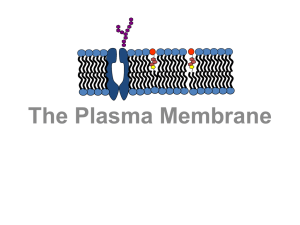
The plasma membrane
... • The phosphate group is attracted to water (hydrophilic ).This means polar. • Fatty acid tails don’t like water and are repelled by water (hydrophobic ...
... • The phosphate group is attracted to water (hydrophilic ).This means polar. • Fatty acid tails don’t like water and are repelled by water (hydrophobic ...
Lecture 4: Cellular Building Blocks
... • Membrane lipids with fatty acyl side chains that are saturated (no double bonds) pack tightly in the membrane and make it less fluid • Lipids that are unsaturated (1, 2, or 3 double bonds) pack loosely and make it more fluid ...
... • Membrane lipids with fatty acyl side chains that are saturated (no double bonds) pack tightly in the membrane and make it less fluid • Lipids that are unsaturated (1, 2, or 3 double bonds) pack loosely and make it more fluid ...
Data/hora: 09/03/2017 07:24:48 Provedor de dados: 189 País
... of enzymatic activity, colipase promotes pancreatic lipase activity in the physiological intestinal conditions by anchoring the enzyme on the surface of lipid droplets. Polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy combined with Brewster angle microscopy studies was performed o ...
... of enzymatic activity, colipase promotes pancreatic lipase activity in the physiological intestinal conditions by anchoring the enzyme on the surface of lipid droplets. Polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy combined with Brewster angle microscopy studies was performed o ...
Bilayers as Protein Solvents: Role of Bilayer Structure and Elastic
... of the endoplasmic reticulum, which is primarily composed of electrically neutral phosphatidylcholines enriched in palmitoyl and oleoyl hydrocarbon chains. However, these one-component POPC bilayers are limited in terms of modeling interactive properties of cell plasma membranes, which, compared wit ...
... of the endoplasmic reticulum, which is primarily composed of electrically neutral phosphatidylcholines enriched in palmitoyl and oleoyl hydrocarbon chains. However, these one-component POPC bilayers are limited in terms of modeling interactive properties of cell plasma membranes, which, compared wit ...
Lanosterol Biosynthesis in the Membrane Environment
... substrates are part of the membrane. These enzymes must actively influence the structure of the lipid bilayer in order to access, steer, and release their reactants. Among the enzymes specialized in lipidic substrates, is the family of monotopic enzymes. Members of this family permanently reside in ...
... substrates are part of the membrane. These enzymes must actively influence the structure of the lipid bilayer in order to access, steer, and release their reactants. Among the enzymes specialized in lipidic substrates, is the family of monotopic enzymes. Members of this family permanently reside in ...
Slide 1
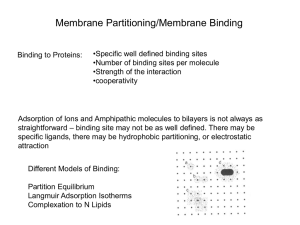
... concentration of free molecule in solution (P). Binding Isotherms are typically analyzed by measuring either the amount of the free ligand in solution or that bound to the bilayer and knowing the total concentration of lipid. An expression was given in Fridays paper presentation: Typically you deriv ...
... concentration of free molecule in solution (P). Binding Isotherms are typically analyzed by measuring either the amount of the free ligand in solution or that bound to the bilayer and knowing the total concentration of lipid. An expression was given in Fridays paper presentation: Typically you deriv ...
Printing – LAB Organic Molecule – Lipid
... 2. All membrane-bound organelles are made from Lipids (Cell Membrane, Nuclear Membrane, inner and outer Mitochondrial Membrane, etc) 3. Membranes come in various shapes depending on function and have proteins embedded in them to facilitate other molecules to pass through them. 4. Lipids are made up ...
... 2. All membrane-bound organelles are made from Lipids (Cell Membrane, Nuclear Membrane, inner and outer Mitochondrial Membrane, etc) 3. Membranes come in various shapes depending on function and have proteins embedded in them to facilitate other molecules to pass through them. 4. Lipids are made up ...
Assessment Test
... 1) The weakest bond between two atoms is the ________ bond. A. Polar B. Ionic C. Hydrogen D. Covalent E. nonpolar 2) All of the following are true concerning enzymes, except that they A. affect only the rate of a chemical reaction B. lower the activation energy required for a reaction C. function as ...
