Lesson Overview
... homeostasis is the most important function of all body systems. For example, reptiles, birds, and mammals cannot excrete salt. Those that spend time hunting or feeding in salt water, such as the marine iguana, have adaptations that allow them to remove salt from their bodies. Marine iguanas maintain ...
... homeostasis is the most important function of all body systems. For example, reptiles, birds, and mammals cannot excrete salt. Those that spend time hunting or feeding in salt water, such as the marine iguana, have adaptations that allow them to remove salt from their bodies. Marine iguanas maintain ...
Cp 2 part 2 STUDY GUIDE
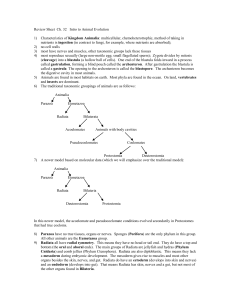
... 3. The three main body parts of an insect are head, abdomen, and legs. 4. 97% of all animal species are classified as arthropods. 5. Cephalopods have the most advanced nervous system and are the smartest of all invertebrates. 6. An octopus has an open circulatory system where the heart circulates bl ...
... 3. The three main body parts of an insect are head, abdomen, and legs. 4. 97% of all animal species are classified as arthropods. 5. Cephalopods have the most advanced nervous system and are the smartest of all invertebrates. 6. An octopus has an open circulatory system where the heart circulates bl ...
Chapter 29 – Invertebrates
... There are more known species of arthropods than all other phyla combined. Chelicerates, arthropods with pincer or fanglike feeding appendages, include class Arachnida (spiders, ticks, scorpions, and mites). A traditional classification scheme groups the insects (class Insecta), centipedes (class Chi ...
... There are more known species of arthropods than all other phyla combined. Chelicerates, arthropods with pincer or fanglike feeding appendages, include class Arachnida (spiders, ticks, scorpions, and mites). A traditional classification scheme groups the insects (class Insecta), centipedes (class Chi ...
lecture notes ch32 Intro Animal Evolution
... sides. Some Bilateria have radial symmetry as adults (e.g. sea stars, sea cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral s ...
... sides. Some Bilateria have radial symmetry as adults (e.g. sea stars, sea cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral s ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... of the signs shows a picture of the animal or its name. What criteria would you use to assign the animal to a phylum? You could start by checking for a cranium and the backbone, which would indicate a vertebrate. If the animal were wormlike and had segmentation, it might be an annelid. If it were wo ...
... of the signs shows a picture of the animal or its name. What criteria would you use to assign the animal to a phylum? You could start by checking for a cranium and the backbone, which would indicate a vertebrate. If the animal were wormlike and had segmentation, it might be an annelid. If it were wo ...
Crustacea
... Sea Cucumbers live on the _________________________________. They don’t have spines, but have a very tough, leathery skin. They have a mouth at one end and an anus at the other end. What do sea cucumbers do when they sense danger? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Sea Cucumbers live on the _________________________________. They don’t have spines, but have a very tough, leathery skin. They have a mouth at one end and an anus at the other end. What do sea cucumbers do when they sense danger? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Lecture 2: Vertebrate Origins
... e. An interesting observation about vertebrates: i. Most animals (invertebrates) are small. Vertebrates however tend to be large. This means that diffusion is no longer sufficient for many bodily functions. This necessitates specialized structures and systems in vertebrates. ii. Basal metabolic rate ...
... e. An interesting observation about vertebrates: i. Most animals (invertebrates) are small. Vertebrates however tend to be large. This means that diffusion is no longer sufficient for many bodily functions. This necessitates specialized structures and systems in vertebrates. ii. Basal metabolic rate ...
Name
... d. is common in radially symmetrical animals e. is associated with motile animals that concentrate sensory organs in a head region 4. A true coelom a. has mesoderm-derived tissues extending from the dorsal and ventral sides that support internal organs b. allows organs to grow and move independently ...
... d. is common in radially symmetrical animals e. is associated with motile animals that concentrate sensory organs in a head region 4. A true coelom a. has mesoderm-derived tissues extending from the dorsal and ventral sides that support internal organs b. allows organs to grow and move independently ...
Lab 6: Animal Diversity
... Use the DIchotomous Key and Skull Characteristics chart to identify the skulls of small mammals found in your pellets and record the number of each type on the accompanying worksheet labeled “Pellet Contents”. Disregard insects that may be found. ...
... Use the DIchotomous Key and Skull Characteristics chart to identify the skulls of small mammals found in your pellets and record the number of each type on the accompanying worksheet labeled “Pellet Contents”. Disregard insects that may be found. ...
