Plasma membrane
... Plasma membrane The plasma membrane or bacterial cytoplasmic membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cel ...
... Plasma membrane The plasma membrane or bacterial cytoplasmic membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cel ...
Mountain Glacier Melt to Contribute 12 Centimeters to World Sea
... ScienceDaily (Jan. 11, 2011) — Melt off from small mountain glaciers and ice caps will contribute about 12 centimetres to world sea-level increases by 2100, according to UBC research published this week in Nature Geoscience. ...
... ScienceDaily (Jan. 11, 2011) — Melt off from small mountain glaciers and ice caps will contribute about 12 centimetres to world sea-level increases by 2100, according to UBC research published this week in Nature Geoscience. ...
Year 12 Revision Quiz
... detergent conc on beetroot discs valid? • Same size /surface area of discs • Same volume of detergent • Same temperature • Use the same beetroot/from same part of the beetroot • Dry discs before weighing (Don’t give controls that have been already described in the ...
... detergent conc on beetroot discs valid? • Same size /surface area of discs • Same volume of detergent • Same temperature • Use the same beetroot/from same part of the beetroot • Dry discs before weighing (Don’t give controls that have been already described in the ...
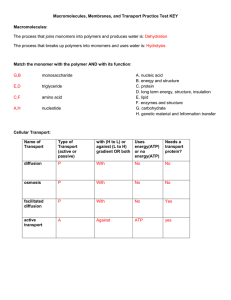
Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice Test KEY
... Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice Test KEY ...
... Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice Test KEY ...
3-3 notes answers
... Notes Chap 3, Sect 3 Organelle – specialized structures within the cell The following organelles are found in both plant and animal cells: Nucleus – controls most of the cell functions Nuclear envelope / nuclear membrane – double layer (2 lipid bilayers) Nuclear pores – small channels scattered over ...
... Notes Chap 3, Sect 3 Organelle – specialized structures within the cell The following organelles are found in both plant and animal cells: Nucleus – controls most of the cell functions Nuclear envelope / nuclear membrane – double layer (2 lipid bilayers) Nuclear pores – small channels scattered over ...
Slide 1
... What are membranes? Membranes are barriers that define compartments • They are made up of a lipid bilayer ...
... What are membranes? Membranes are barriers that define compartments • They are made up of a lipid bilayer ...
Amazing Cells Build-A-Membrane
... 2. Fold the phospholipid bilayer along the dotted lines and tape the edges together to form a fully enclosed rectangular box. 3. Cut out each protein (pages S3 and S4) along the solid black lines and fold along the dotted lines. 4. Form a 3-D shape by joining the protein sides and tops together a ...
... 2. Fold the phospholipid bilayer along the dotted lines and tape the edges together to form a fully enclosed rectangular box. 3. Cut out each protein (pages S3 and S4) along the solid black lines and fold along the dotted lines. 4. Form a 3-D shape by joining the protein sides and tops together a ...
Manual
... by hydrogen bonds, each forming a half channel. The tryptophan residues along the channel are both hydrophobic as well as capable of long range electrostatic interactions. The activity of the channel measured in planar lipid bilayers requires the channel form of the peptide . Gramicidin exhibits a s ...
... by hydrogen bonds, each forming a half channel. The tryptophan residues along the channel are both hydrophobic as well as capable of long range electrostatic interactions. The activity of the channel measured in planar lipid bilayers requires the channel form of the peptide . Gramicidin exhibits a s ...
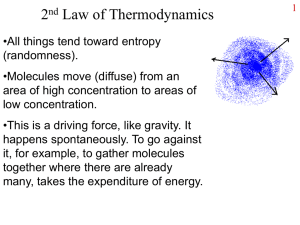
Transport
... •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
... •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
CellMembranes - Mexico Central School District
... This keep the membrane fluid, but not too fluid - It keeps the membrane from turning to mush! Without cholesterol a cell would need a cell wall. ...
... This keep the membrane fluid, but not too fluid - It keeps the membrane from turning to mush! Without cholesterol a cell would need a cell wall. ...
슬라이드 1
... + membrane protein-cytoskeletal interactions (recently). - Membrane fluidity involves the movement not only of lipid molecules but also of the different proteins. - The importance of protein movement in membranes a) the transfer of substrates in mitochondria and chloroplast. b) the assembly of multi ...
... + membrane protein-cytoskeletal interactions (recently). - Membrane fluidity involves the movement not only of lipid molecules but also of the different proteins. - The importance of protein movement in membranes a) the transfer of substrates in mitochondria and chloroplast. b) the assembly of multi ...