... 1) The weakest bond between two atoms is the ________ bond. A. Polar B. Ionic C. Hydrogen D. Covalent E. nonpolar 2) All of the following are true concerning enzymes, except that they A. affect only the rate of a chemical reaction B. lower the activation energy required for a reaction C. function as ...
Data/hora: 18/04/2017 14:16:42 Provedor de dados: 189 País
... formation of cuticular wax layers and in defence mechanisms against pathogens. In this study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and a lipid, l-α--palmitoyl-phosphatidyl glycerol. This crystal structure was solved a ...
... formation of cuticular wax layers and in defence mechanisms against pathogens. In this study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and a lipid, l-α--palmitoyl-phosphatidyl glycerol. This crystal structure was solved a ...
amphipathic
... form hydrogen bonds with water • Hydrophobic tails (non-polar) are excluded by water molecules ...
... form hydrogen bonds with water • Hydrophobic tails (non-polar) are excluded by water molecules ...
WKS 8.1 - Blair Community Schools
... 11. Why do proteins stay within the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... 11. Why do proteins stay within the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
Single particle cryo-EM of membrane proteins in lipid nanodisc
... In the last few years, major technological breakthroughs enabled single particle cryo-EM to become the technique of choice for structure determination of many challenging biological macromolecules. Atomic structures of many membrane proteins that are refractory to crystallization have now determined ...
... In the last few years, major technological breakthroughs enabled single particle cryo-EM to become the technique of choice for structure determination of many challenging biological macromolecules. Atomic structures of many membrane proteins that are refractory to crystallization have now determined ...
Chp3-Cells_TEST REVIEW
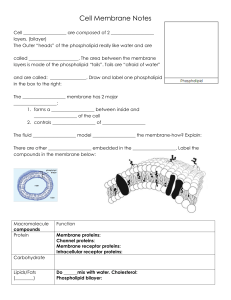
... 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: What is the fluid mosaic model?, What are the functions of the following structures: Channel and marker proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids(phosphates and lipids), phospholipid Bilayer, Selectively Permeable. 3. Be able to identify/draw/label diagram of plasma (cell) m ...
... 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: What is the fluid mosaic model?, What are the functions of the following structures: Channel and marker proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids(phosphates and lipids), phospholipid Bilayer, Selectively Permeable. 3. Be able to identify/draw/label diagram of plasma (cell) m ...
Recitation 2 Solutions
... Also, if carbohydrates were stored as monosaccharides, instead of polysaccharides, they would exert much higher osmotic pressure on the cell. For example 1000 glucose molecule would exert 1000 times the osmotic pressure of a single glycogen molecule, causing water to move in. If it were not for poly ...
... Also, if carbohydrates were stored as monosaccharides, instead of polysaccharides, they would exert much higher osmotic pressure on the cell. For example 1000 glucose molecule would exert 1000 times the osmotic pressure of a single glycogen molecule, causing water to move in. If it were not for poly ...
Cell Membrane and Regulation
... being pushed away by the water on the inside and outside of the cell. ...
... being pushed away by the water on the inside and outside of the cell. ...
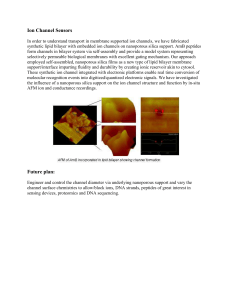
Ion Channel Sensors
... Ion Channel Sensors In order to understand transport in membrane supported ion channels, we have fabricated synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectiv ...
... Ion Channel Sensors In order to understand transport in membrane supported ion channels, we have fabricated synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectiv ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
... endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
... endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
Cell Membrane and Regulation
... The phospholipid bilayer is fluid like a soap bubble. Lipids move around in their side of the bilayer Lipid molecules do NOT move from one layer to the other. (**rare**) ...
... The phospholipid bilayer is fluid like a soap bubble. Lipids move around in their side of the bilayer Lipid molecules do NOT move from one layer to the other. (**rare**) ...
LIPIDS IN MEMBRANES –
... Biophysicists started to characterize the lipids which became available with chemically defined structures. Simple model membranes have been investigated by different methods such as calorimetry, x-ray diffraction, different spectroscopy methods, etc. The phase behavior of these model systems depend ...
... Biophysicists started to characterize the lipids which became available with chemically defined structures. Simple model membranes have been investigated by different methods such as calorimetry, x-ray diffraction, different spectroscopy methods, etc. The phase behavior of these model systems depend ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.