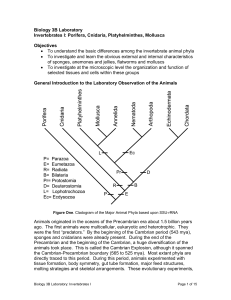
Biology 3B Laboratory Invertebrates I: Porifera, Cnidaria
... Platyhelminthes (flat worms) and the Mollusca. The Annelida (segmented worms) will be covered in the next lab, Invertebrates II. PHYLUM PORIFERA Animals without tissues The “monophyletic origin of animals hypothesis” asserts that all animal groups evolved from the one protistan clade. They diversifi ...
... Platyhelminthes (flat worms) and the Mollusca. The Annelida (segmented worms) will be covered in the next lab, Invertebrates II. PHYLUM PORIFERA Animals without tissues The “monophyletic origin of animals hypothesis” asserts that all animal groups evolved from the one protistan clade. They diversifi ...
Invert Flip Note Packet
... Sea Cucumbers live on the _________________________________. They don’t have spines, but have a very tough, leathery skin. They have a mouth at one end and an anus at the other end. What do sea cucumbers do when they sense danger? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Sea Cucumbers live on the _________________________________. They don’t have spines, but have a very tough, leathery skin. They have a mouth at one end and an anus at the other end. What do sea cucumbers do when they sense danger? ___________________________________________________________________ ...
BioSem 2spr13 Review Sheet
... Diversity in arthropods-what are the largest classes of arthropods? What are the characteristics of insects? To what segment are the legs and wings attached in an insect? What structures do insects use for gas exchange? In crayfish, what are their gills attached to? Why is this beneficial? ...
... Diversity in arthropods-what are the largest classes of arthropods? What are the characteristics of insects? To what segment are the legs and wings attached in an insect? What structures do insects use for gas exchange? In crayfish, what are their gills attached to? Why is this beneficial? ...
Unit 2 Study Guide - Madison County Schools
... central vacuole to store water, 3) cell wall made of cellulose (bacteria and fungi also have cell walls but they are not made of cellulose) ...
... central vacuole to store water, 3) cell wall made of cellulose (bacteria and fungi also have cell walls but they are not made of cellulose) ...
Arthropoda
... the communication mechanism in some bees known as the bee dance, through which one bee tells others information about the location of flower fields and other sources of nectar. ...
... the communication mechanism in some bees known as the bee dance, through which one bee tells others information about the location of flower fields and other sources of nectar. ...
Revision questions
... 1. Name two classes of Chelicerata and give one example. 2. There are three types of modified legs in this group. What are their names and how are they used? 3. True or false Xiphosura is a marine class Horseshoe crab is a true crab which belongs to class of Xiphosura Xiphosura use book lungs to bre ...
... 1. Name two classes of Chelicerata and give one example. 2. There are three types of modified legs in this group. What are their names and how are they used? 3. True or false Xiphosura is a marine class Horseshoe crab is a true crab which belongs to class of Xiphosura Xiphosura use book lungs to bre ...
M Standard 11- - ALCOSbiologyPowerPoints
... Which animal does NOT have external fertilization? • A. clams • B. humans • C. sponges • D. insects Hint: Decide what the question IS asking. It IS asking about the ...
... Which animal does NOT have external fertilization? • A. clams • B. humans • C. sponges • D. insects Hint: Decide what the question IS asking. It IS asking about the ...
Studyguide for Exam 2 Spring 2012 Chapter 7 Marine Animals
... Which phyla are mainly marine? Which phyla are mainly in water? Which phyla have some success on land? Burgess shale fossils Mudslide on the british Columbia continental shelf preserved soft bodied invertebrates from right after the Cambrian era •Many body plans are now extinct •Only one chordate fo ...
... Which phyla are mainly marine? Which phyla are mainly in water? Which phyla have some success on land? Burgess shale fossils Mudslide on the british Columbia continental shelf preserved soft bodied invertebrates from right after the Cambrian era •Many body plans are now extinct •Only one chordate fo ...
M5L5 Phylum Annelida Segmented Worms
... with movement as well. Some polychaetes are tube worms. These tubes will be burrowed in the mud and the worms have reduced parapodia. Some have tentacles which allow them to filter feed of particles in the water. In annelids, blood is moved throughout the body entirely within blood vessels. Therefor ...
... with movement as well. Some polychaetes are tube worms. These tubes will be burrowed in the mud and the worms have reduced parapodia. Some have tentacles which allow them to filter feed of particles in the water. In annelids, blood is moved throughout the body entirely within blood vessels. Therefor ...
Introduction to animals
... echinoderms (starfish) have fluid-filled internal cavities giving them support • Called hydrostatic skeletons ...
... echinoderms (starfish) have fluid-filled internal cavities giving them support • Called hydrostatic skeletons ...
Annelid Test Zoology B
... Short Answer Please answer the following questions in complete sentences. 33. What main function AND what body system does the clitellum serve? The function of the clitellum is mucous secretion during copulation and cocoon formation after copulation. ...
... Short Answer Please answer the following questions in complete sentences. 33. What main function AND what body system does the clitellum serve? The function of the clitellum is mucous secretion during copulation and cocoon formation after copulation. ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.