厦门大学细胞生物学课程试卷
... (3) Degradation: proteins that are not specifically retrieved from endosomes are transported to lysosomes, where they are degraded. 5. Summary the way that membrane protein associate with the lipid bilayer. (10) A: Most trans-membrane proteins are thought to extend across the bilayer as (1) a single ...
... (3) Degradation: proteins that are not specifically retrieved from endosomes are transported to lysosomes, where they are degraded. 5. Summary the way that membrane protein associate with the lipid bilayer. (10) A: Most trans-membrane proteins are thought to extend across the bilayer as (1) a single ...
cell membrane
... – located in lipid bilayer – made of amino acids which contain polar and non-polar sides • Non-polar repelled by water on both sides of bilayer, this holds proteins in place. – proteins able to move along bilayer ...
... – located in lipid bilayer – made of amino acids which contain polar and non-polar sides • Non-polar repelled by water on both sides of bilayer, this holds proteins in place. – proteins able to move along bilayer ...
Chapter 8 Questions
... 8. Explain why the presence of dissolved particles on one side of a membrane results in diffusion of water across the membrane. 9. List two ways that a cell can move a substance against its concentration gradient. 10. Based on what you have learned about homeostasis and osmosis, why should humans av ...
... 8. Explain why the presence of dissolved particles on one side of a membrane results in diffusion of water across the membrane. 9. List two ways that a cell can move a substance against its concentration gradient. 10. Based on what you have learned about homeostasis and osmosis, why should humans av ...
Name
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
The Cell Membrane 2015
... the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across them and others cannot. ...
... the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across them and others cannot. ...
Slide 1
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
Lecture 8: The cell membrane
... separates it from its environment. Yet at the same time, it must allow for interaction between the cell and its environment. ...
... separates it from its environment. Yet at the same time, it must allow for interaction between the cell and its environment. ...
Slide ()
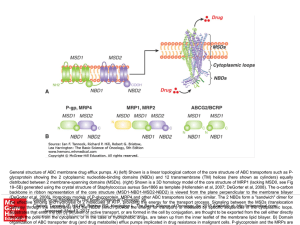
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
concentration
... proteins on the outside of the bilayer – allow cells to communicate with each other carbohydrates ...
... proteins on the outside of the bilayer – allow cells to communicate with each other carbohydrates ...
Chapter 7 Questions What criteria of a substance determines if it will
... 2. Explain the Fluid Mosaic model of the cell membrane and describe the functions of the proteins that are embedded in the membrane. 3. How is it possible that a protein can be embedded in the plasma membrane and also have regions that are attracted to the intracellular and extracellular regions of ...
... 2. Explain the Fluid Mosaic model of the cell membrane and describe the functions of the proteins that are embedded in the membrane. 3. How is it possible that a protein can be embedded in the plasma membrane and also have regions that are attracted to the intracellular and extracellular regions of ...
Eukaryotic cell Plasma membrane
... • The phospholipid molecules and all lipid molecules that make the core of cell membrane are amphipathic molecules. They composed of: • a. Hydrophilic (water-loving) polar head group directed toward outside, and • b. Hydrophobic (water-hating) non-polar tails of fatty acid chains (one usually unsat ...
... • The phospholipid molecules and all lipid molecules that make the core of cell membrane are amphipathic molecules. They composed of: • a. Hydrophilic (water-loving) polar head group directed toward outside, and • b. Hydrophobic (water-hating) non-polar tails of fatty acid chains (one usually unsat ...
Shape matters in protein mobility within membranes - ICAM
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
Chapter 5.1 Notes
... intra – between, among ie. Hilo to Kona extra – outside of (extracellular would be outside the cell) glyco – containing sugar/carbohydrates (sugar-coated) ...
... intra – between, among ie. Hilo to Kona extra – outside of (extracellular would be outside the cell) glyco – containing sugar/carbohydrates (sugar-coated) ...
Membrane Transport notes
... b. -proteins inserted in bilayer for movement of molecules c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
... b. -proteins inserted in bilayer for movement of molecules c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
Cell Membranes and Signaling
... A membrane’s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The general structure of membranes is known as the fluid mosaic model. Phospholipids form a bilayer which is like a “lake” in which a variety of proteins “float.” ...
... A membrane’s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The general structure of membranes is known as the fluid mosaic model. Phospholipids form a bilayer which is like a “lake” in which a variety of proteins “float.” ...
Mycolic acid export to the outer membrane of mycobacteria
... Our research program lies at the interface of chemistry and biology, and involves the use of chemical, biochemical, genetic and biophysical approaches to characterize both the chemistry and biology of a given system. The problem that my group is interested in studying is membrane biogenesis, i.e. ho ...
... Our research program lies at the interface of chemistry and biology, and involves the use of chemical, biochemical, genetic and biophysical approaches to characterize both the chemistry and biology of a given system. The problem that my group is interested in studying is membrane biogenesis, i.e. ho ...
individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
pogil 3
... 11. In the phospholipid bilayer of Model 2, what do the light gray wiggly protrusions, or tails, represent? The spheres? ...
... 11. In the phospholipid bilayer of Model 2, what do the light gray wiggly protrusions, or tails, represent? The spheres? ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.