Chapter Eight Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological
... Temperature Transition in Lipid Bilayer • With heat, membranes become more disordered; ...
... Temperature Transition in Lipid Bilayer • With heat, membranes become more disordered; ...
Document
... Temperature Transition in Lipid Bilayer • With heat, membranes become more disordered; ...
... Temperature Transition in Lipid Bilayer • With heat, membranes become more disordered; ...
HERE
... 3. The lipid bilayer forms because there is __water__ both inside and _outside_ of the cell. 4. The phosphate _head_ of a phospholipid is polar. It is _attracted_ to water. 5. The long fatty acid _tails_ of a phospholipid are nonpolar. They are _afraid of/ repelled by_ water. 6. The lipid bilayer fo ...
... 3. The lipid bilayer forms because there is __water__ both inside and _outside_ of the cell. 4. The phosphate _head_ of a phospholipid is polar. It is _attracted_ to water. 5. The long fatty acid _tails_ of a phospholipid are nonpolar. They are _afraid of/ repelled by_ water. 6. The lipid bilayer fo ...
Fluid Mosaic Model
... consists of one or more stretches of nonpolar amino acids hydrophilic parts are exposed on either end of the bilayer ...
... consists of one or more stretches of nonpolar amino acids hydrophilic parts are exposed on either end of the bilayer ...
Biozentrum: Research group Martin Spiess
... divide the cell interior into separate compartments and organelles. They consist of lipids and embedded membrane proteins. Our group works for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of how ...
... divide the cell interior into separate compartments and organelles. They consist of lipids and embedded membrane proteins. Our group works for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of how ...
1. Name two functions of the cell membrane
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Receptors bind to "ligand" and transmit a signal across the membrane ...
... Receptors bind to "ligand" and transmit a signal across the membrane ...
Enzymes
... The transport of polar compounds through the inner hydrophobic core of lipid bilayer requires a significant amount of energy Charged or hydrophilic compounds are not able to pass it or the transport of them is highly limited. There are only one excetion: the water. Its permeation is free. The gases ...
... The transport of polar compounds through the inner hydrophobic core of lipid bilayer requires a significant amount of energy Charged or hydrophilic compounds are not able to pass it or the transport of them is highly limited. There are only one excetion: the water. Its permeation is free. The gases ...
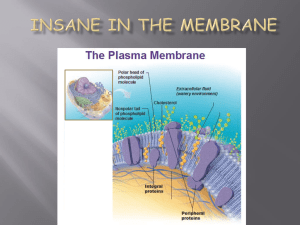
Biological membranes are sheet-like structures
... All Biological Membranes are made of the same basic structure. This is composed of molecules called Phospholipids, which form a Phospholipid Bilayer. Phospholipids are fats. They are composed of two Fatty Acid 'tails' and a Phosphate 'head'. The Phosphate 'heads' are Hydrophilic whereas the Fatty Ac ...
... All Biological Membranes are made of the same basic structure. This is composed of molecules called Phospholipids, which form a Phospholipid Bilayer. Phospholipids are fats. They are composed of two Fatty Acid 'tails' and a Phosphate 'head'. The Phosphate 'heads' are Hydrophilic whereas the Fatty Ac ...
Chapter 9 Membranes, con`t.
... by specific membranes • Membranes serve as barriers to contain most substances on one side or the other • Only small, lipid soluble, molecules are permeable to membranes ...
... by specific membranes • Membranes serve as barriers to contain most substances on one side or the other • Only small, lipid soluble, molecules are permeable to membranes ...
Cell Membrane - Red Hook Central Schools
... Endocytosis (moving into cell) phagocytosis = “cellular eating” ...
... Endocytosis (moving into cell) phagocytosis = “cellular eating” ...
H/Ws 1 to 4
... - Gets larger as cell grow so little cytoplasm. Cytosol therefore a small proportion of cell and ratio of membrane surface area to cytosolic volume is great, even for a large plant. Q: What is the fluid mosaic model? A: A membrane and various proteins embedded or attached to the double phospholipids ...
... - Gets larger as cell grow so little cytoplasm. Cytosol therefore a small proportion of cell and ratio of membrane surface area to cytosolic volume is great, even for a large plant. Q: What is the fluid mosaic model? A: A membrane and various proteins embedded or attached to the double phospholipids ...
Model lipid bilayer
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, increasing stability and allowing the use of characterization tools not possible in bulk solution. These advantages come at the cost of unwanted substrate interactions which can denature membrane proteins.