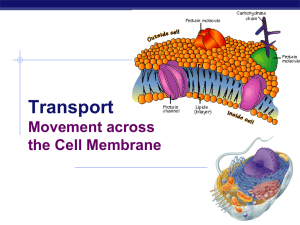
Cell Structures and Functions
... • In plants, made of the polysaccharide cellulose as well as the proteins pectin and lignin. Actually 2 layers, depending on the cell function, the thicknesses of each vary. – Contain openings lined with membrane called Plasmodesmata, that allow things to enter the cell. • In fungi, made of nitrogen ...
... • In plants, made of the polysaccharide cellulose as well as the proteins pectin and lignin. Actually 2 layers, depending on the cell function, the thicknesses of each vary. – Contain openings lined with membrane called Plasmodesmata, that allow things to enter the cell. • In fungi, made of nitrogen ...
The Phospholipid Bilayer - Advanced
... "tails." That is, the head of the molecule is hydrophilic (water-loving), and the tail is hydrophobic (water-fearing). Cytosol and extracellular fluid - the insides and outsides of the cell - are made up of mostly water. In this watery environment, the water loving heads point out towards the water, ...
... "tails." That is, the head of the molecule is hydrophilic (water-loving), and the tail is hydrophobic (water-fearing). Cytosol and extracellular fluid - the insides and outsides of the cell - are made up of mostly water. In this watery environment, the water loving heads point out towards the water, ...
Biomolecules at interfaces at atomistic resolution
... experiments in the Brezesinski group from the Möhwald department. Three sample biomolecules consisting of an antimicrobial or an amyloid peptide and DNA shall be investigated. The aim is to understand or predict the conformational transition of the peptides upon adsorption to lipid monolayers, the e ...
... experiments in the Brezesinski group from the Möhwald department. Three sample biomolecules consisting of an antimicrobial or an amyloid peptide and DNA shall be investigated. The aim is to understand or predict the conformational transition of the peptides upon adsorption to lipid monolayers, the e ...
AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW-Chapter 2
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain the significance of organelles. What are the costs and benefits of having large compartmentalized cells? What is the primary function of a cell membrane? What characteristics of membranes allow them to contribute to metabolic activity? T ...
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain the significance of organelles. What are the costs and benefits of having large compartmentalized cells? What is the primary function of a cell membrane? What characteristics of membranes allow them to contribute to metabolic activity? T ...
Biological Membranes and Transport
... Are thin, fluid and flexible (shape changes as cell grows and moves) Can fuse with or pinch off sections (vesicles) ...
... Are thin, fluid and flexible (shape changes as cell grows and moves) Can fuse with or pinch off sections (vesicles) ...
Membranes and transport - part 1
... Are thin, fluid and flexible (shape changes as cell grows and moves) Can fuse with or pinch off sections (vesicles) ...
... Are thin, fluid and flexible (shape changes as cell grows and moves) Can fuse with or pinch off sections (vesicles) ...
4-2: Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell
... Prominent in cells that export large amounts of proteins from the cell or use in cell ...
... Prominent in cells that export large amounts of proteins from the cell or use in cell ...
Cell membranes
... A. The structure of the cell membrane B. The structure of the cell wall C. The fact that the membrane is made up mostly of water D. The fact that the membrane is always changing, so it seems to be “fluid” E. The fact that the membrane is made up of lipids, and they tend to “flow” ...
... A. The structure of the cell membrane B. The structure of the cell wall C. The fact that the membrane is made up mostly of water D. The fact that the membrane is always changing, so it seems to be “fluid” E. The fact that the membrane is made up of lipids, and they tend to “flow” ...
CLASS COPY Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice
... facilitated diffusion active transport ...
... facilitated diffusion active transport ...
Complex Lipids
... lipids set tail to tail. Hydrophobic tails point towards each other Hydrophilic heads point out from each other enabling them to be close to water. Membranes have liquid like characteristics because the unsaturated fatty acids prevent tight packing in the lipid bilayer. An important component of a m ...
... lipids set tail to tail. Hydrophobic tails point towards each other Hydrophilic heads point out from each other enabling them to be close to water. Membranes have liquid like characteristics because the unsaturated fatty acids prevent tight packing in the lipid bilayer. An important component of a m ...
