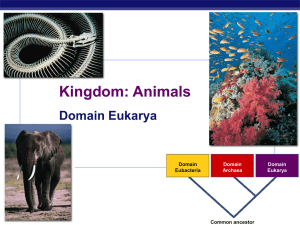
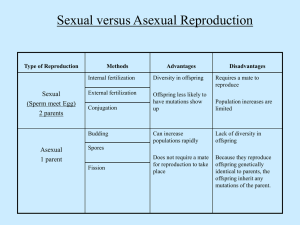
Characteristics ~
... Though not all animals have a skeleton, those that do can be divided into two groups: – Those with an exoskeleton – a hard, waxy coating on the outside of the body that protects internal organs, provides a framework for support, and a place for muscle attachment. ...
... Though not all animals have a skeleton, those that do can be divided into two groups: – Those with an exoskeleton – a hard, waxy coating on the outside of the body that protects internal organs, provides a framework for support, and a place for muscle attachment. ...
Invertebrate Phyla Notes
... c. Arthropods are made up of _______cells__________, __________tissues___________, _________organs_______, and _________systems_______. d. Crustaceans, like _crabs, crayfish, lobster, shrimp, barnacles_ live in __water___ and breathe with gills. They have five or more pair of walking legs and four o ...
... c. Arthropods are made up of _______cells__________, __________tissues___________, _________organs_______, and _________systems_______. d. Crustaceans, like _crabs, crayfish, lobster, shrimp, barnacles_ live in __water___ and breathe with gills. They have five or more pair of walking legs and four o ...
Phylum: Mollusca
... intended only for internal use by VFU Brno students during their preparation for credits in zoology. Further dissemination of this file is forbidden. ...
... intended only for internal use by VFU Brno students during their preparation for credits in zoology. Further dissemination of this file is forbidden. ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... The bodies of cnidarians are described in one of two ways, depending on whether the opening of the gastrovascular cavity is ventral or dorsal ...
... The bodies of cnidarians are described in one of two ways, depending on whether the opening of the gastrovascular cavity is ventral or dorsal ...
Document
... a. populations b. people or individual organisms c. genes d. a and c e. all of the above 9. Which of the following is the correct order for life in the fossil record? (Yes, we did not talk about the first cat, but I think it is pretty obvious.) a. First cat, first prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizin ...
... a. populations b. people or individual organisms c. genes d. a and c e. all of the above 9. Which of the following is the correct order for life in the fossil record? (Yes, we did not talk about the first cat, but I think it is pretty obvious.) a. First cat, first prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizin ...
Animal Unit - Jifted Land
... reproductive organs, waste removal organs, bristles, intestine, and an anus Chapter Review 1. Organisms that make their own food are called autotrophs. 2. Height or length is not one of the major characteristics biologists use to classify animals. 3. An animal with many lines of symmetry has radial ...
... reproductive organs, waste removal organs, bristles, intestine, and an anus Chapter Review 1. Organisms that make their own food are called autotrophs. 2. Height or length is not one of the major characteristics biologists use to classify animals. 3. An animal with many lines of symmetry has radial ...
Classification - WordPress.com
... 1. I can state what is meant by the term classification. 2. I can describe the difference between invertebrates and vertebrates and their subdivisions using examples. 3. I can describe the differences between plants that are flowering or non-flowering. ...
... 1. I can state what is meant by the term classification. 2. I can describe the difference between invertebrates and vertebrates and their subdivisions using examples. 3. I can describe the differences between plants that are flowering or non-flowering. ...
Lecture 13 - Some animals - Worms, arthropods and echinoderms
... • gas exchange : tracheae – tubes that open to the air via the spiracles along the body • spiracles lead to tracheal tubules that carry air to the muscles – gas exhange • inspiration through the thoracic spiracles and expiration through the abdominal spiracles ...
... • gas exchange : tracheae – tubes that open to the air via the spiracles along the body • spiracles lead to tracheal tubules that carry air to the muscles – gas exhange • inspiration through the thoracic spiracles and expiration through the abdominal spiracles ...
Ch 14 Quiz Review - Mrs. Pierce`s Class
... 41. A spider’s two main body parts consist of an abdomen and a(n) ____________________. 42. A phase in the life of many insects, ____________________ is a rapid change from an immature form to an adult form. 43. The class of mollusks that use a radula is known as the ____________________. 44. The bu ...
... 41. A spider’s two main body parts consist of an abdomen and a(n) ____________________. 42. A phase in the life of many insects, ____________________ is a rapid change from an immature form to an adult form. 43. The class of mollusks that use a radula is known as the ____________________. 44. The bu ...
1008invertebrates - Michigan State University
... first to encounter food, danger, and other stimuli. In most bilateral animals, cephalization also includes the development of a central nervous system concentrated in the head … A head end is an adaptation for movement … The symmetry of an animal generally fits its lifestyle. Many radial animals are ...
... first to encounter food, danger, and other stimuli. In most bilateral animals, cephalization also includes the development of a central nervous system concentrated in the head … A head end is an adaptation for movement … The symmetry of an animal generally fits its lifestyle. Many radial animals are ...
Marine Invertebrates_7c (Arthropods, Echinoderms, Chordates)
... Sea cucumbers are worm-like; elongated along the oral-aboral axis, as if pulled/stretched from the mouth and anus ...
... Sea cucumbers are worm-like; elongated along the oral-aboral axis, as if pulled/stretched from the mouth and anus ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Does not grow; must be shed & replaced 2. endoskeleton: internal skeleton Can support a large, heavy body Grows as the animal grows Circulatory System FUNCTION: Moves materials to and from the cells 1. open—fluid pumped from vessels into body cavity, then returned to vessels (Ex. arthropods ...
