budding, fragmentation, gemmules, pedal laceration ~Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes *Sexual ~offspring are not genetically identical to their parents ~speci ...
... ~offspring produced rapidly ~individuals don’t have to find a mate ~species can’t change quickly with a changing environment ~types include budding, fragmentation, gemmules, pedal laceration ~Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes *Sexual ~offspring are not genetically identical to their parents ~speci ...
Unit 12 Invertebrate Evolution Notes
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. ...
... More than a million extant species of animals are known, and at least as many more will probably be identified by future biologists. ...
BY 124 SI 10/06/15 Why were Phylum Nematoda and Phylum
... Why were Phylum Nematoda and Phylum Arthropoda recently classified into a clade called Ecdysozoa? They both undergo ecdysis which is the molting of their exoskeletons Phylum Nematoda are also known as the ______________. They do/do not have a circulatory system. They are unsegmented and are ________ ...
... Why were Phylum Nematoda and Phylum Arthropoda recently classified into a clade called Ecdysozoa? They both undergo ecdysis which is the molting of their exoskeletons Phylum Nematoda are also known as the ______________. They do/do not have a circulatory system. They are unsegmented and are ________ ...
Feeding and Digestion
... b. Parasitic Symbionts - Parasites live within or on a host organism, where they feed on tissues or on blood and other body fluids. c. Mutualistic Symbionts - relationships in which both participants benefit; example: Reef-building corals depend on symbiotic algae that live within their tissues for ...
... b. Parasitic Symbionts - Parasites live within or on a host organism, where they feed on tissues or on blood and other body fluids. c. Mutualistic Symbionts - relationships in which both participants benefit; example: Reef-building corals depend on symbiotic algae that live within their tissues for ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.