Investigating the organization, assembly and physical properties of
... each lipid and characterize how this affects the system, as follows. The lipid bilayer surface structure will be visualized with atomic force microscopy at high spatial resolution (subnanometer), revealing phase segregation in single layers and the height of stacked membrane layers. Neutron reflecti ...
... each lipid and characterize how this affects the system, as follows. The lipid bilayer surface structure will be visualized with atomic force microscopy at high spatial resolution (subnanometer), revealing phase segregation in single layers and the height of stacked membrane layers. Neutron reflecti ...
Review For Final I - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... • multiply each exam score by 0.4 • add the three numbers together • subtract this sum from the average you want to get • divide the difference by 40 for the percent score you need ...
... • multiply each exam score by 0.4 • add the three numbers together • subtract this sum from the average you want to get • divide the difference by 40 for the percent score you need ...
membrane model
... Names _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ ...
... Names _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ ...
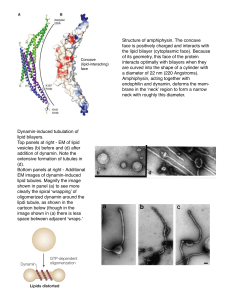
Structure of amphiphysin. The concave face is positively charged
... shown in panel (a) to see more clearly the spiral ʻwrappingʼ of oligomerized dynamin around the lipdi tubule, as shown in the cartoon below (though in the image shown in (a) there is less space between adjacent ʻwraps.ʼ ...
... shown in panel (a) to see more clearly the spiral ʻwrappingʼ of oligomerized dynamin around the lipdi tubule, as shown in the cartoon below (though in the image shown in (a) there is less space between adjacent ʻwraps.ʼ ...
Chemistry of Macromolecules
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
Induction of membrane hole by pH low
... (POPC). The pHLIP rapidly attaches to the surface of the POPC and rests there for a long time. However, if it breaks through the energy barrier of the surface, it rapidly inserts into the bilayer and, surprisingly, it induces the membrane to form a 0.5-2 ns hole parallel to the inserted PHLIP, acros ...
... (POPC). The pHLIP rapidly attaches to the surface of the POPC and rests there for a long time. However, if it breaks through the energy barrier of the surface, it rapidly inserts into the bilayer and, surprisingly, it induces the membrane to form a 0.5-2 ns hole parallel to the inserted PHLIP, acros ...
Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
... This surrounds the cell & controls what moves in and out of the cell like a gatekeeper Made of two layers of phospholipids (aka phospholipid bilayer) ...
... This surrounds the cell & controls what moves in and out of the cell like a gatekeeper Made of two layers of phospholipids (aka phospholipid bilayer) ...
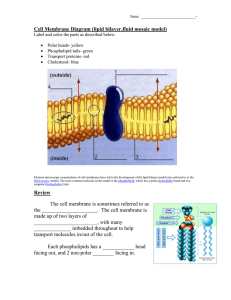
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.