Membranes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... lipid-soluble particles across a semipermeable membrane is called passive transport because the cell does not use ...
... lipid-soluble particles across a semipermeable membrane is called passive transport because the cell does not use ...
DOC
... directly in cells of the poikilothermic eukaryote Tetrahymena pyriformis by freeze-etch electron microscopy. Moreover, the effect of temperature on the smooth microsomal membrane vesicles isolated from these cells, as well as on the extracted membrane lipids, has been examined by fluorescence probin ...
... directly in cells of the poikilothermic eukaryote Tetrahymena pyriformis by freeze-etch electron microscopy. Moreover, the effect of temperature on the smooth microsomal membrane vesicles isolated from these cells, as well as on the extracted membrane lipids, has been examined by fluorescence probin ...
Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall
... Location: membrane Found in together; the between the phosphate phospholipids heads are not in the bilayer. attached to each other ...
... Location: membrane Found in together; the between the phosphate phospholipids heads are not in the bilayer. attached to each other ...
16-17 membrane notes
... • UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS make “kinks” so phospholipids can’t pack as close together (remain fluid @ colder temps) CHOLESTEROL (in animal cells only) makes membranes less fluid at higher temps (keep phospholipids from moving around) makes membranes more fluid at lower temps (keep phospholipids from ...
... • UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS make “kinks” so phospholipids can’t pack as close together (remain fluid @ colder temps) CHOLESTEROL (in animal cells only) makes membranes less fluid at higher temps (keep phospholipids from moving around) makes membranes more fluid at lower temps (keep phospholipids from ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CH 7
... A. The phospholipid bilayer • Composed of two layers of phospholipids • hydrophobic tails face in, polar heads face out • prevents soluble material from passing across the membrane and allows for diffusion of small nonpolar molecules across the membrane ...
... A. The phospholipid bilayer • Composed of two layers of phospholipids • hydrophobic tails face in, polar heads face out • prevents soluble material from passing across the membrane and allows for diffusion of small nonpolar molecules across the membrane ...
Cellular Organelle
... Cell membrane, continued… • These lipids form a “lipid bilayer”: • Bilayer is flexible, giving the cell different shapes. • Some chemicals stick out of the bilayer to allow for cell identification. Some are proteins that act as channels to allow big molecules (like sugar) to go through. ...
... Cell membrane, continued… • These lipids form a “lipid bilayer”: • Bilayer is flexible, giving the cell different shapes. • Some chemicals stick out of the bilayer to allow for cell identification. Some are proteins that act as channels to allow big molecules (like sugar) to go through. ...
Text 3
... Membrane Proteins […] It seems both reasonable and important to discriminate between two categories of proteins bound to membranes, which we have termed peripheral and integral1 proteins. […] A peripheral protein is held to the membrane only by rather weak noncovalent (perhaps mainly electrostatic) ...
... Membrane Proteins […] It seems both reasonable and important to discriminate between two categories of proteins bound to membranes, which we have termed peripheral and integral1 proteins. […] A peripheral protein is held to the membrane only by rather weak noncovalent (perhaps mainly electrostatic) ...
Nanodevices
... processes require input of energy and a nearly error free genetic coding program Biological nanodevices are specially folded during their synthesis (i) to recognize specific ligands (often small molecule) that can enter into a crevice in the molecule or (ii) to change configuration in the presence o ...
... processes require input of energy and a nearly error free genetic coding program Biological nanodevices are specially folded during their synthesis (i) to recognize specific ligands (often small molecule) that can enter into a crevice in the molecule or (ii) to change configuration in the presence o ...
Can use more than once
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم The Plasma Membrane Membrane Functions
... Can comprise up to 50% of animal plasma membrane Hydrophilic OH groups toward surface Smaller than a phospholipid and less amphipathic (having both polar and non-polar regions of the molecule) Other molecules include ceramides and sphingolipds - amino alcohols with fatty ...
... Can comprise up to 50% of animal plasma membrane Hydrophilic OH groups toward surface Smaller than a phospholipid and less amphipathic (having both polar and non-polar regions of the molecule) Other molecules include ceramides and sphingolipds - amino alcohols with fatty ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.