... Does not grow; must be shed & replaced 2. endoskeleton: internal skeleton Can support a large, heavy body Grows as the animal grows Circulatory System FUNCTION: Moves materials to and from the cells 1. open—fluid pumped from vessels into body cavity, then returned to vessels (Ex. arthropods ...
25-1 PowerPoint
... More than 95 percent of animal species are informally called invertebrates. Invertebrates include at least 33 phyla. Invertebrates include sea stars, worms, jellyfishes, and insects, like butterflies. They range in size from dust mites to giant squid more than 20 meters long. ...
... More than 95 percent of animal species are informally called invertebrates. Invertebrates include at least 33 phyla. Invertebrates include sea stars, worms, jellyfishes, and insects, like butterflies. They range in size from dust mites to giant squid more than 20 meters long. ...
chapter 25 section 1 notes
... Animals are all heterotrophs; they obtain nutrients and energy by eating other organisms. Animals are also multicellular; their bodies are composed of many cells. The cells that make up animal bodies are eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Unlike the cells of algae, fungi ...
... Animals are all heterotrophs; they obtain nutrients and energy by eating other organisms. Animals are also multicellular; their bodies are composed of many cells. The cells that make up animal bodies are eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Unlike the cells of algae, fungi ...
File
... Phylum: Echinodermata The word Echinodermata means “spiny skin”. These animals demonstrate secondary radial symmetry as adults (evolved from bilateral symmetry back to radial symmetry) while the larvae stage still exhibits bilateral symmetry. They are probably more closely related to the vertebrate ...
... Phylum: Echinodermata The word Echinodermata means “spiny skin”. These animals demonstrate secondary radial symmetry as adults (evolved from bilateral symmetry back to radial symmetry) while the larvae stage still exhibits bilateral symmetry. They are probably more closely related to the vertebrate ...
PRIMARY PRODUCTION IN MARINE AND FRESHWATER
... 1. Organisms in Phylum Annelidia (pronounce: an-el-eh-dah) are segmented worms that lay eggs. From the Annelidia poster, annelids are the most structurally developed worms with a true ___________________________ and complex _______________________________ system. Most annelids have bristles called _ ...
... 1. Organisms in Phylum Annelidia (pronounce: an-el-eh-dah) are segmented worms that lay eggs. From the Annelidia poster, annelids are the most structurally developed worms with a true ___________________________ and complex _______________________________ system. Most annelids have bristles called _ ...
Invertebrates
... pizza) • An animal has bilateral symmetry if it can be divided down its length into similar right and left halves forming mirror images of each other. (like humans) ...
... pizza) • An animal has bilateral symmetry if it can be divided down its length into similar right and left halves forming mirror images of each other. (like humans) ...
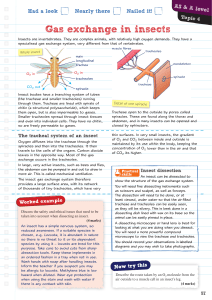
Gas exchange in insects - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... chitin (a structural polysaccharide), which keeps them open, but is also impermeable to gases. Smaller tracheoles spread through insect tissues and even into individual cells. They have no chitin, so are freely permeable to gases. ...
... chitin (a structural polysaccharide), which keeps them open, but is also impermeable to gases. Smaller tracheoles spread through insect tissues and even into individual cells. They have no chitin, so are freely permeable to gases. ...
A worm that turned - Gesundheitsindustrie BW
... A conserved cassette of two antagonistic genes, which have been shown to be inverted in fruit flies relative to frogs, is the most convincing evidence so far for substantiating the assumption that the dorsoventral axis was inverted. Drosophila expresses a gene (Dpp, decapentaplegic) on the dorsal s ...
... A conserved cassette of two antagonistic genes, which have been shown to be inverted in fruit flies relative to frogs, is the most convincing evidence so far for substantiating the assumption that the dorsoventral axis was inverted. Drosophila expresses a gene (Dpp, decapentaplegic) on the dorsal s ...
SCULPtURE LEARNiNG PLAzA
... Habitat/diet: Termites obtain nutrients from wood and plant matter, but cannot digest it themselves. They have microbacteria in their gut that aid in digestion. Macrotermes lives in savannas and grasslands. Status: Not yet assessed by IUCN Range: Macrotermes contains about 350 species which are foun ...
... Habitat/diet: Termites obtain nutrients from wood and plant matter, but cannot digest it themselves. They have microbacteria in their gut that aid in digestion. Macrotermes lives in savannas and grasslands. Status: Not yet assessed by IUCN Range: Macrotermes contains about 350 species which are foun ...
Evolution of Animal Body Plan
... nerve cord that connects it to other areas of the body. • The annelids have nephridia in each segment, which excrete nitrogenous wastes. ...
... nerve cord that connects it to other areas of the body. • The annelids have nephridia in each segment, which excrete nitrogenous wastes. ...
Echinoderms “Spiny Skin”
... Why is more advanced then the ones above? What is the phylum and class of the sixth picture? Why is that organisms different then the others in its phylum? What is the phylum of the last picture? What body form is it? What are its stinging cells called? ...
... Why is more advanced then the ones above? What is the phylum and class of the sixth picture? Why is that organisms different then the others in its phylum? What is the phylum of the last picture? What body form is it? What are its stinging cells called? ...
The Five Kingdoms
... Live in both aquatic & land environments Plants do not move Examples include: mosses, ferns, grasses, shrubs, flowering plants (angiosperms), trees (gymnosperms) ...
... Live in both aquatic & land environments Plants do not move Examples include: mosses, ferns, grasses, shrubs, flowering plants (angiosperms), trees (gymnosperms) ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.